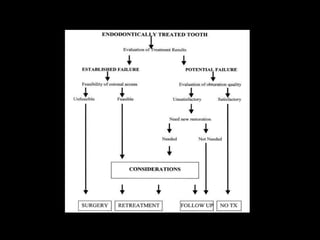
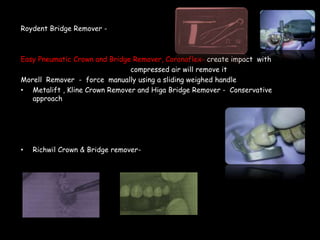
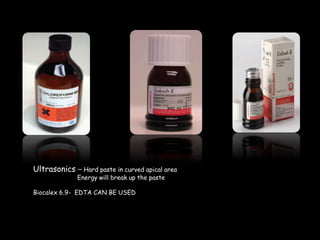
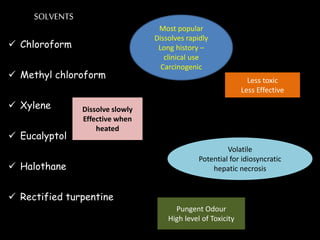
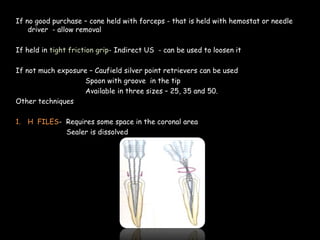
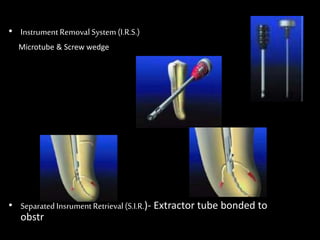
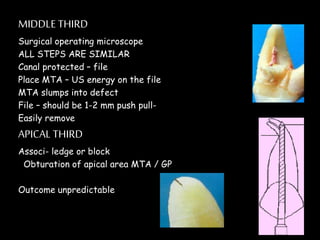
Endodontic retreatment involves removing previous root canal fillings and materials to address treatment failure. Success is defined as an asymptomatic tooth with healthy surrounding tissue and bone fill on radiographs. Causes of failure include missed canals, improper length determination, ledges, and perforations. The objectives of retreatment are to regain access, remove all materials, disinfect canals, and obtain proper seal length. Techniques include removing posts, solvents or heat to remove fillings, bypassing ledges or separated instruments, and repairing any perforations. Proper case selection, access, and following technical protocols are important for success.