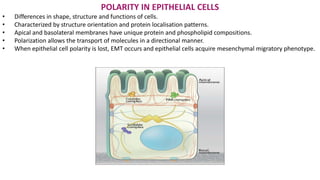
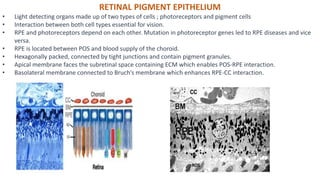
Epithelial tissue forms protective sheets covering body surfaces and lining organs, with distinct apical and basal surfaces connected by various junctions for communication and polarity. The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) plays a crucial role in vision, including light absorption, maintaining the structural integrity of the retina, and the transport of essential nutrients, while also engaging in phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments. Additionally, RPE communicates with neighboring tissues through secretion and maintains immune privilege by modulating immune responses within the eye.