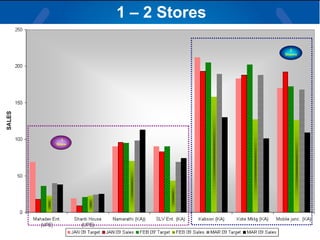
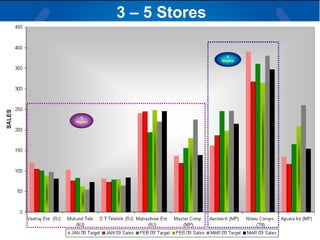
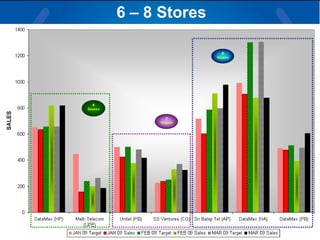
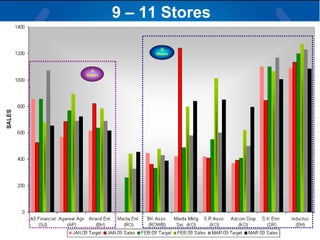
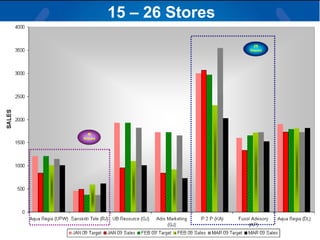
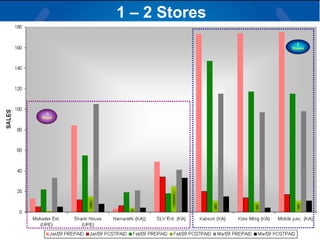
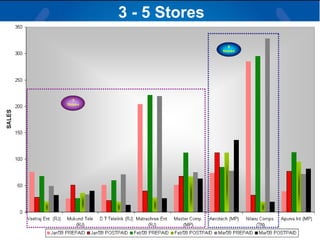
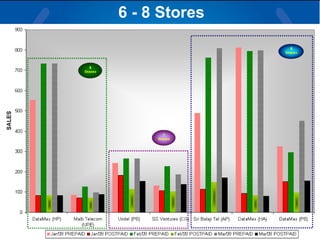
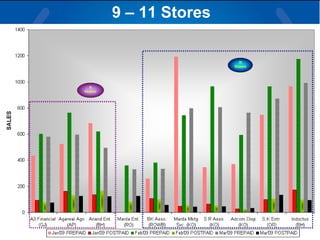
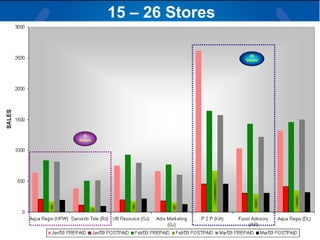
The document summarizes a retail analysis report for Tata Teleservices Ltd (TTSL) in India. It discusses the Indian telecom industry and major players. It then discusses TTSL, including its retail sector with over 3,100 outlets. The analysis examines sales trends and prepaid vs postpaid trends to identify top-performing and under-performing vendors. It concludes with recommendations to improve vendor performance through training and development.