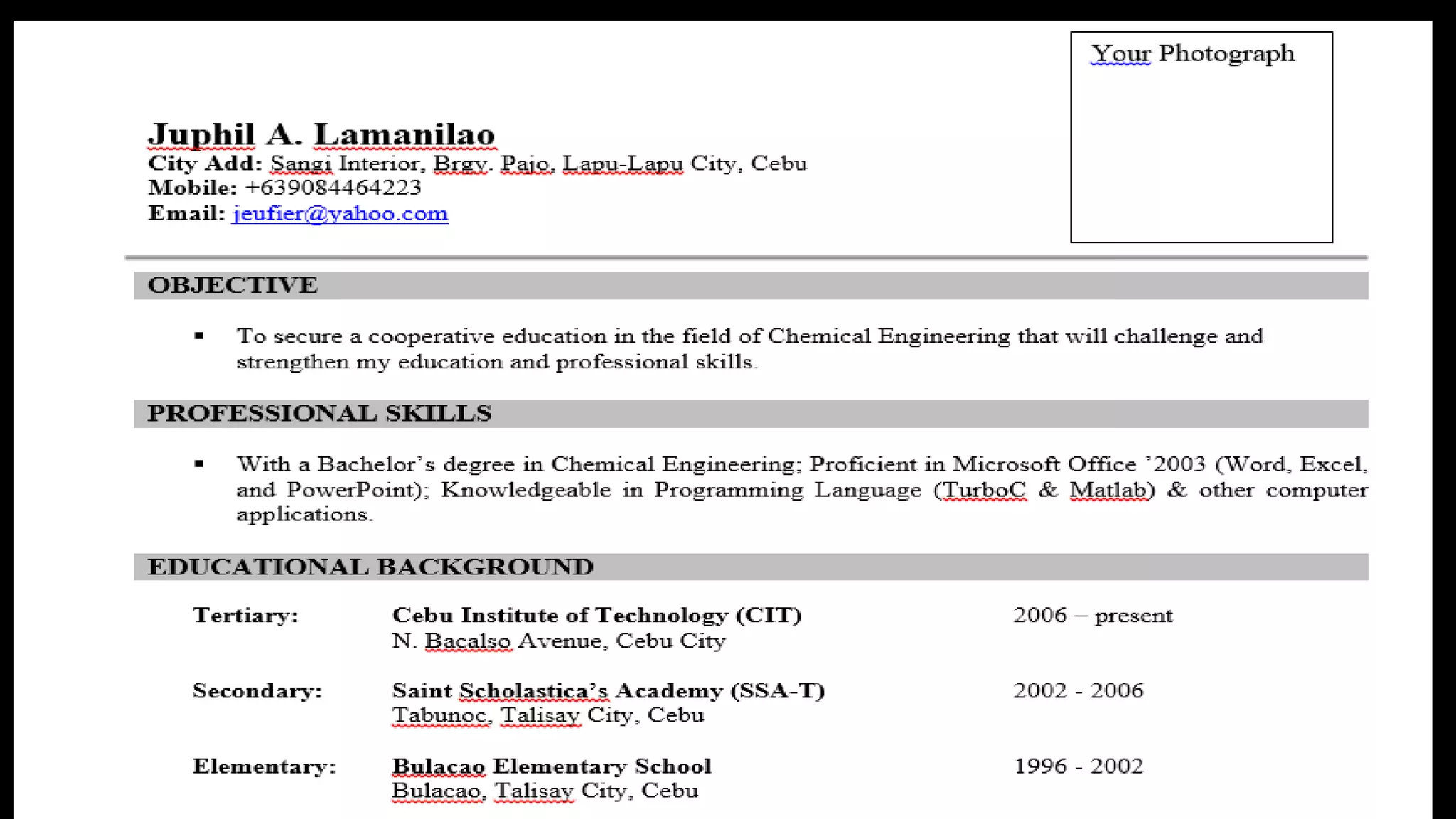
The document provides guidance on preparing resumes, CVs, and biodatas for engineering students. It explains the differences between these documents and recommends including key information like name, contact details, education history, skills, work experience, and references. The document also offers tips for preparing for interviews such as researching the company, practicing common questions, dressing professionally, maintaining eye contact, and following up with a thank you letter.