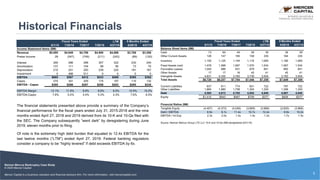
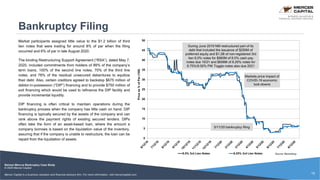
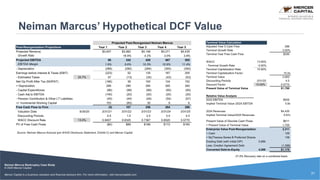
Neiman Marcus, a luxury retailer, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy on May 7, 2020, primarily due to a heavy debt burden exacerbated by COVID-19 shutdowns and a decline in traditional retail sales. The company, which has a long history and operates several high-end brands, struggled with financial issues stemming from private equity acquisitions and an industry shift towards e-commerce. The bankruptcy plan includes substantial debt equity conversions and a commitment from creditors for additional financing to maintain operations during the restructuring process.