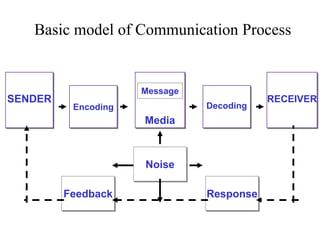
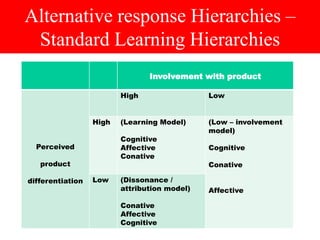
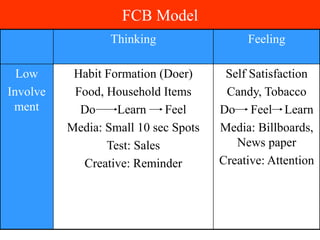
The document discusses communication processes and models for effective communication. It provides information on how the Mumbai police implemented an initiative called "Honk More Wait More" to reduce excessive honking in traffic by extending red light times when decibel levels exceed 85 dB. It then summarizes several communication models including the basic communication process model involving a sender, encoding, message, medium, decoding, receiver and feedback. It also outlines stages in the AIDA model and innovation adoption model as well as factors involving cognitive, affective and behavioral responses.