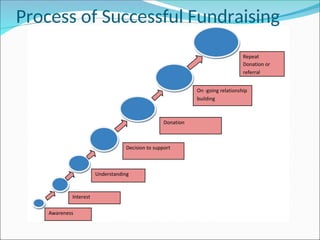
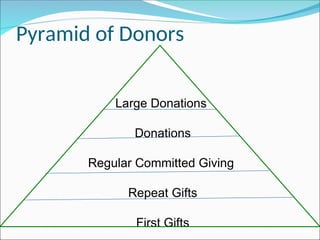
The document outlines the key concepts and strategies involved in resource mobilization and fundraising for NGOs, emphasizing the importance of diversifying income sources and building relationships with donors. It provides tactical advice on successful fundraising processes, principles, and techniques, including the significance of addressing various stakeholders and understanding donor perspectives. Additionally, it discusses different methods for raising funds from individuals, businesses, and other sources to ensure long-term sustainability and support for organizational goals.