This document discusses resource management in the cloud using a resource scheduler. It covers key aspects of resource scheduling including:
1) Estimating current and predicting future resource consumption of consumers like VMs and containers on resource producers like servers.
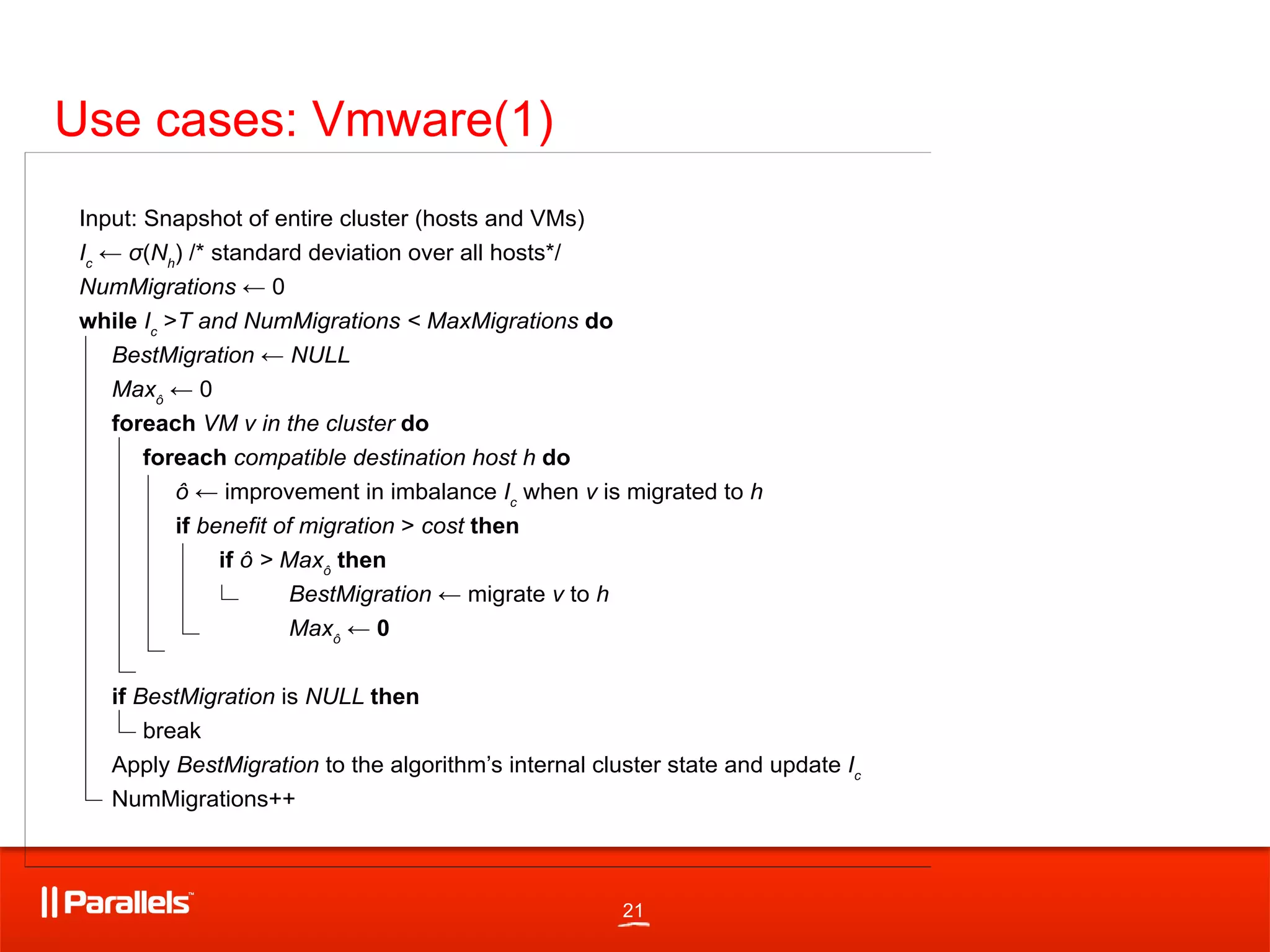
2) Detecting overload on resource producers to trigger optimal placement of consumers through techniques like migration.
3) Factors considered in optimal placement decisions including SLA compliance, affinity/anti-affinity rules, and resource availability.
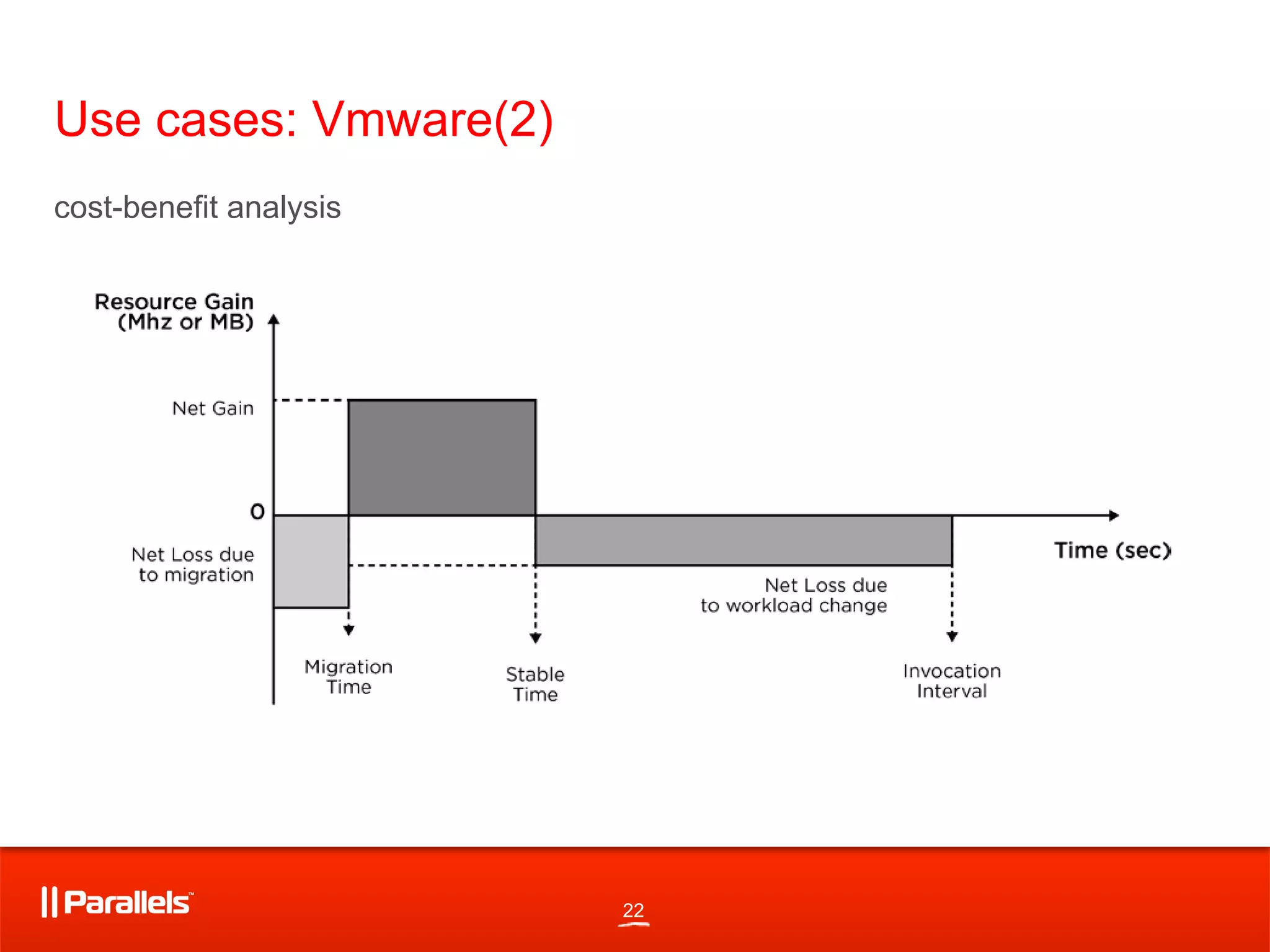
4) Techniques for migration of consumers between resource producers including estimation of migration costs and impact on performance.
5) Administrative aspects of resource scheduling including resource pool configuration, migration thresholds, and operational modes.