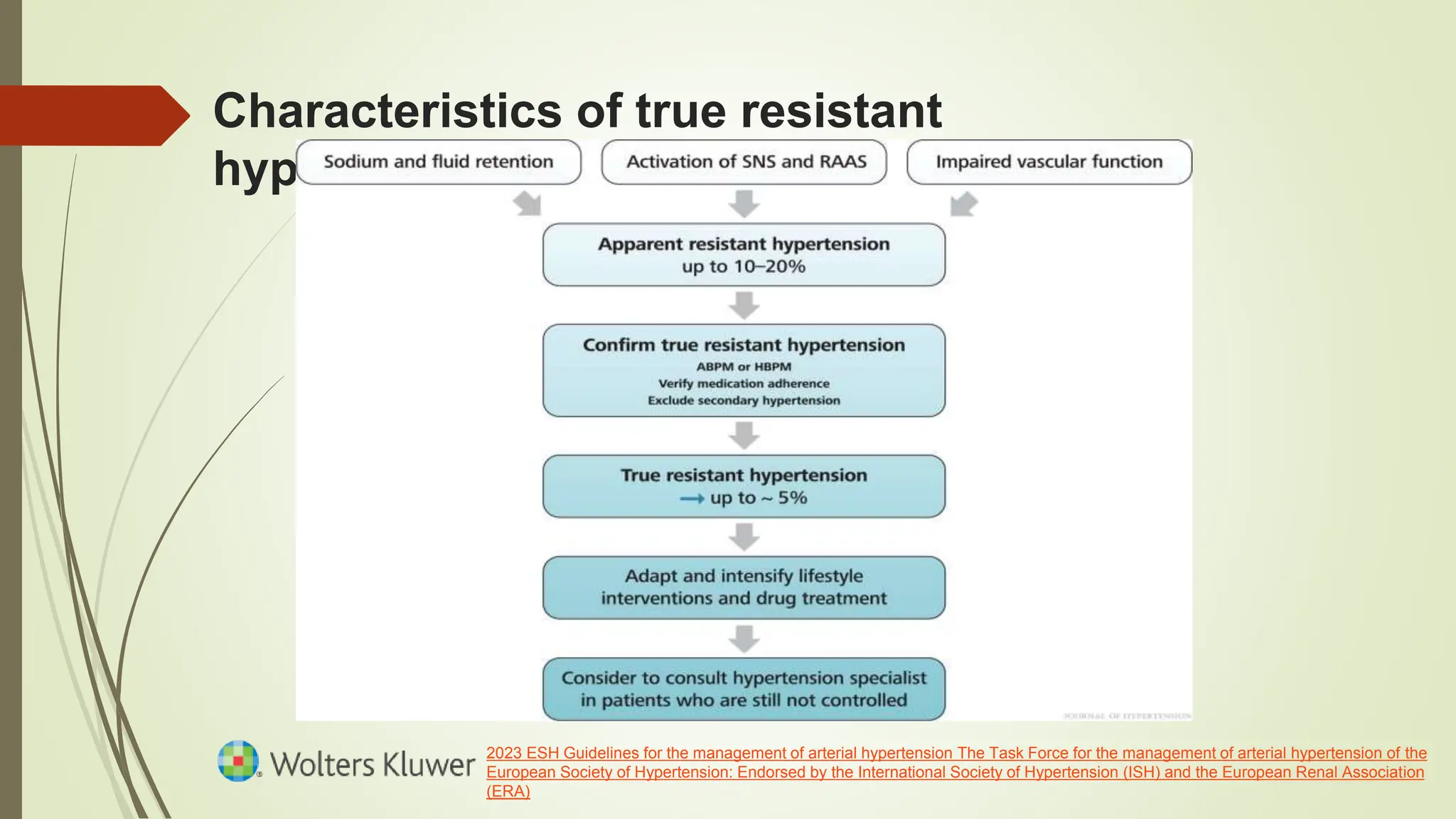
This document discusses the management of resistant hypertension. It defines resistant hypertension as BP that remains above goal despite treatment with three or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic. It provides characteristics of true resistant hypertension and outlines a management algorithm. Device-based treatments for resistant hypertension discussed include carotid baroreceptor stimulation and arteriovenous anastomosis. Drug classes are identified where abrupt withdrawal can cause complications due to effects like sympathetic overactivity, fluid retention, or risk of angina.







![ In obese patients,GLP1 receptor agonists can reduce body weight [759], modestly lower BP and improve
CV prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes or with established CVD
Bariatric surgery can lower BP, CV risk factors and risk of CV events in severely obese patients and may,
thus, reduce the burden of antihypertensive medication when these patients have resistant
hypertension
In patients eligible for treatment with SGLT2is their use may add a moderate BP-lowering effect to the
background antihypertensive therapy for resistant hypertensive patients
Finally, compared with valsartan alone, the sacubitril–valsartan combination did not lower
hospitalization for HF and death in patients with HFpEF , but did reduce significantly the NYHA class of
the patients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resistanthypertensionmanagement-240216143422-38aaf8d9/75/Resistant-Hypertension-Management-2024pptx-9-2048.jpg)


![Carotid baroreceptor stimulation
Stretch-sensitive baroreceptors located in the carotid sinus and the aortic arch are involved in
short-term and long-term BP regulation.
Carotid baroreceptor stimulation was associated with a reduction of sympathetic nerve activity
in studies on hypertensive patients
The first-generation bilateral electrical stimulation device (Rheos, CVRx) was tested in a double-
blind, randomized, sham-controlled pivotal trial, which included 265 patients with resistant
hypertension [798].
At 6 months, the office BP fall was significantly larger in the treatment group compared with the
sham group. However, the study failed to meet two of the five co-primary endpoints, and safety
was not established.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resistanthypertensionmanagement-240216143422-38aaf8d9/75/Resistant-Hypertension-Management-2024pptx-12-2048.jpg)



