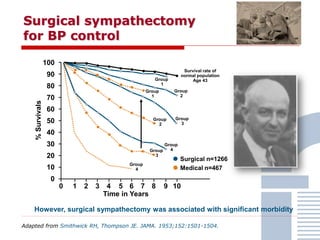
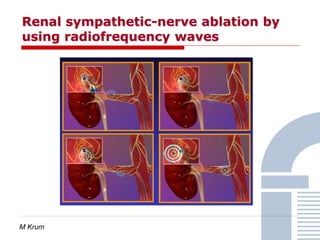
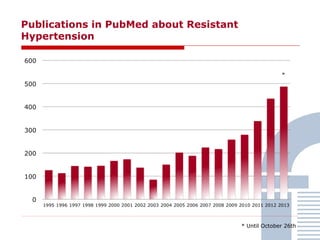
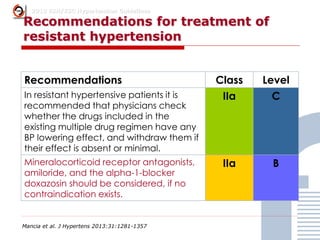
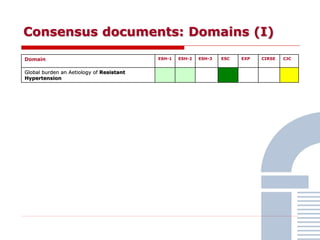
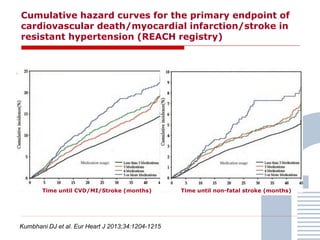
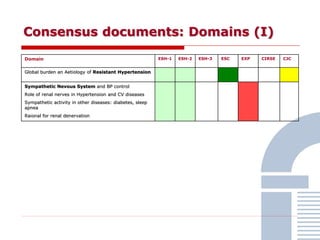
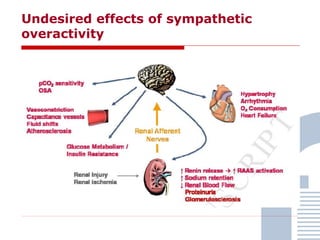
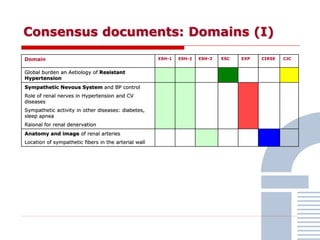
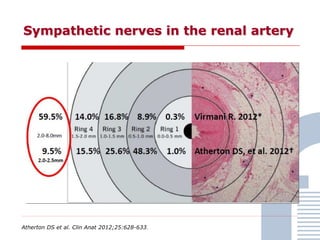
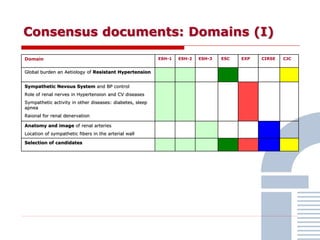
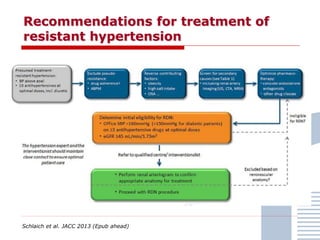
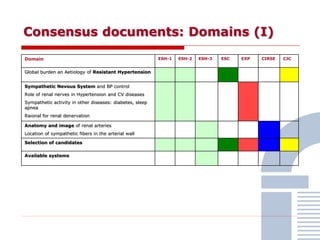
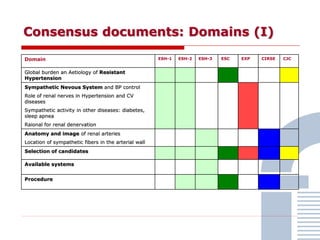
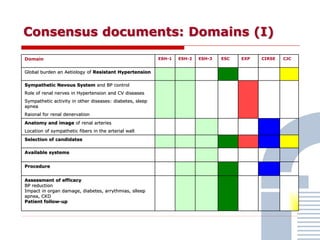
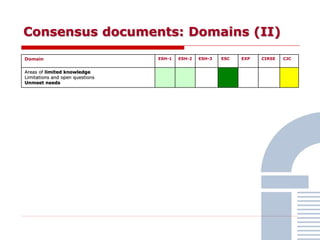
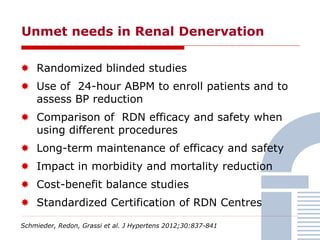
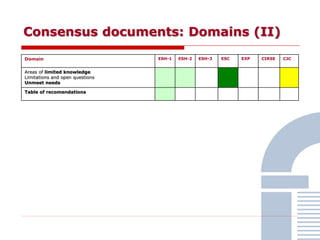
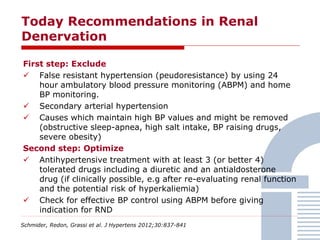
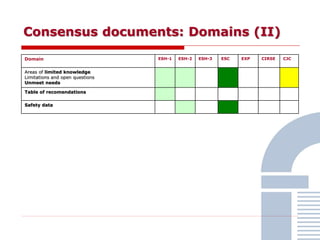
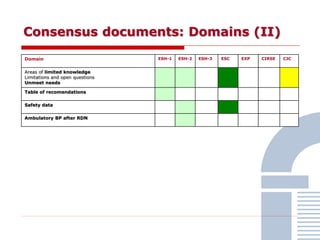
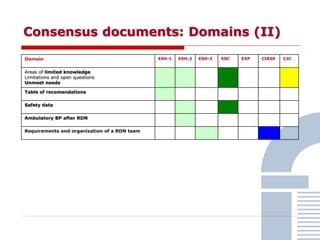
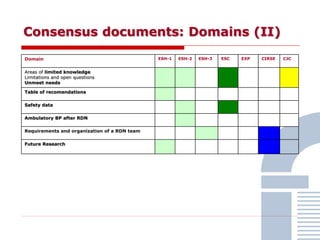
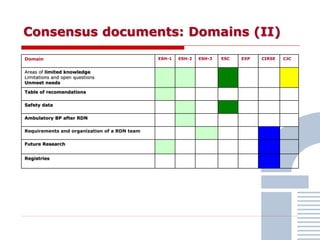
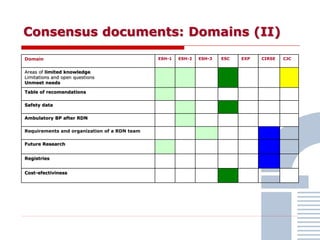
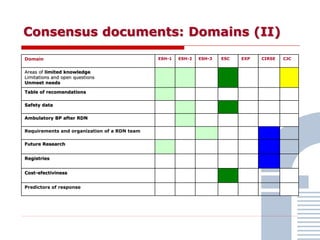
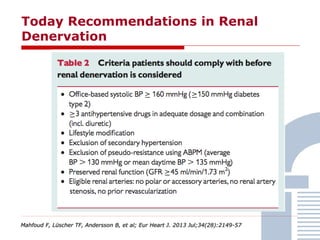
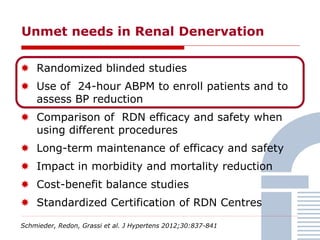
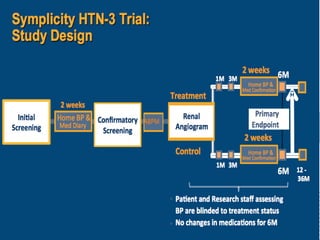
The document discusses consensus documents on catheter-based renal denervation (RDN) for treatment of resistant hypertension. It summarizes that there are 7 consensus documents from scientific societies and groups published between 2012-2014 that cover domains such as the pathophysiology of hypertension, rationale for RDN, candidate selection criteria, procedural aspects, efficacy assessment, safety data, and recommendations. There are still many unmet needs including randomized blinded studies, long-term data on efficacy and safety, and impact on patient outcomes. Overall the consensus documents provide guidance on RDN but more research is still required.