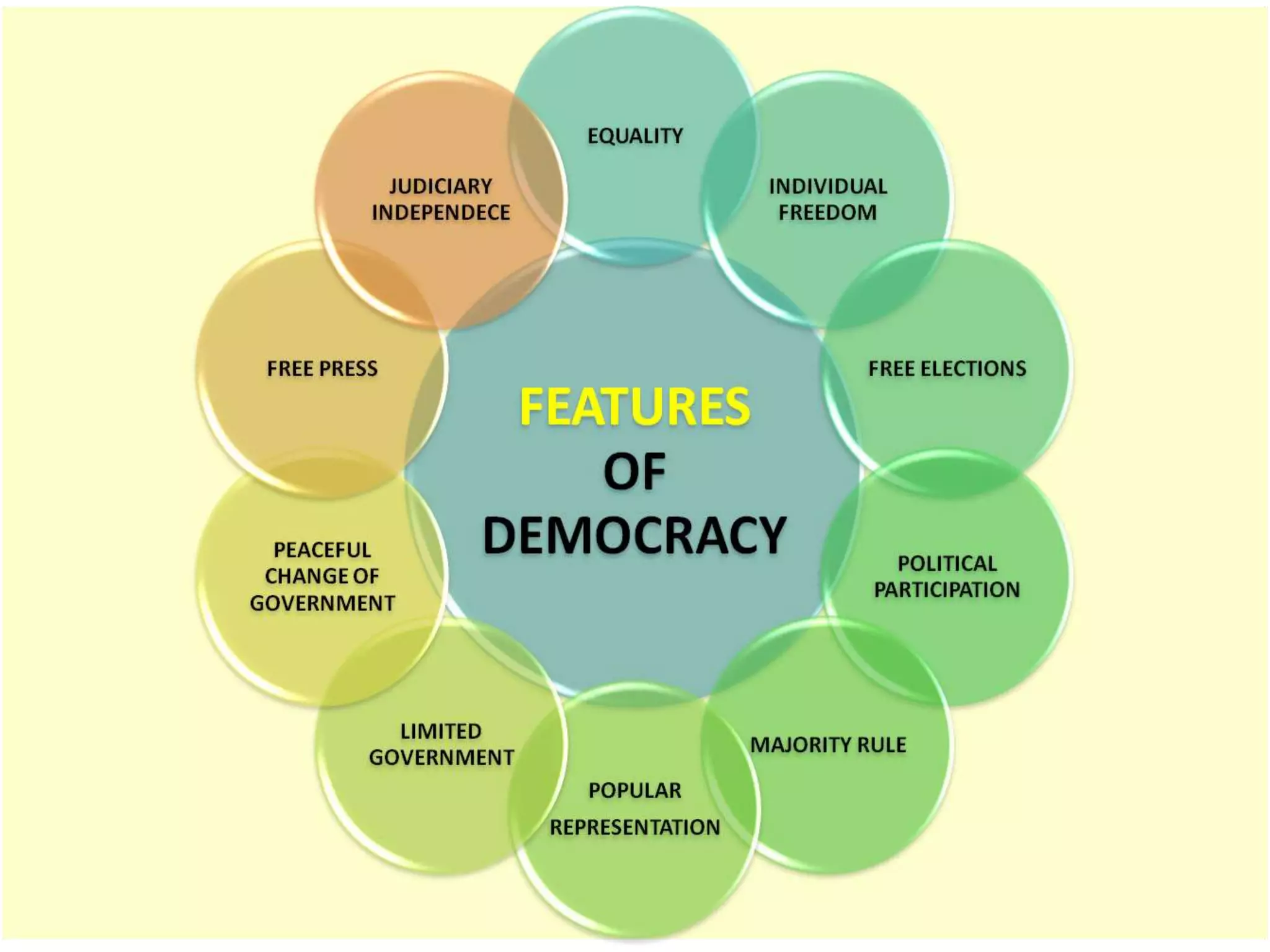
Democracy originates from ancient Greek meaning "rule of the people". The fundamental principle of democracy is that governing power is exercised based on the judgment of adult citizens through free and fair elections. Democracies can take different forms depending on the level of citizen participation. While democracy protects citizen interests and prevents monopoly of power, it also risks misuse of funds, corruption, and wrong choices due to emphasis on quantity over quality.