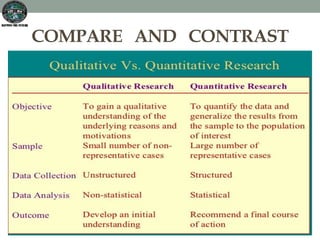
This document discusses and compares qualitative and quantitative research methods. It outlines two main types of research methods: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative methods are used to gather rich, detailed data through tools like interviews, focus groups, and observation. Quantitative methods are used to gather numeric data through surveys and questionnaires to quantify attitudes and behaviors. Both methods are useful for research, but qualitative explores phenomena while quantitative identifies patterns in large populations.