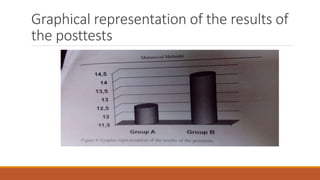
This study examined the impact of pre-reading and during-reading questions on vocabulary learning and retention in EFL classes. 88 intermediate English students were divided into two groups - one received texts with pre-reading questions and the other with inserted questions. Both groups read passages and completed vocabulary tests after each session for 5 sessions. After 2 weeks, a final vocabulary test was administered to measure retention. Results showed that the group with inserted questions performed better on vocabulary tests after each session and on the final retention test, rejecting the hypotheses that question type would not impact learning or retention. The findings suggest that during-reading questions lead to greater vocabulary gains and retention than pre-reading questions.