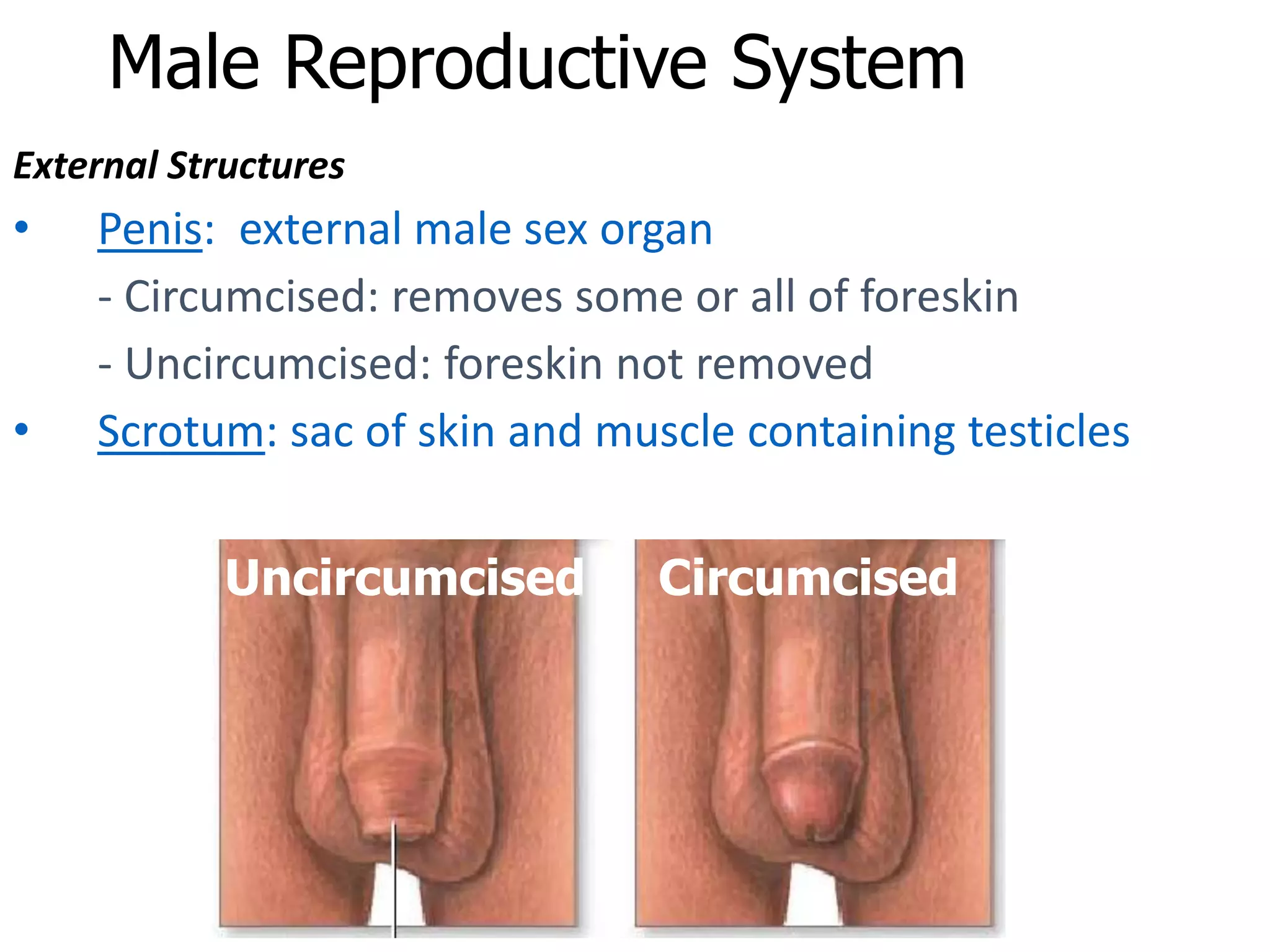
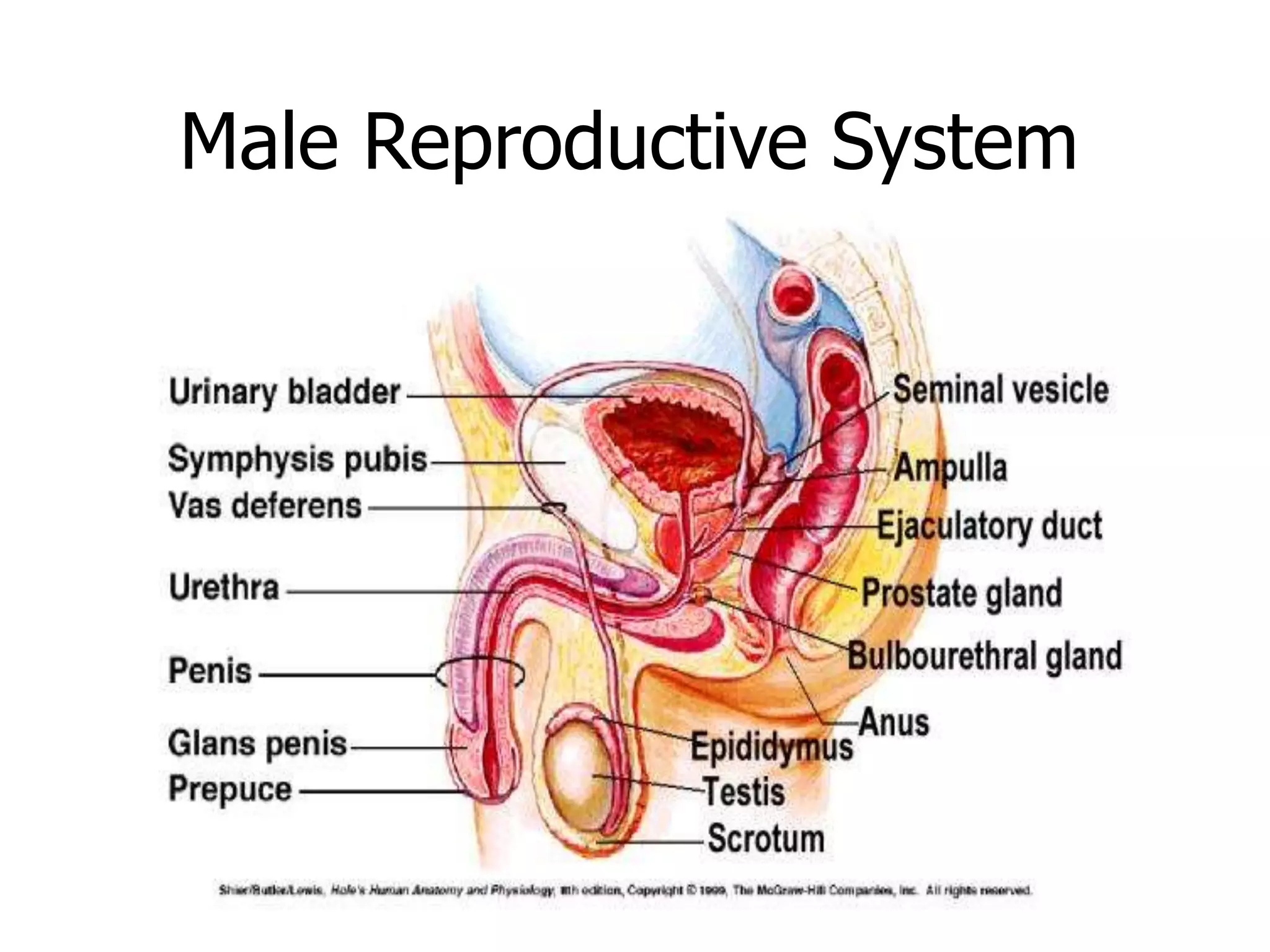
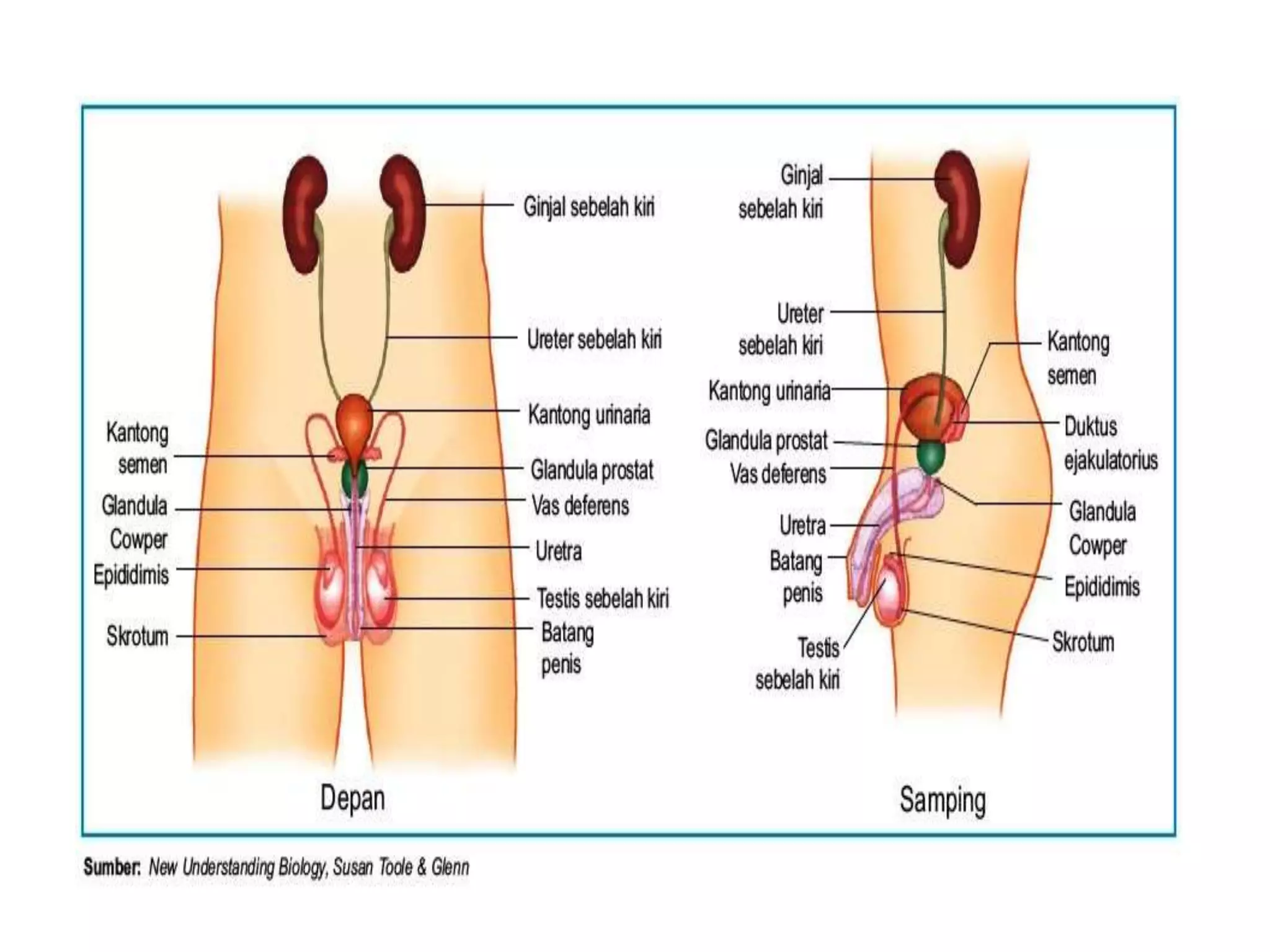
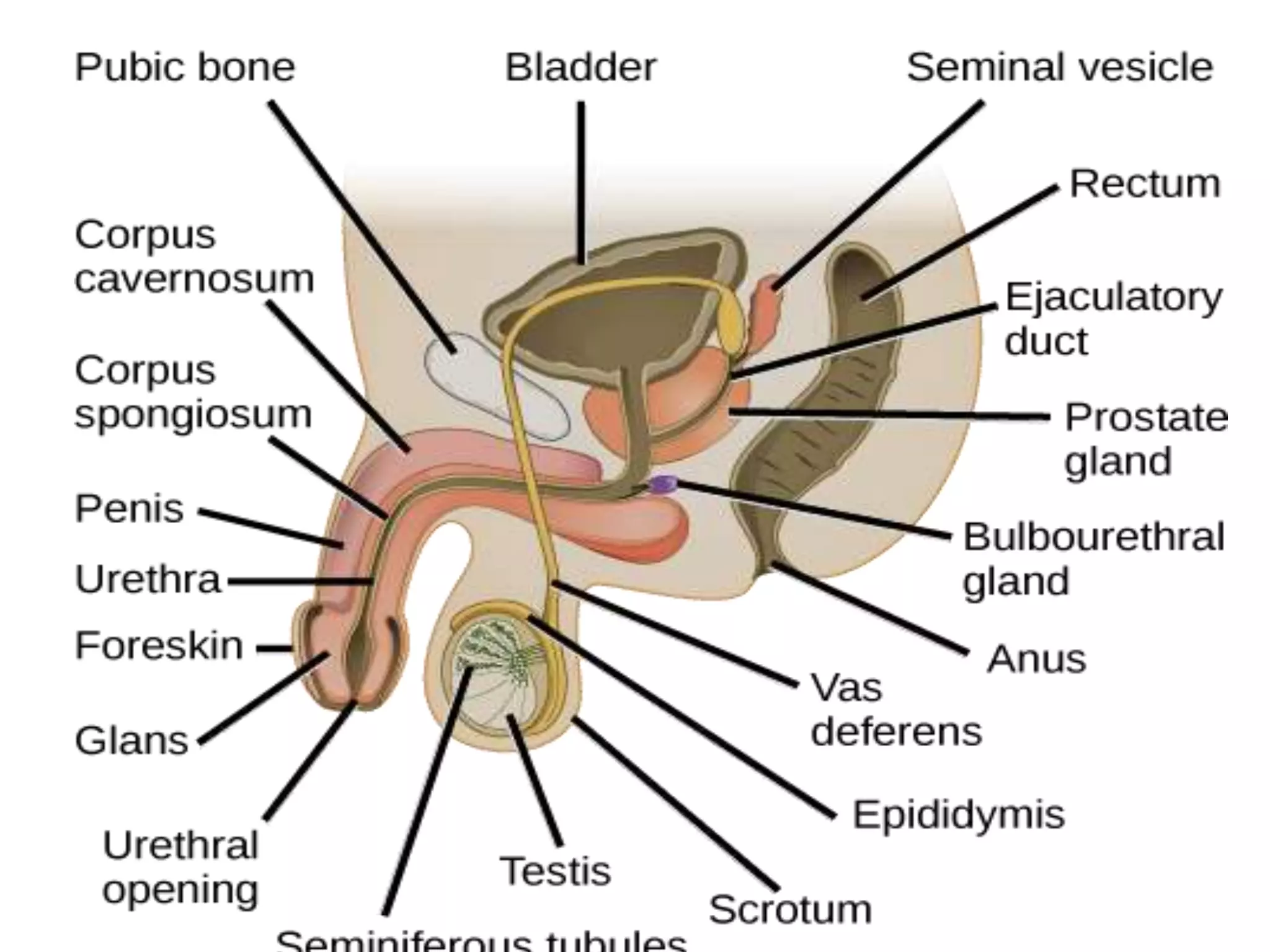
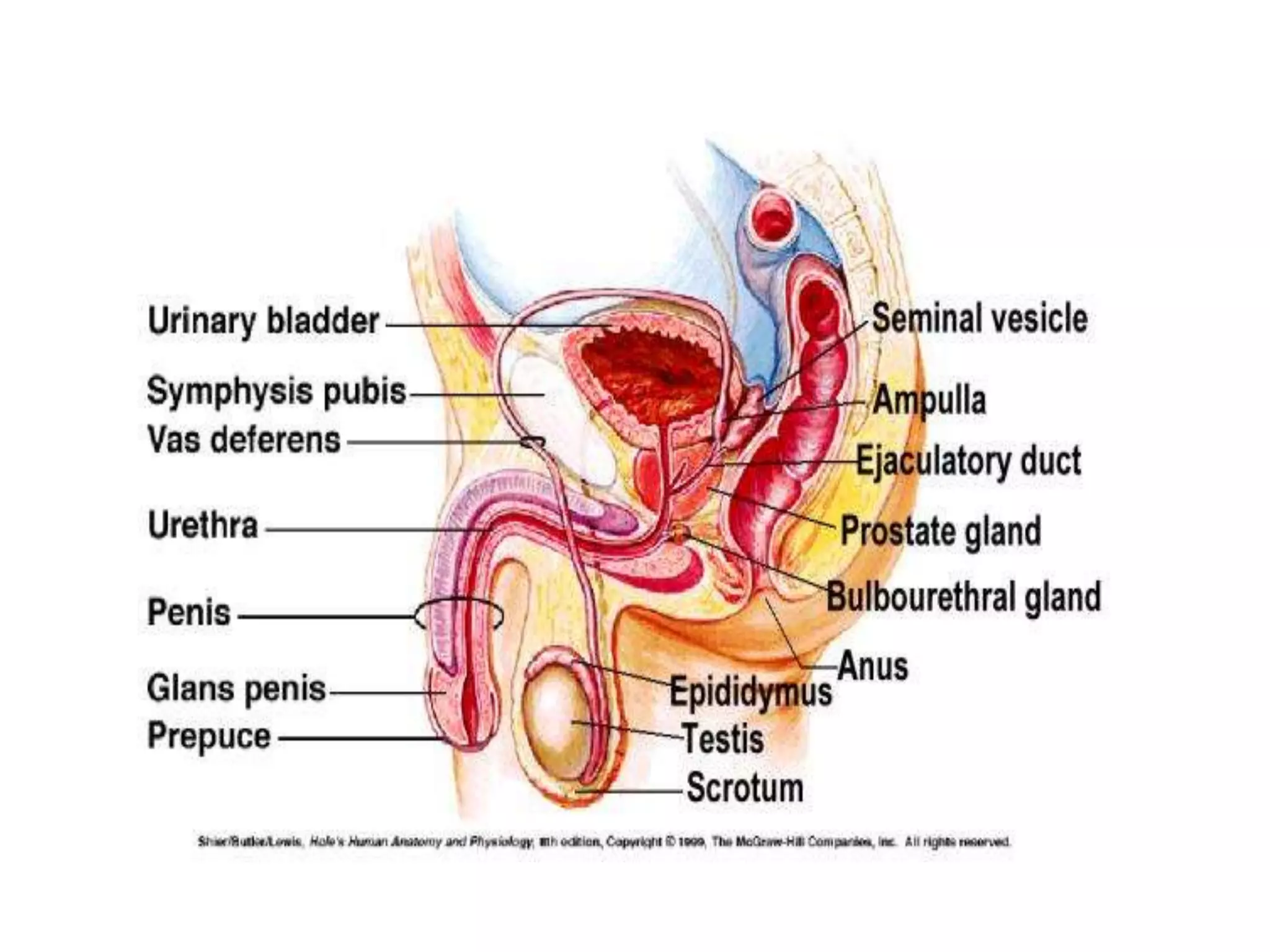
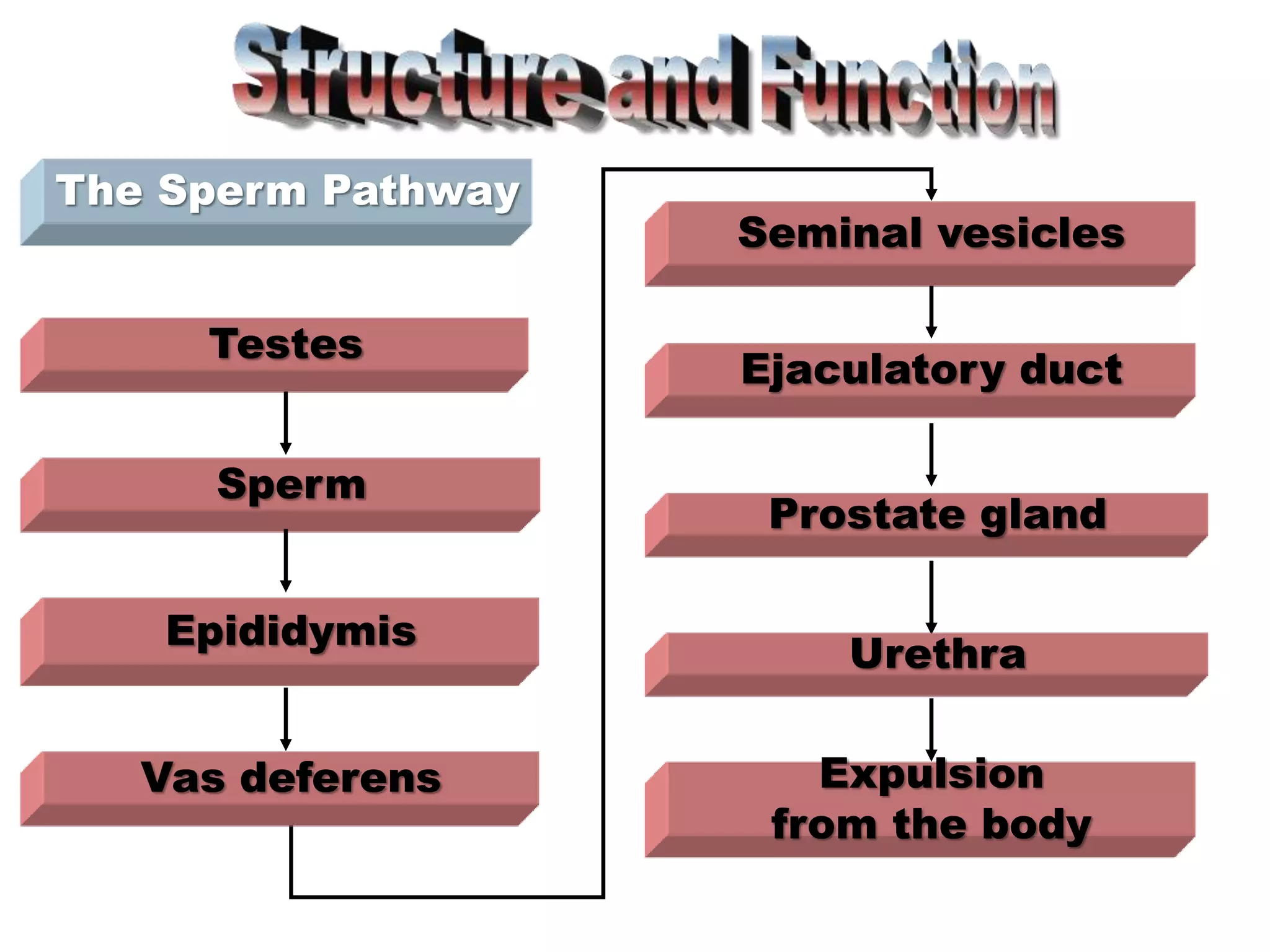
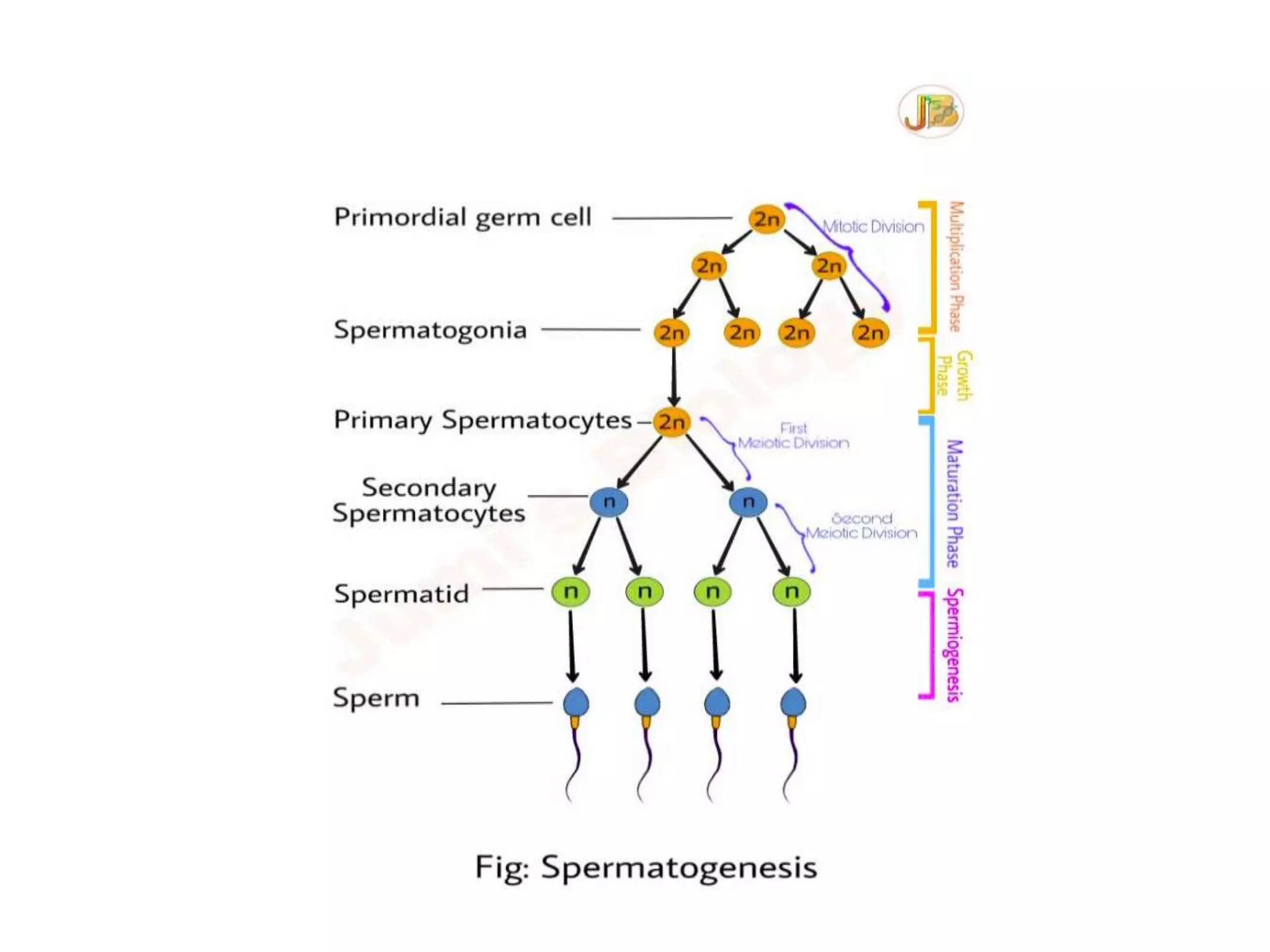
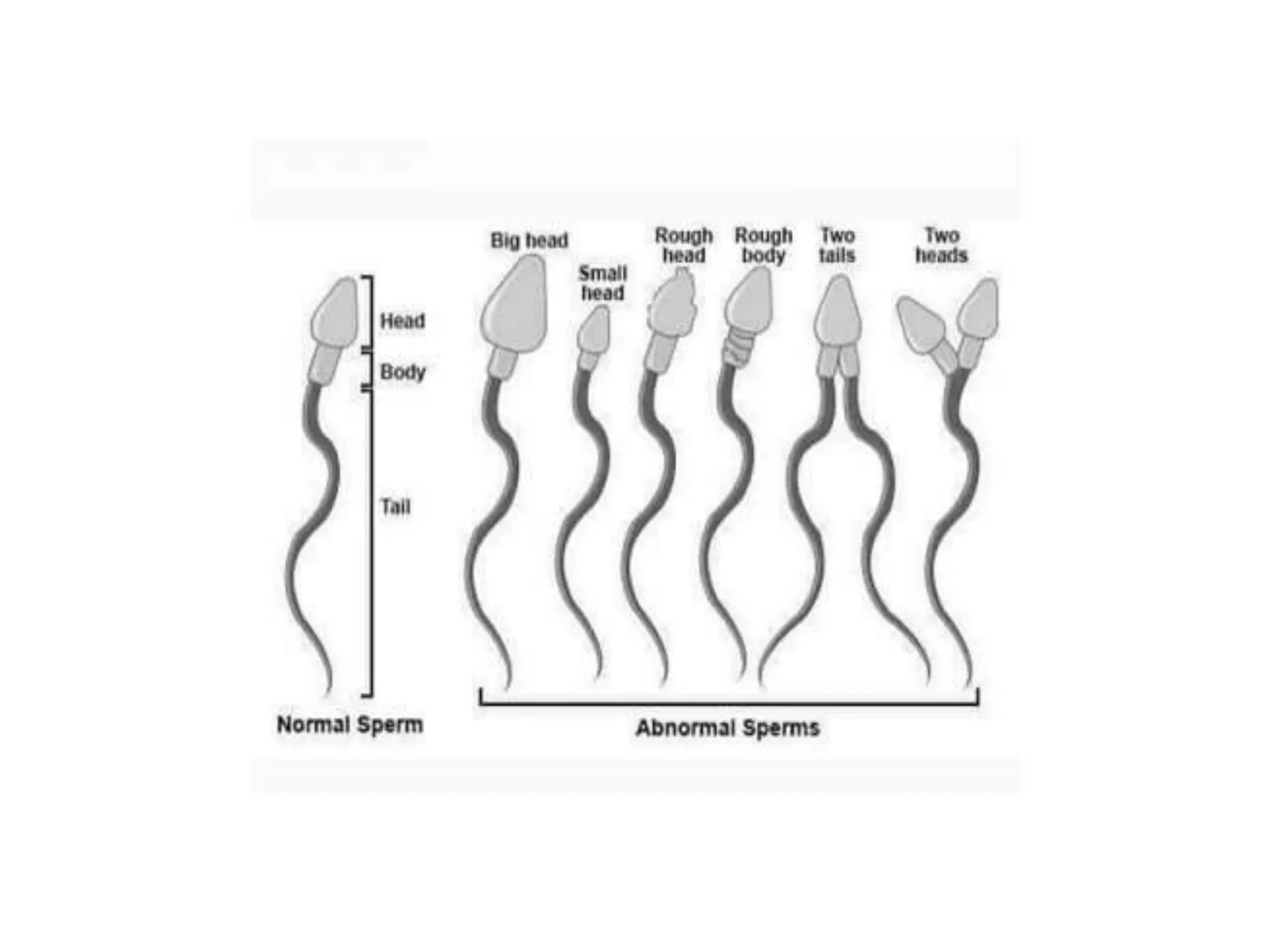
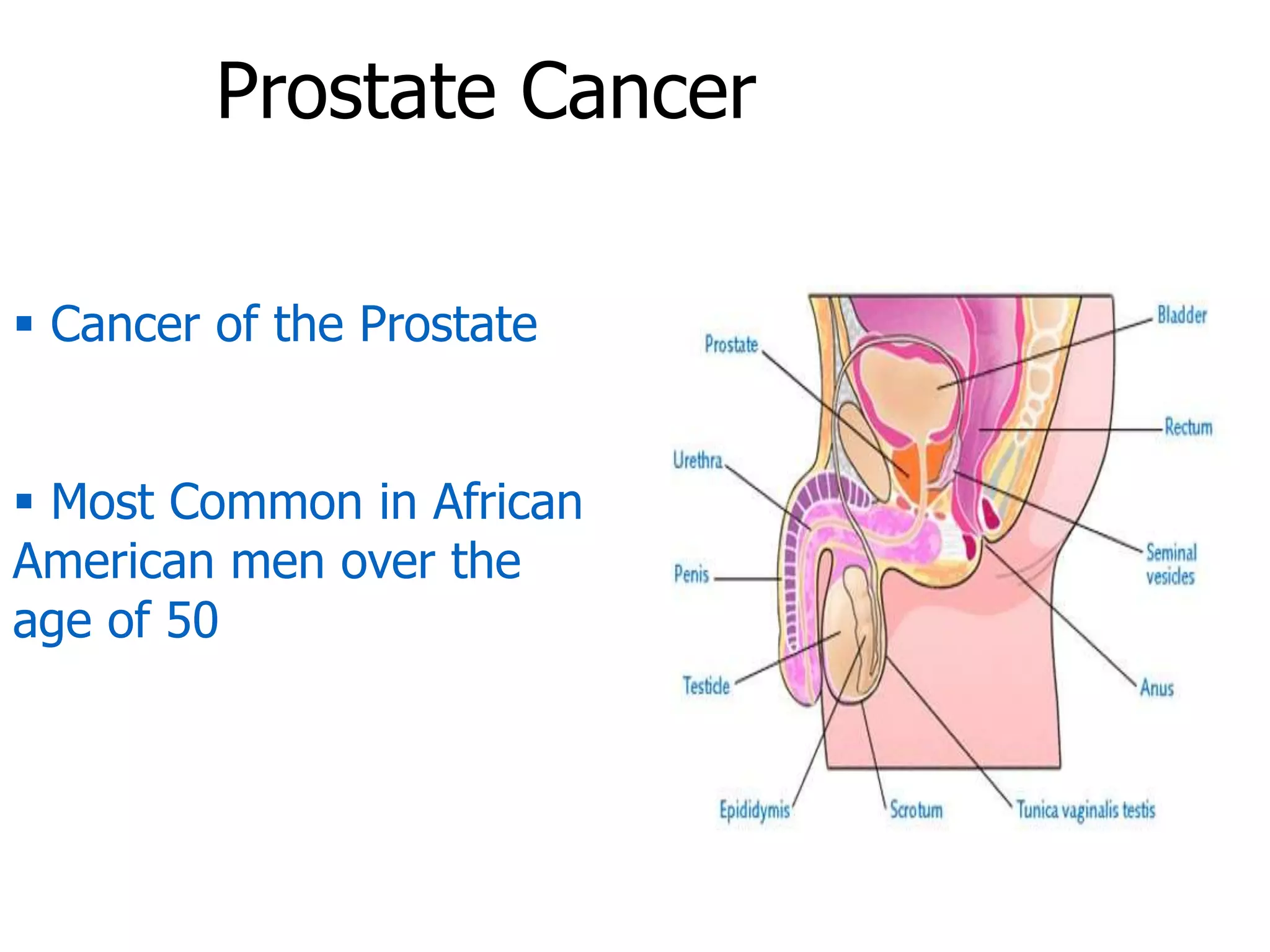
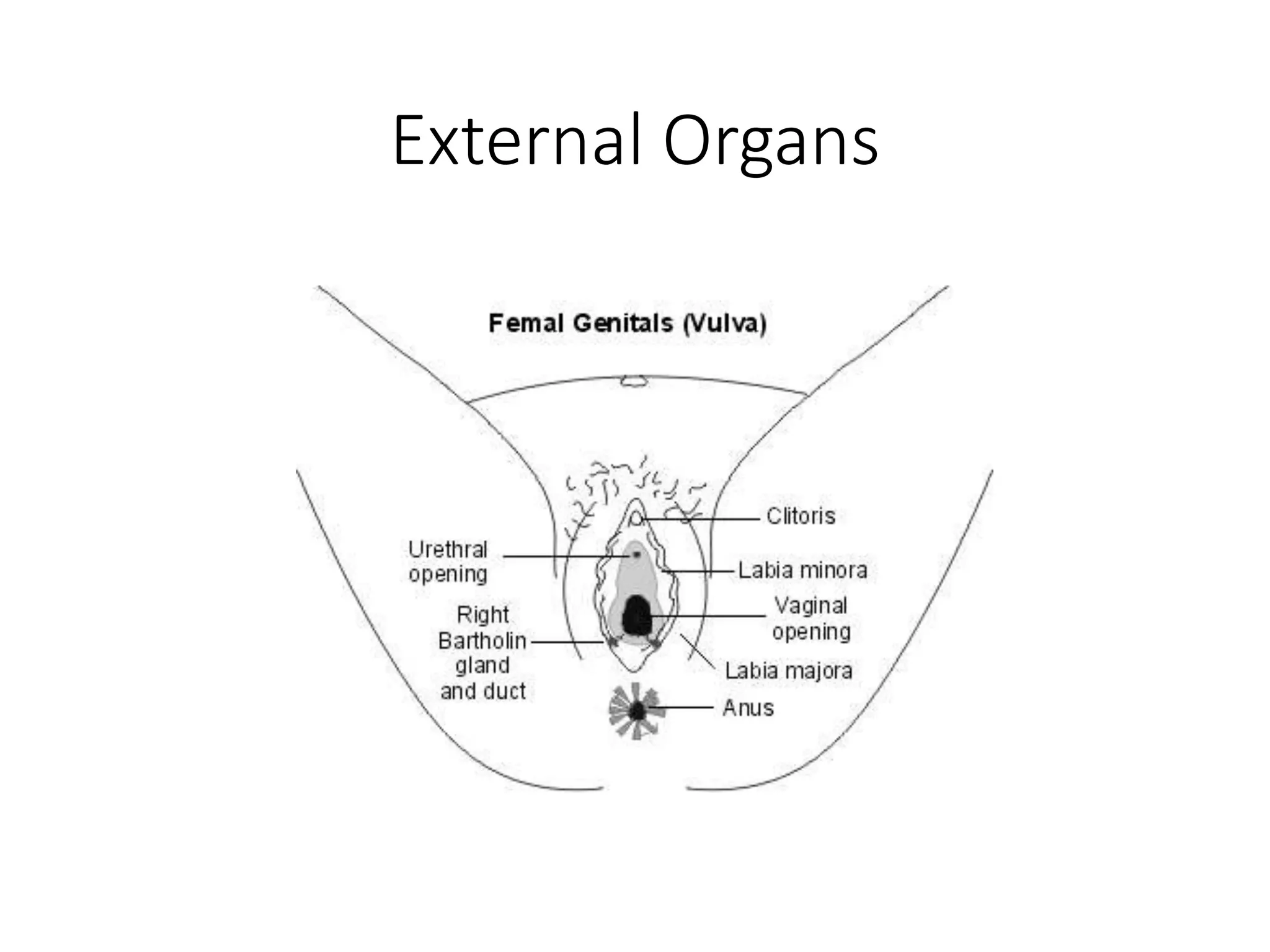
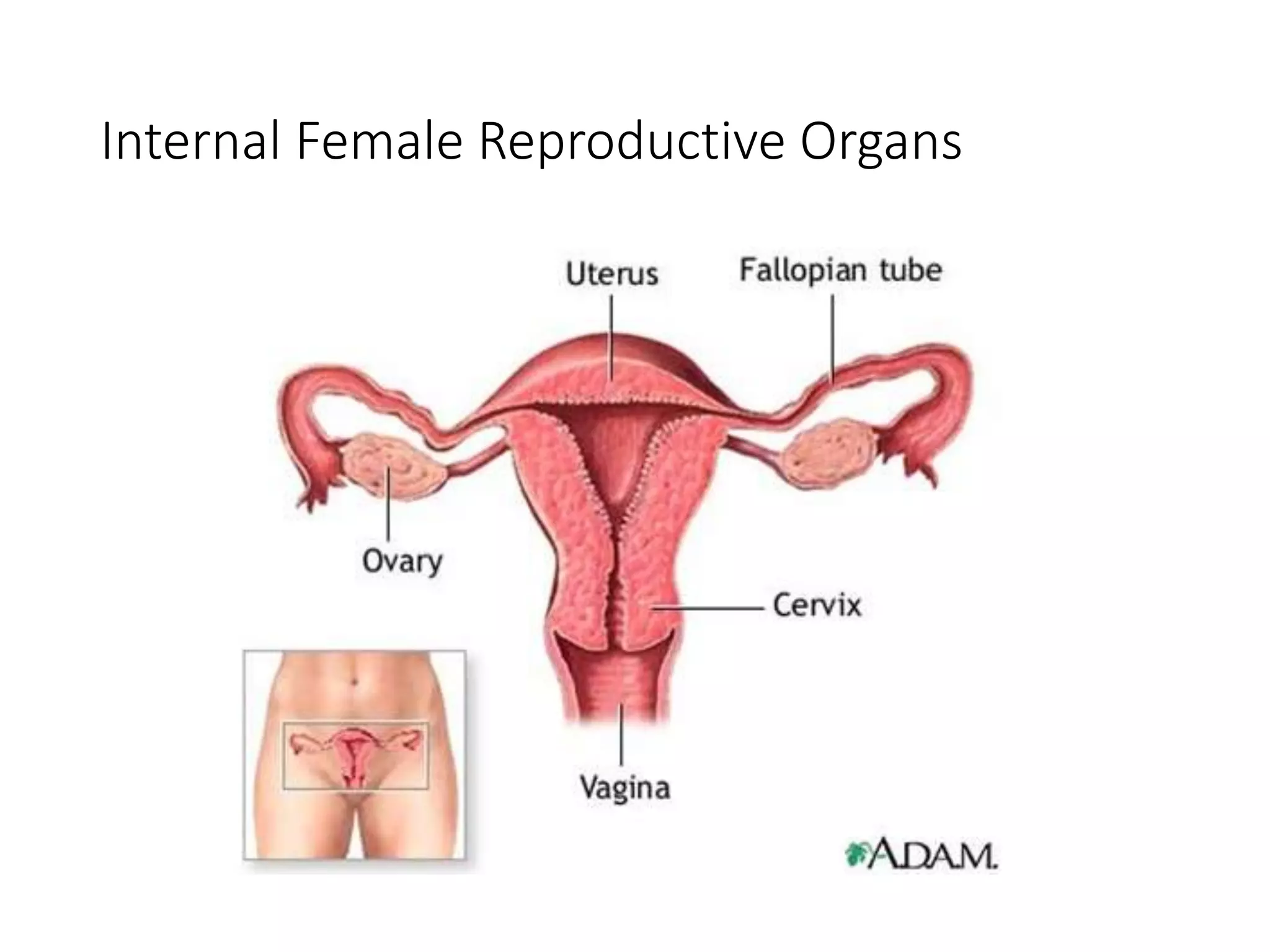
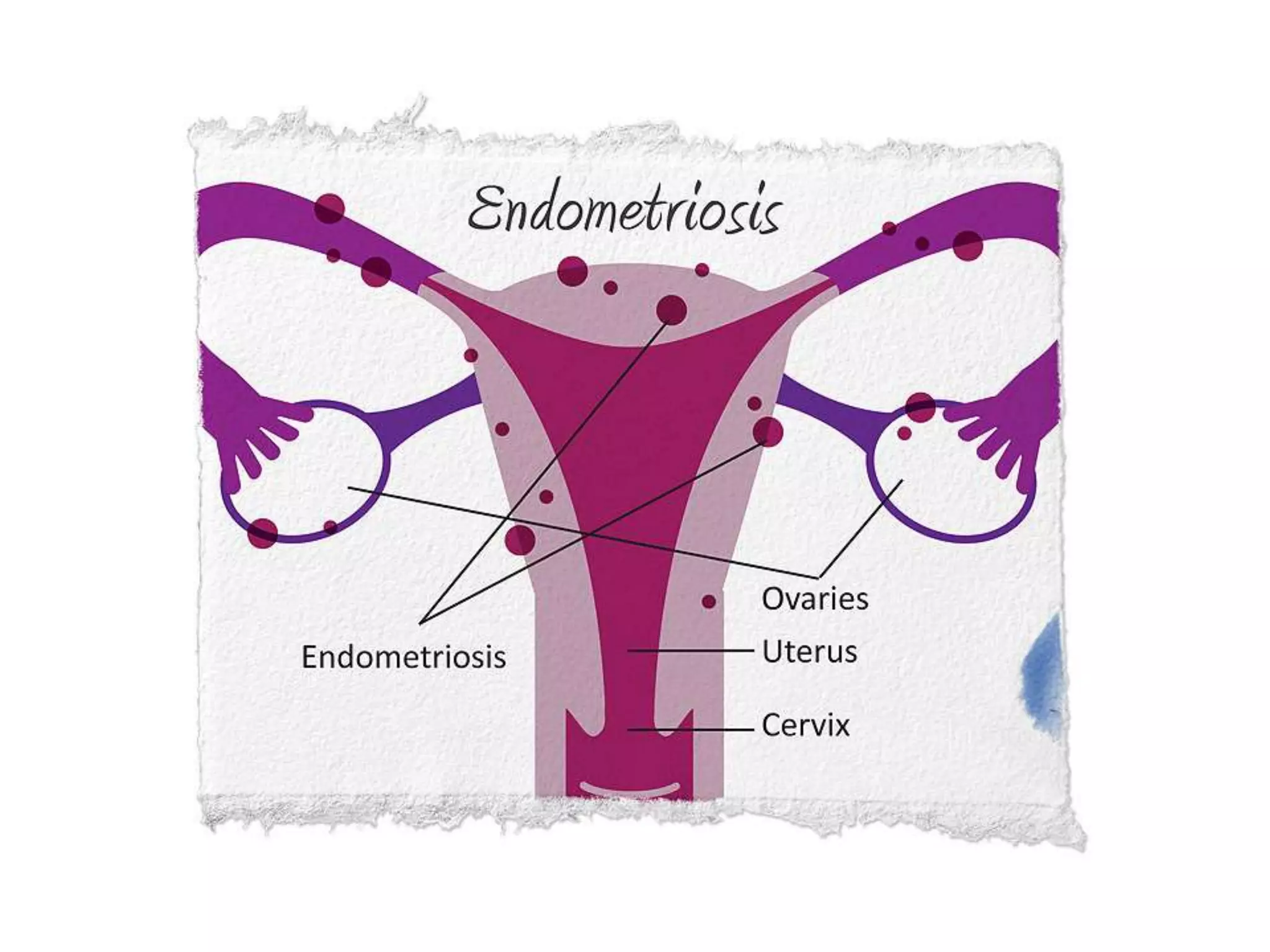
The document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. For males, it describes the external structures of the penis and scrotum, and internal structures including the prostate, vas deferens, epididymis, testicles, urethra, and seminal vesicles. It discusses sperm production and pathways, and disorders like prostate cancer, testicular cancer, and impotence. For females, it outlines the external structures of the mons pubis, labia, and clitoris, and internal structures of the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It provides one example of a female reproductive disorder, endometriosis, which involves endometrial tissue growing outside the uterus