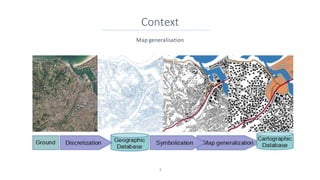
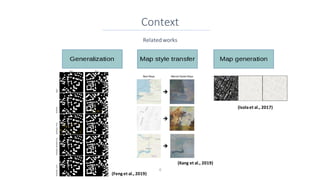
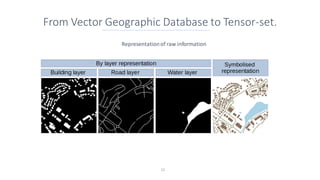
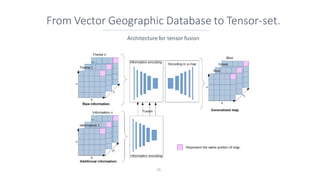
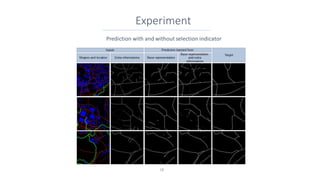
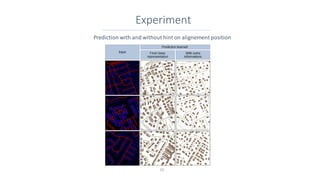
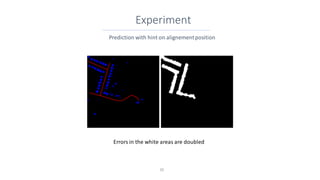
This document discusses representing vector geographic data as tensors for use in deep learning-based map generalization. It presents problems with traditional vector representations, such as a lack of spatial context and overlapping geometries. The authors propose a layered tensor representation of the data that embeds additional contextual information. They conduct experiments on road network selection and alignment using their tensor-based approach and find it performs better than methods without the contextual information.