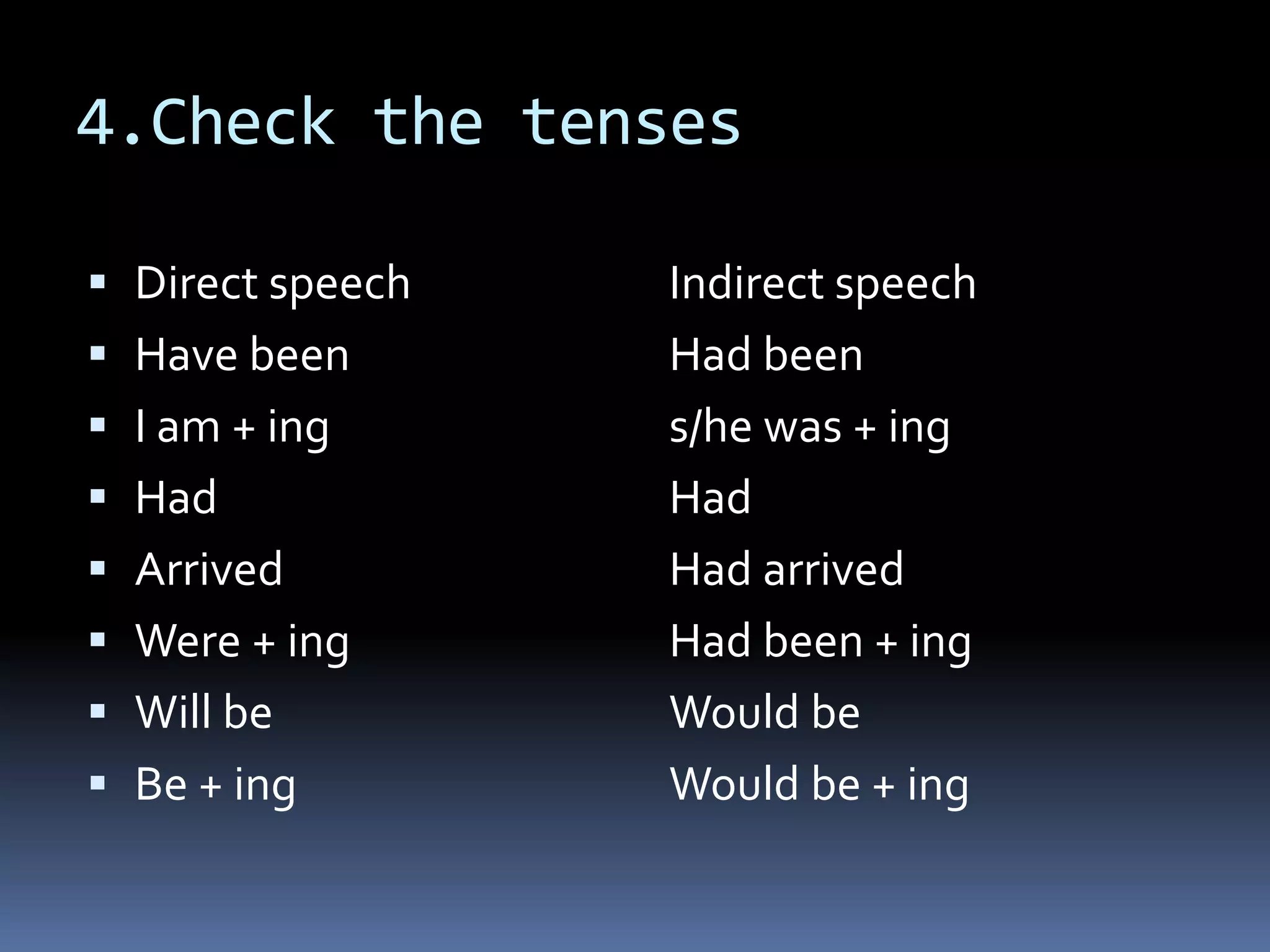
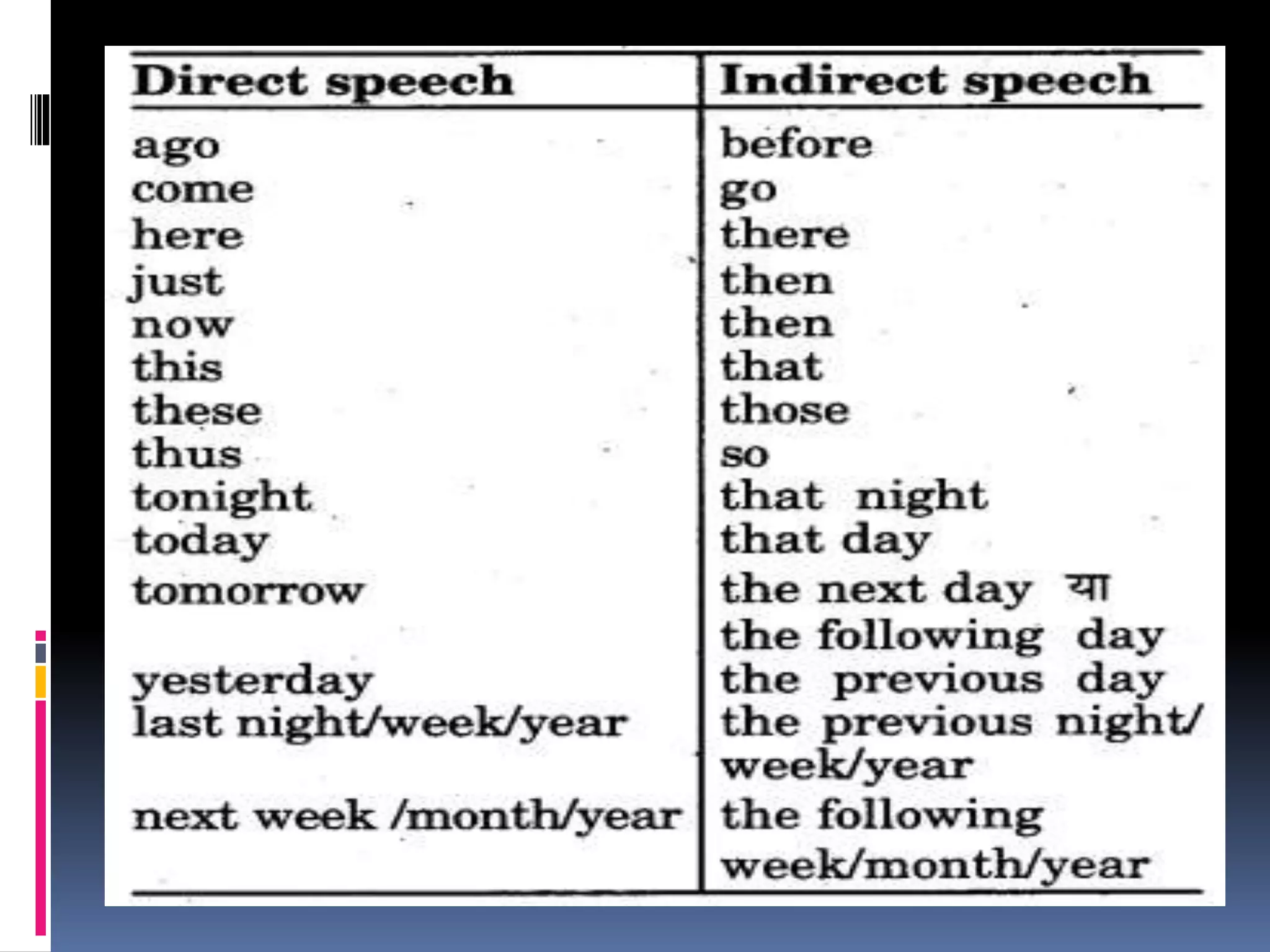
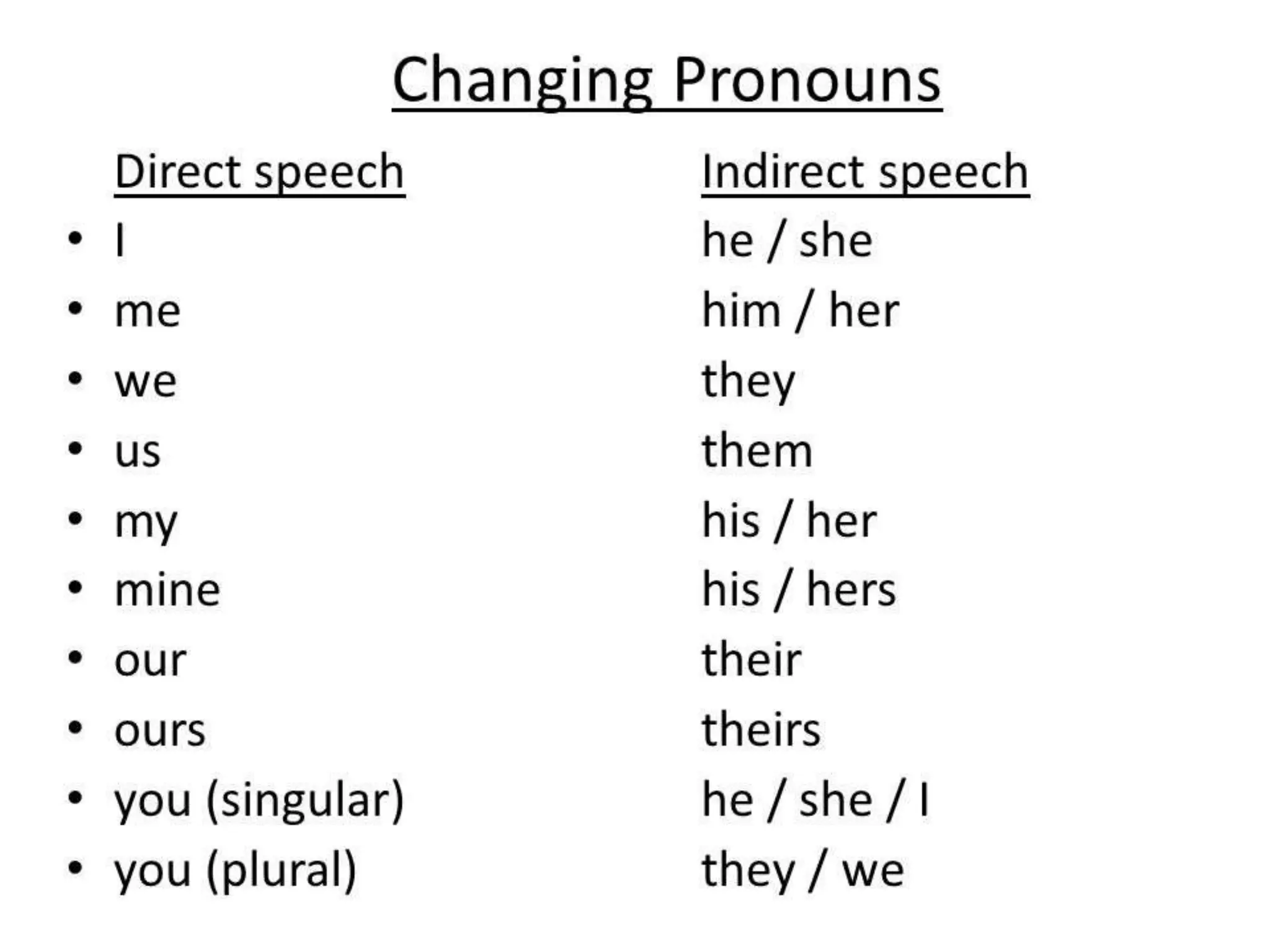
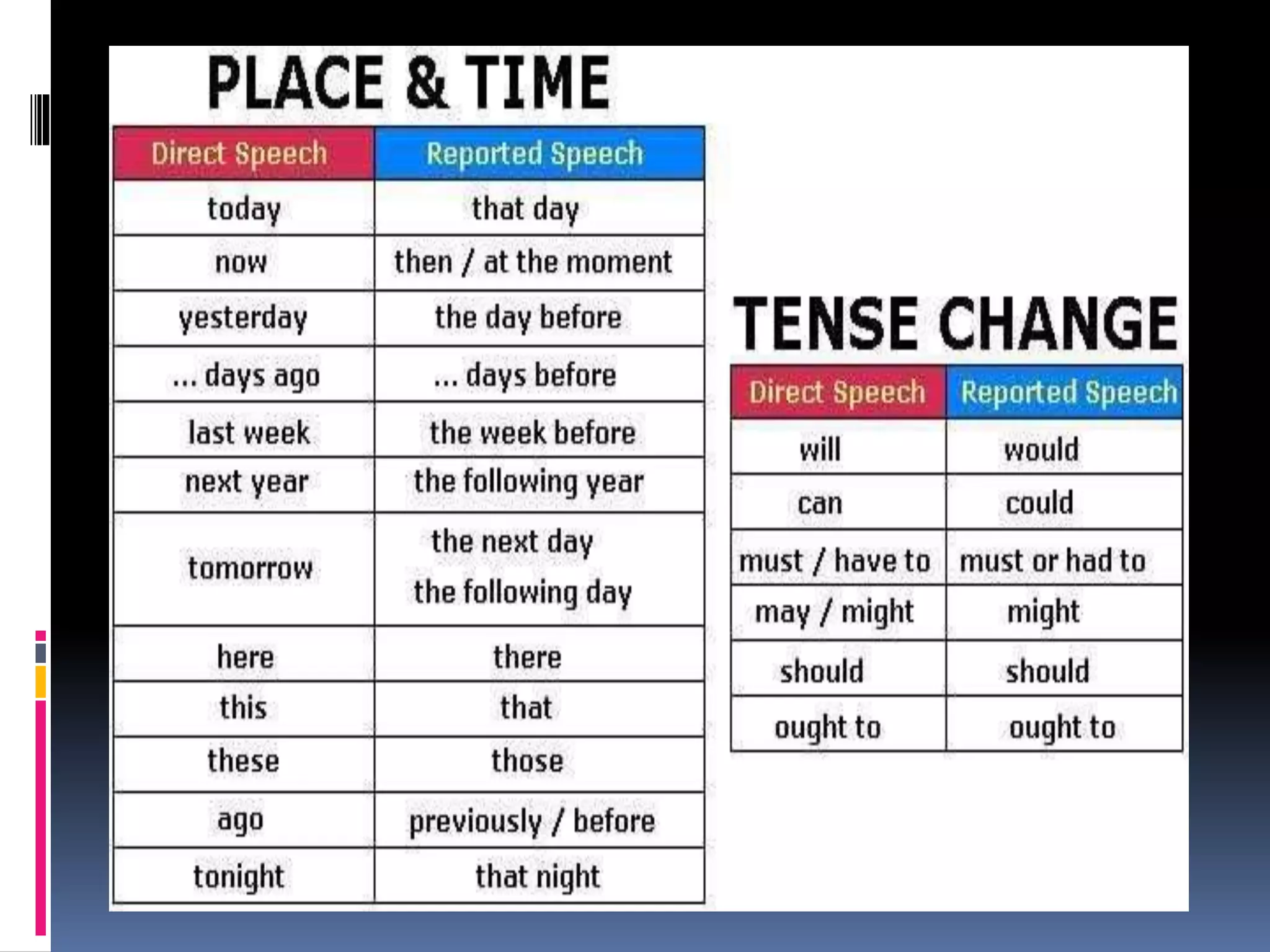
This document discusses the rules for changing direct speech to reported or indirect speech in English. It states that when the reporting verb is in the past tense, the present tenses in the direct speech change to the corresponding past tenses. It also covers exceptions when tenses do not change, such as for habitual actions or with future/present reporting verbs. The document outlines the specific tense changes that occur and how to handle interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences in indirect speech.