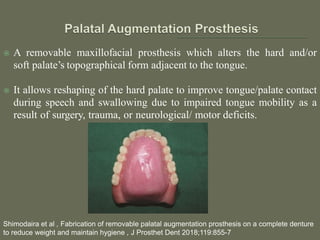
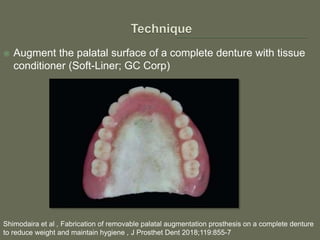
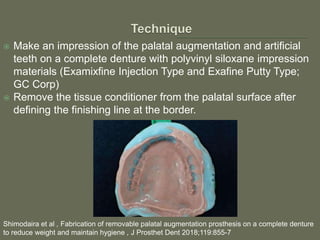
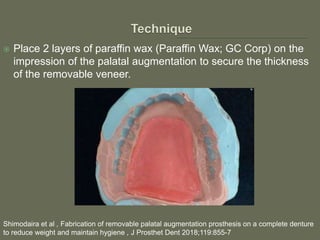
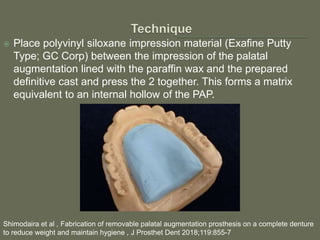
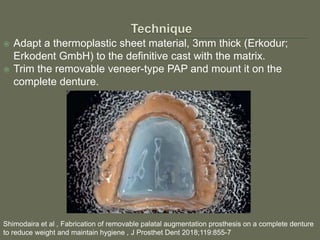
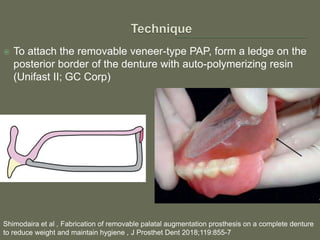
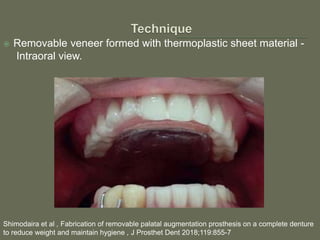
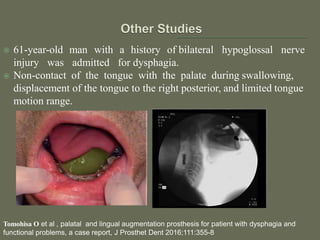
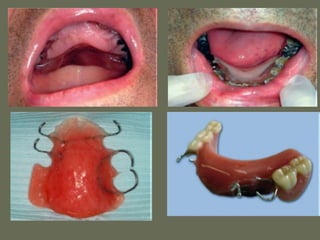
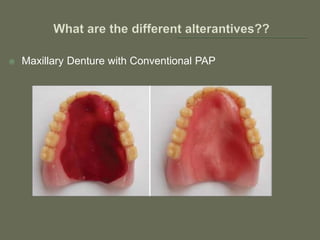
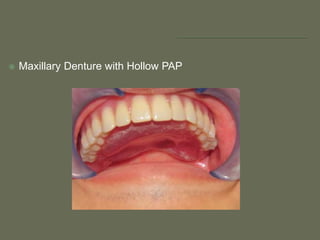
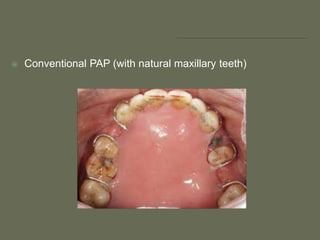
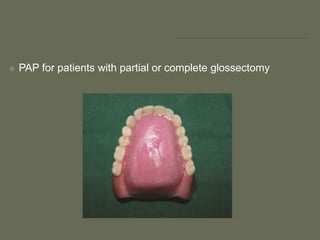
The document discusses a removable maxillofacial prosthesis designed to enhance tongue/palate contact, aiding individuals with swallowing and speech difficulties due to conditions such as stroke and neurological deficits. It highlights a methodology for fabricating a lightweight palatal augmentation prosthesis (PAP) while maintaining hygiene by using a removable veneer-type design. Clinical outcomes indicate significant weight reduction and effective functionality, affirming the technique's potential for improving the quality of life for affected patients.