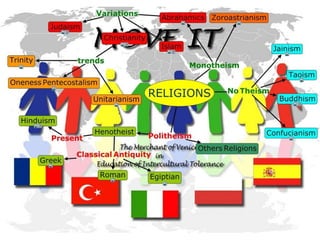
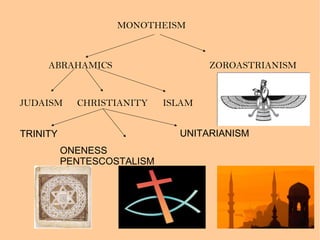
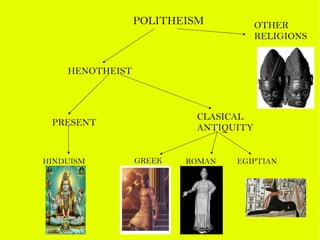
The document provides information about the five largest religions in the world: Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Judaism. It gives brief overviews of the origins, beliefs, and number of followers for each religion. Key facts include Christianity and Islam being the two largest with over 2 billion and 1.3 billion followers respectively, Hinduism having the third largest number of followers at 870 million, and Buddhism and Judaism being the fourth and fifth largest religions.





![Islam (Arabic: الإسلام al-’islām, pronounced [ʔɪsˈlæːm] ) is the monotheistic religion articulated by the Qur’an, a text considered by its adherents to be the verbatim word oF God (Arabic: الله , Allah), and by the teachings and normative example (called the Sunnah and composed of Hadith) of Muhammad, often considered by them to be the last prophet of God. In addition to referring to the religion itself, the word Islam means 'submission to God', 'peace', and 'way to peace'. An adherent of Islam is called a Muslim. I S L A M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luisreligiones-110616172140-phpapp01/85/Religions-9-320.jpg)


