1. Muscle relaxants are commonly used to facilitate intubation in burn, trauma, and critically ill patients by paralyzing the muscles and preventing complications during the intubation process like laryngospasm.
2. However, muscle relaxants can also cause problems in some patients, like hyperkalemia in patients with specific pathologies, and hemodynamic instability.
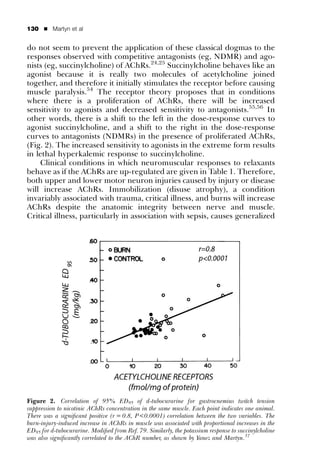
3. The response of muscles to depolarizing and nondepolarizing muscle relaxants can be altered in burn, trauma, and critically ill patients due to changes in the expression of acetylcholine receptors on muscle membranes.