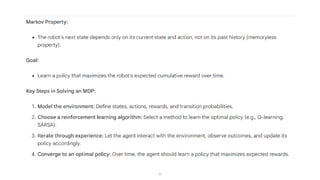
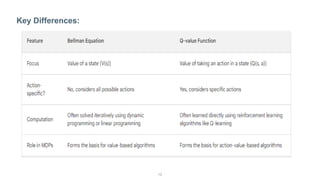
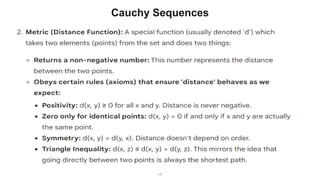
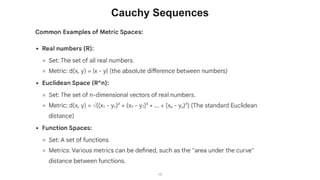
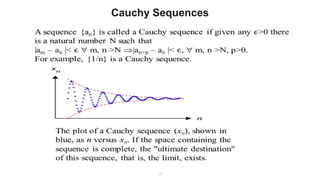
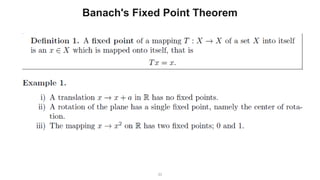
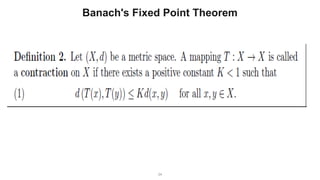
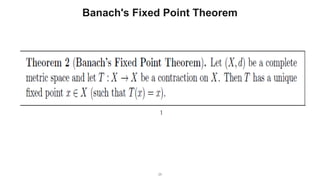
The document describes the Markov Decision Process (MDP) as a mathematical framework for modeling sequential decision-making problems under uncertainty, emphasizing the importance of the Markov property. It introduces the Bellman equation, which helps optimize decision-making by linking the value of states to immediate rewards and future values. Additionally, it discusses Banach's fixed point theorem, which aids in proving convergence in reinforcement learning algorithms like value iteration and policy iteration.



![4
Bellman Equation in MDP
The Bellman equation is a cornerstone of Markov Decision
Processes (MDPs), providing a powerful tool for understanding
and optimizing sequential decision-making under uncertainty.
The standard Bellman equation expresses the value of
a state (V(s)) as the expected reward of taking the best
action from that state, considering both the
immediate reward and the discounted value of the
next state reached:
V(s) = max_a [ R(s, a) + γ * Σ P(s', s, a) *
V(s') ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-2-240925111233-d27bfa66/85/Reinforcement-learning-Markov-decisions-process-mdp-ppt-4-320.jpg)

![6
The optimal Bellman equation emphasizes finding the
optimal value function (V*): the function that assigns the
highest possible expected total reward to each state under
the optimal policy.
optimOptimal Bellman Equationation
V*(s) = max_a [ R(s, a) + γ * Σ P(s', s, a) * V*(s’) ]
This equation essentially says that the optimal value of a state
is equal to the immediate reward you get by taking the best
possible action in that state, plus the discounted value of the
next state you reach under the optimal policy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module-2-240925111233-d27bfa66/85/Reinforcement-learning-Markov-decisions-process-mdp-ppt-6-320.jpg)