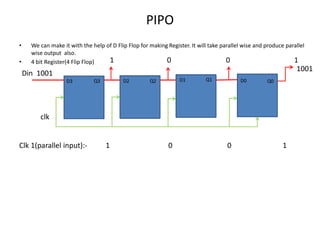
Registers are high-speed memory units that are part of a computer's processor. They can hold data like bit sequences or single pieces of information. Registers are made up of flip flops, with multiple flip flops combined to create registers of different bit sizes (e.g. 4 flip flops for a 4-bit register). Registers can be constructed to operate in different input/output configurations, including serial input serial output (SISO), serial input parallel output (SIPO), parallel input serial output (PISO), and parallel input parallel output (PIPO).