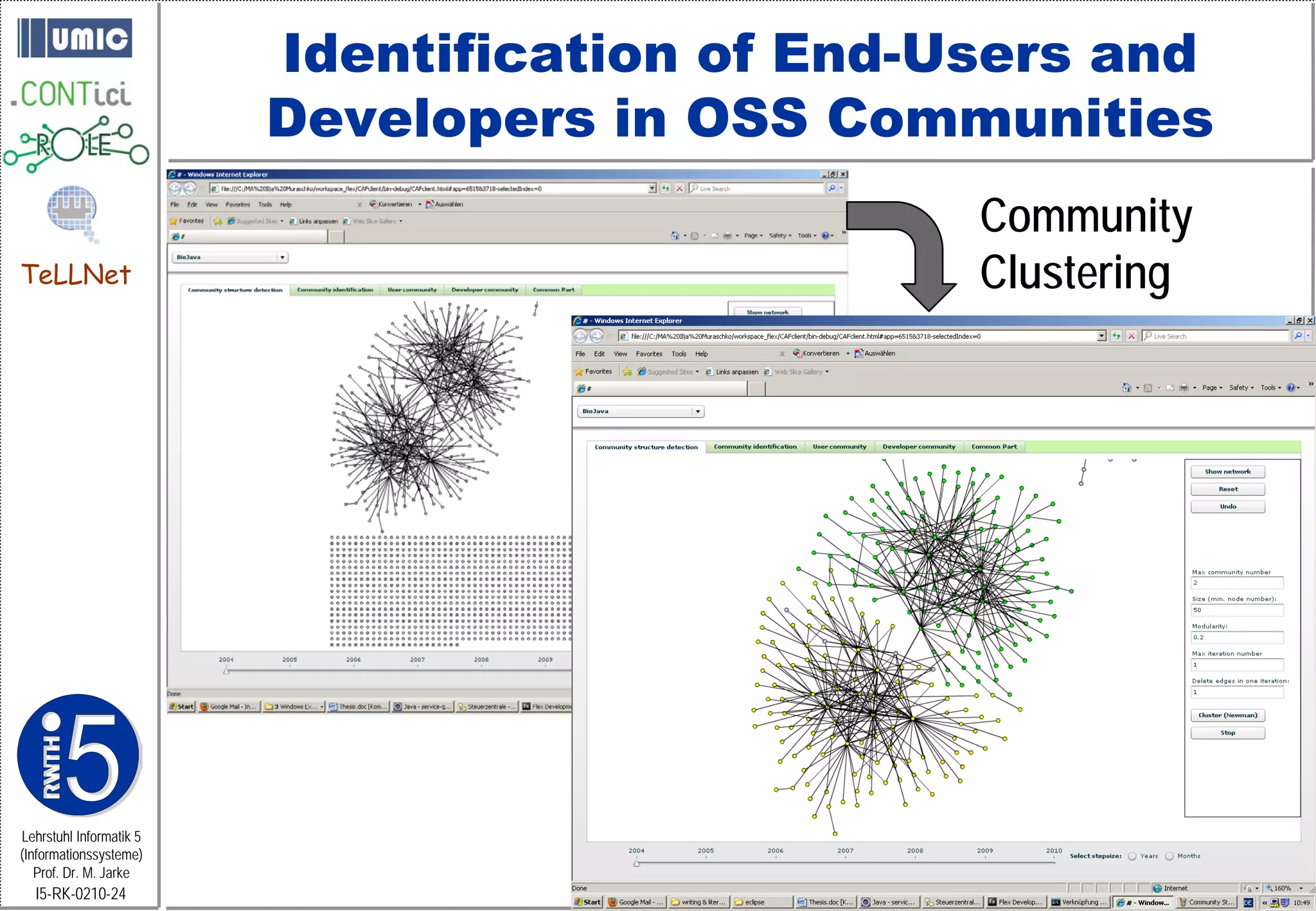
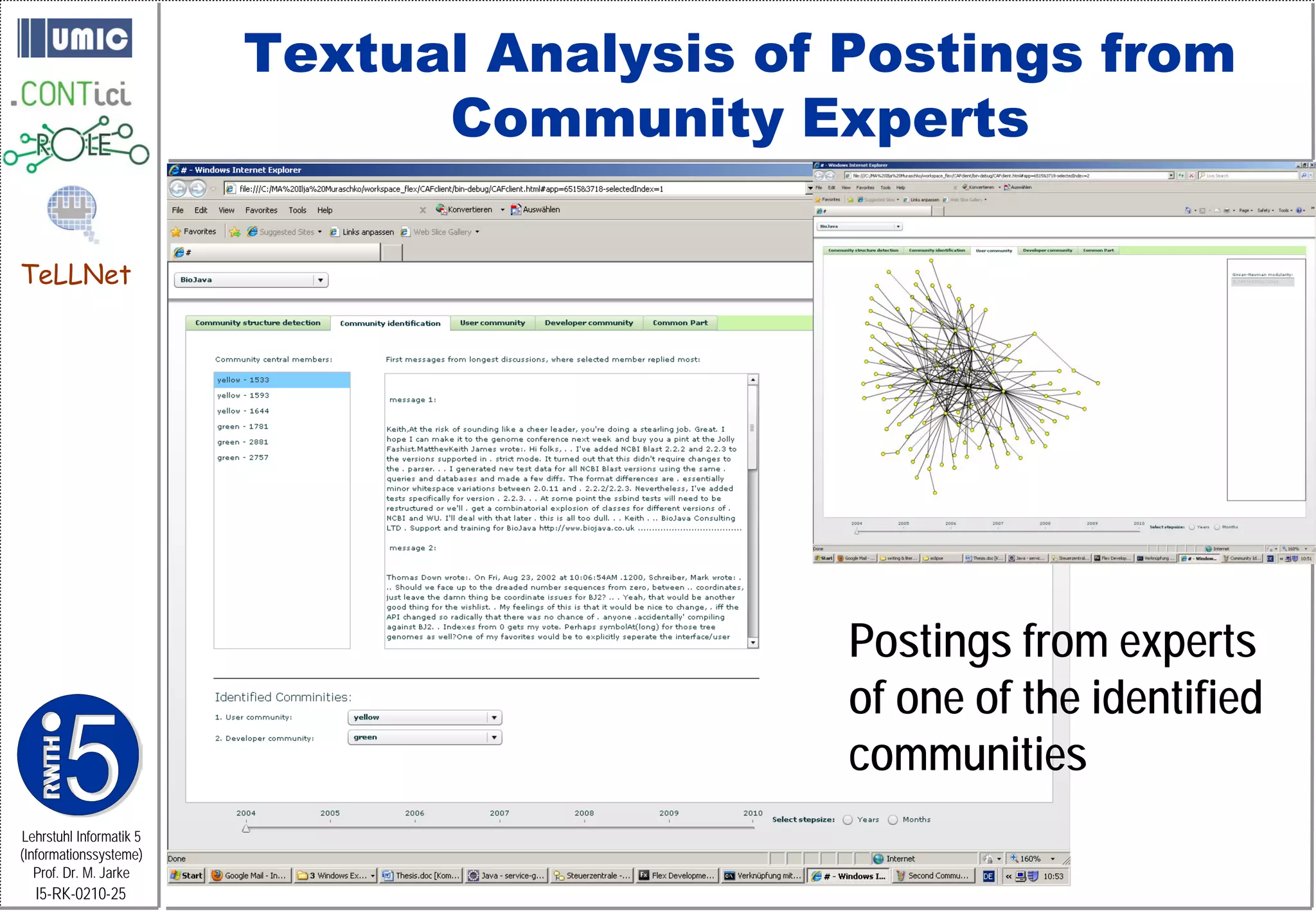
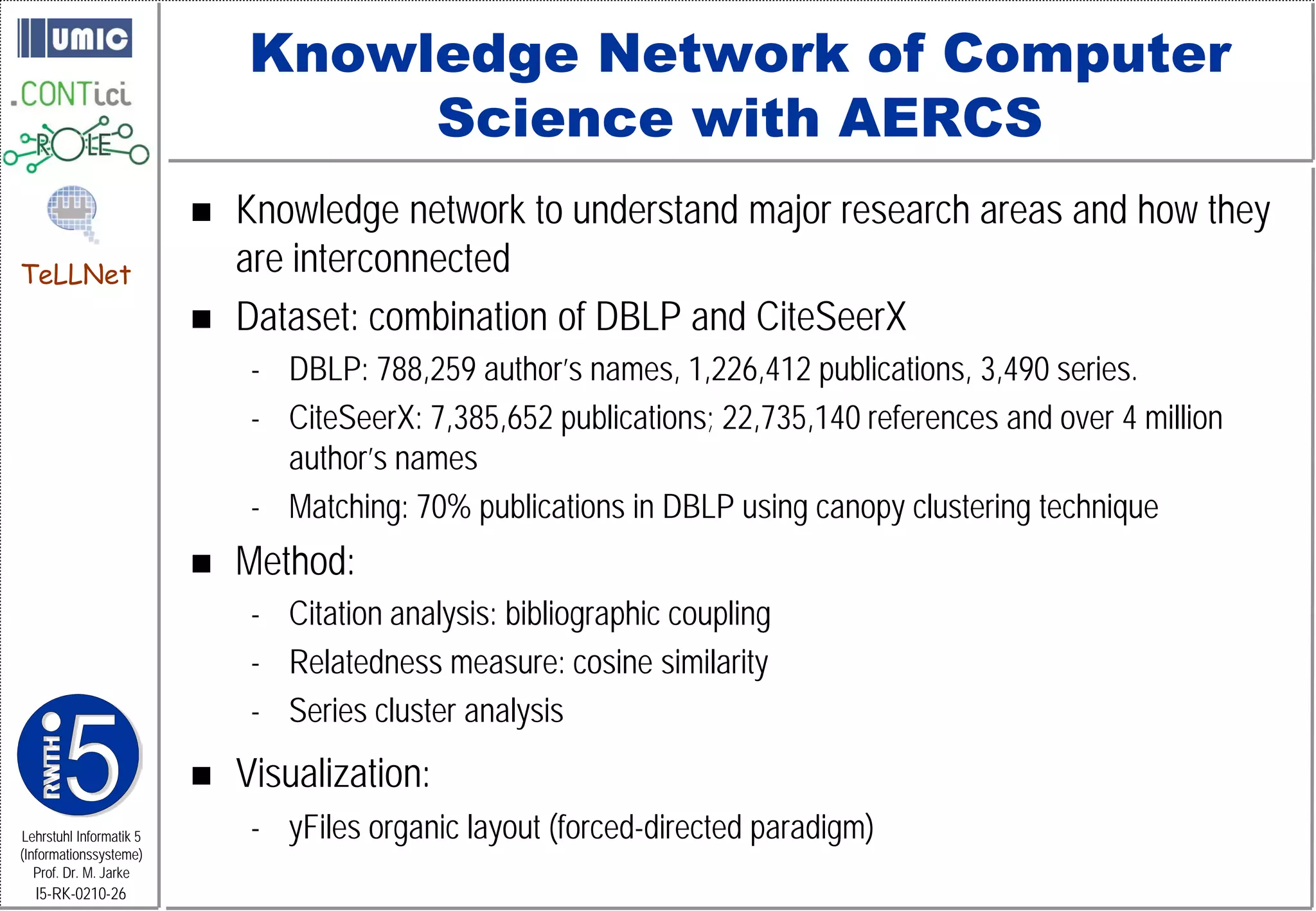
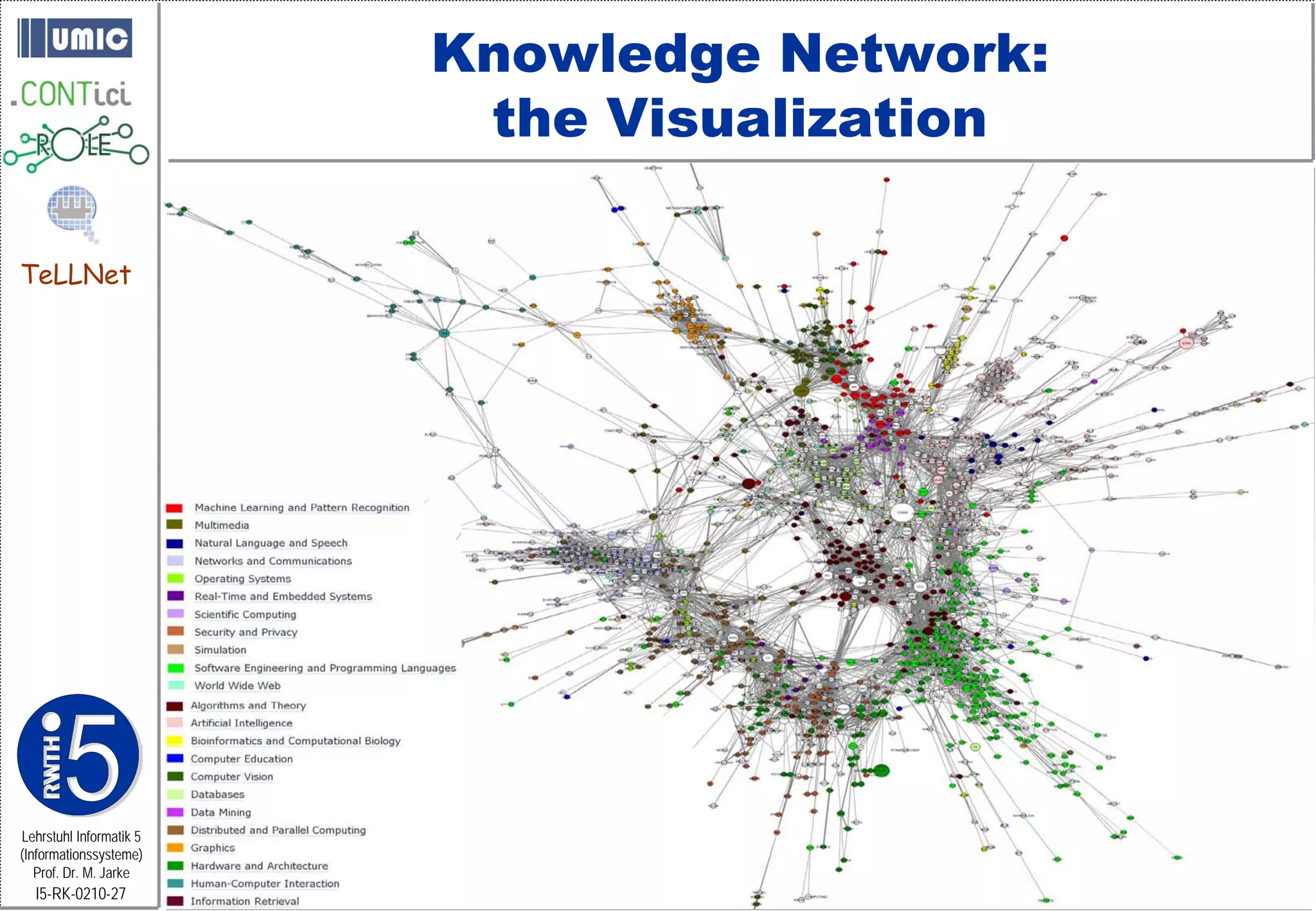
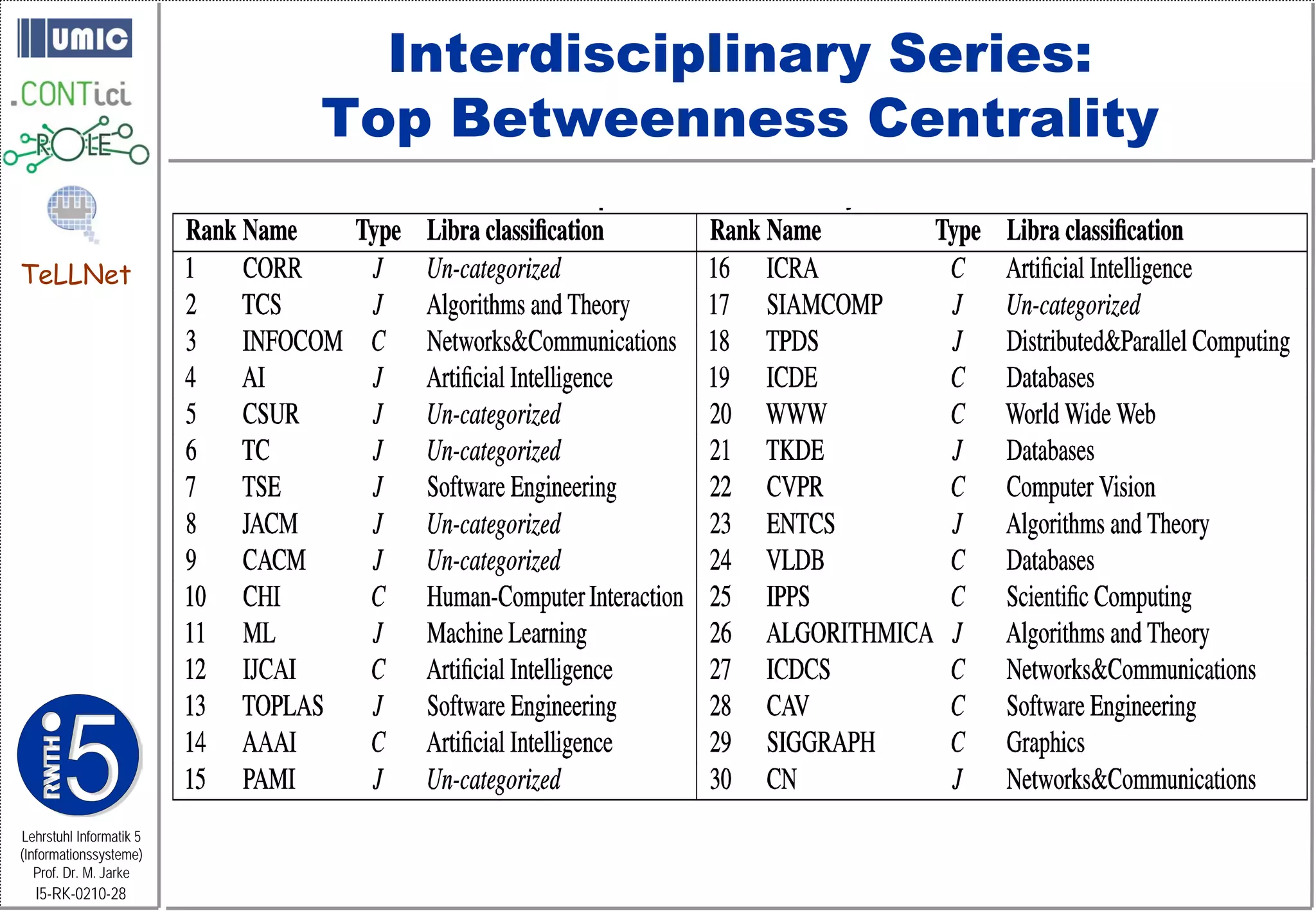
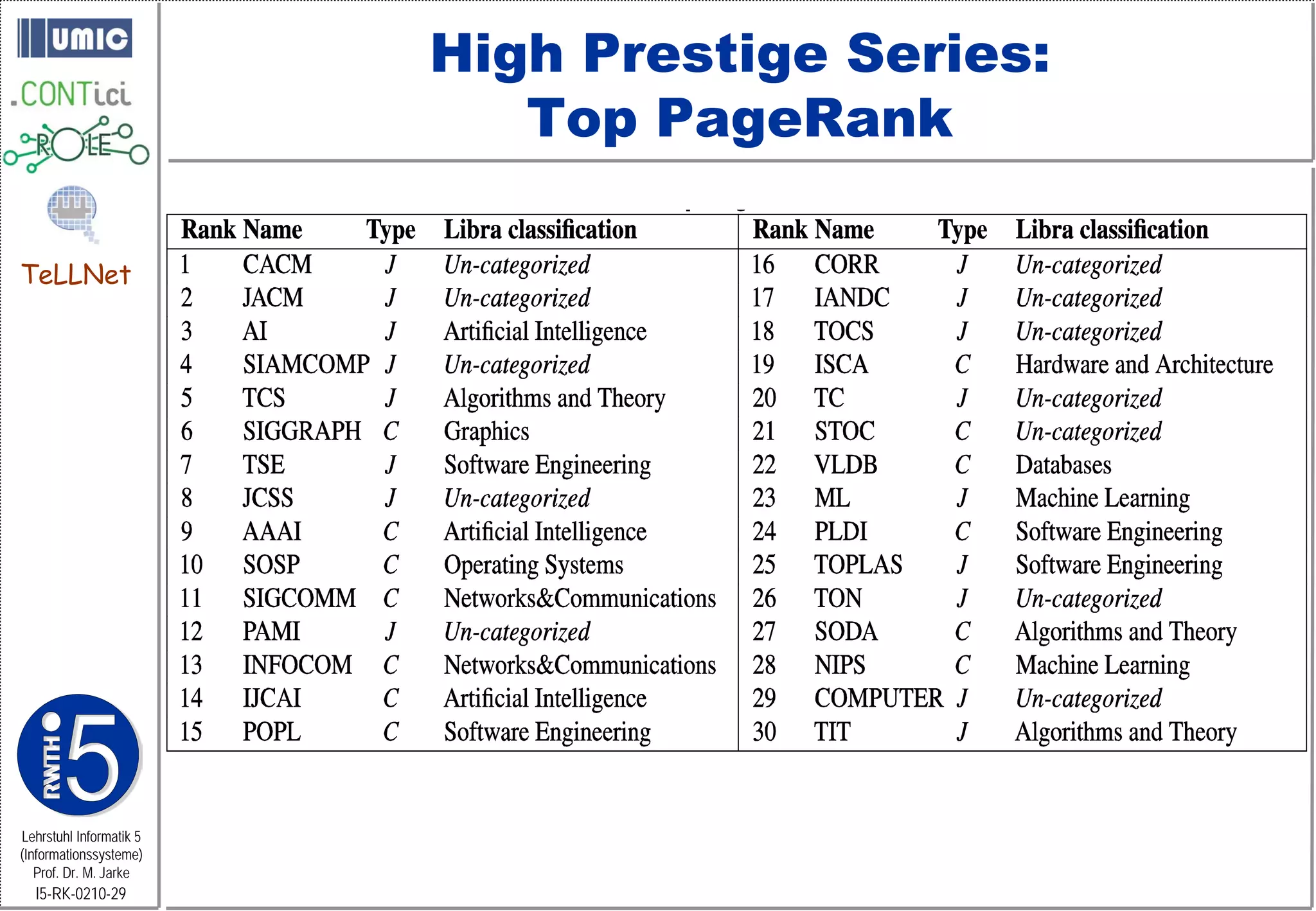
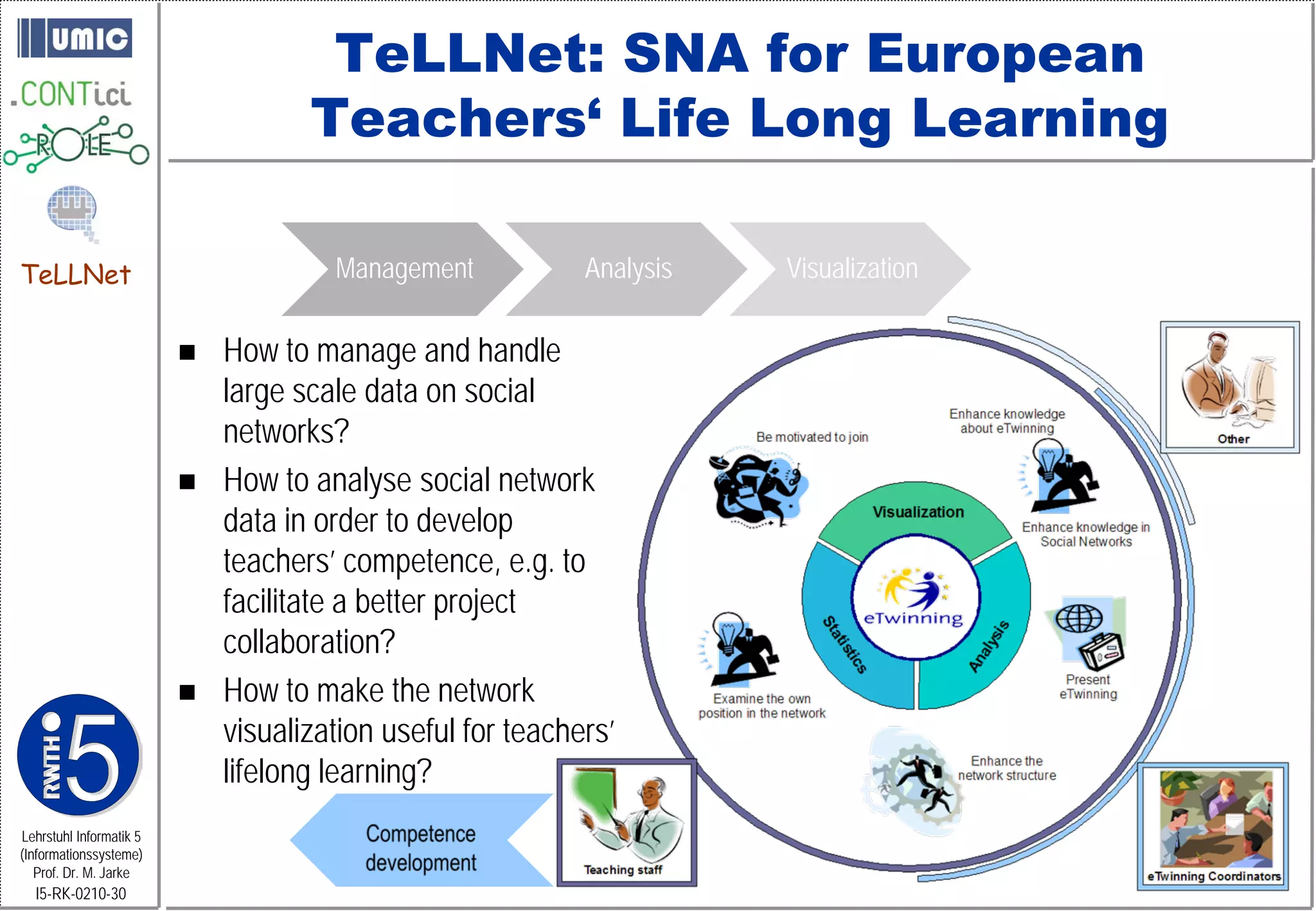
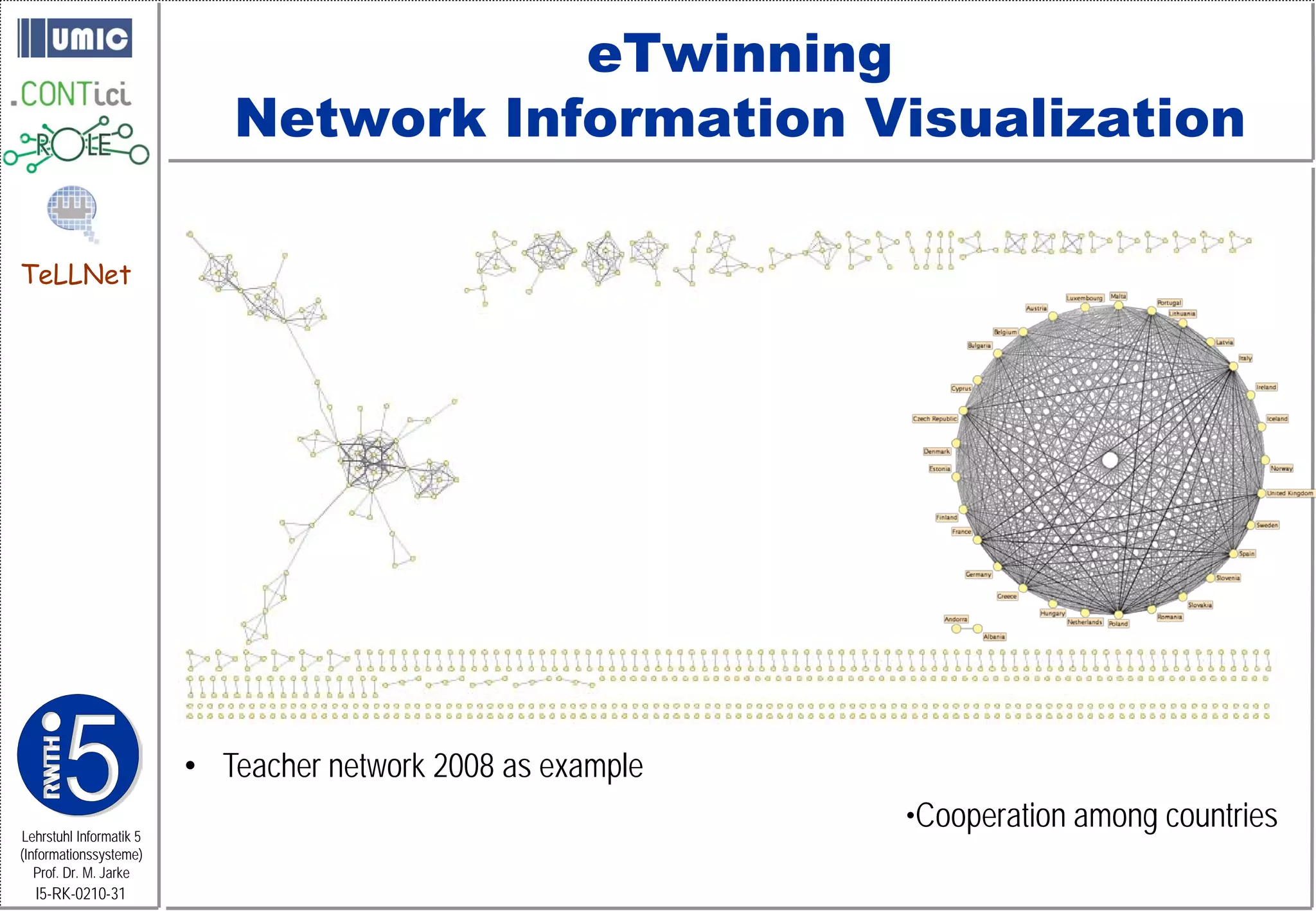
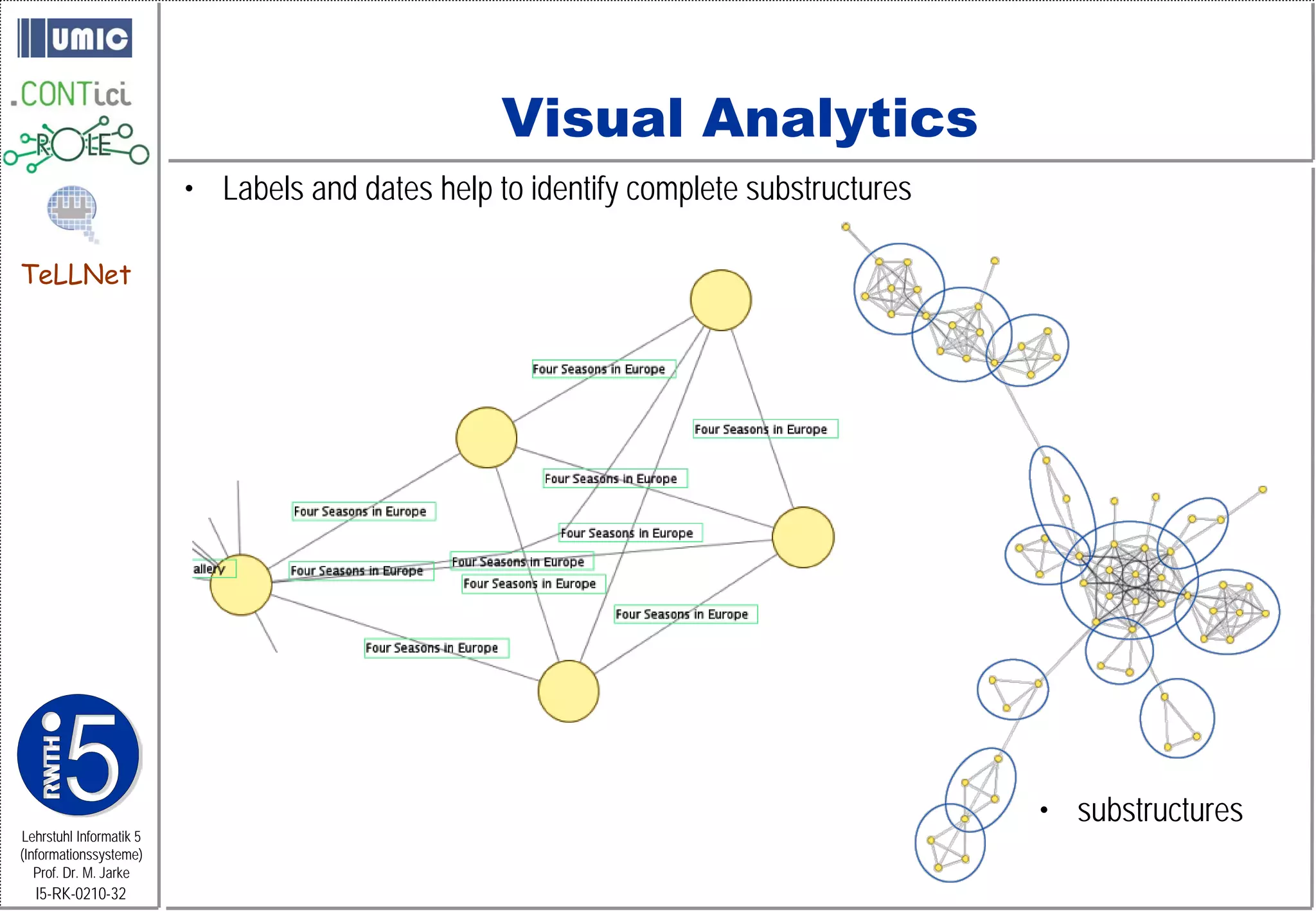
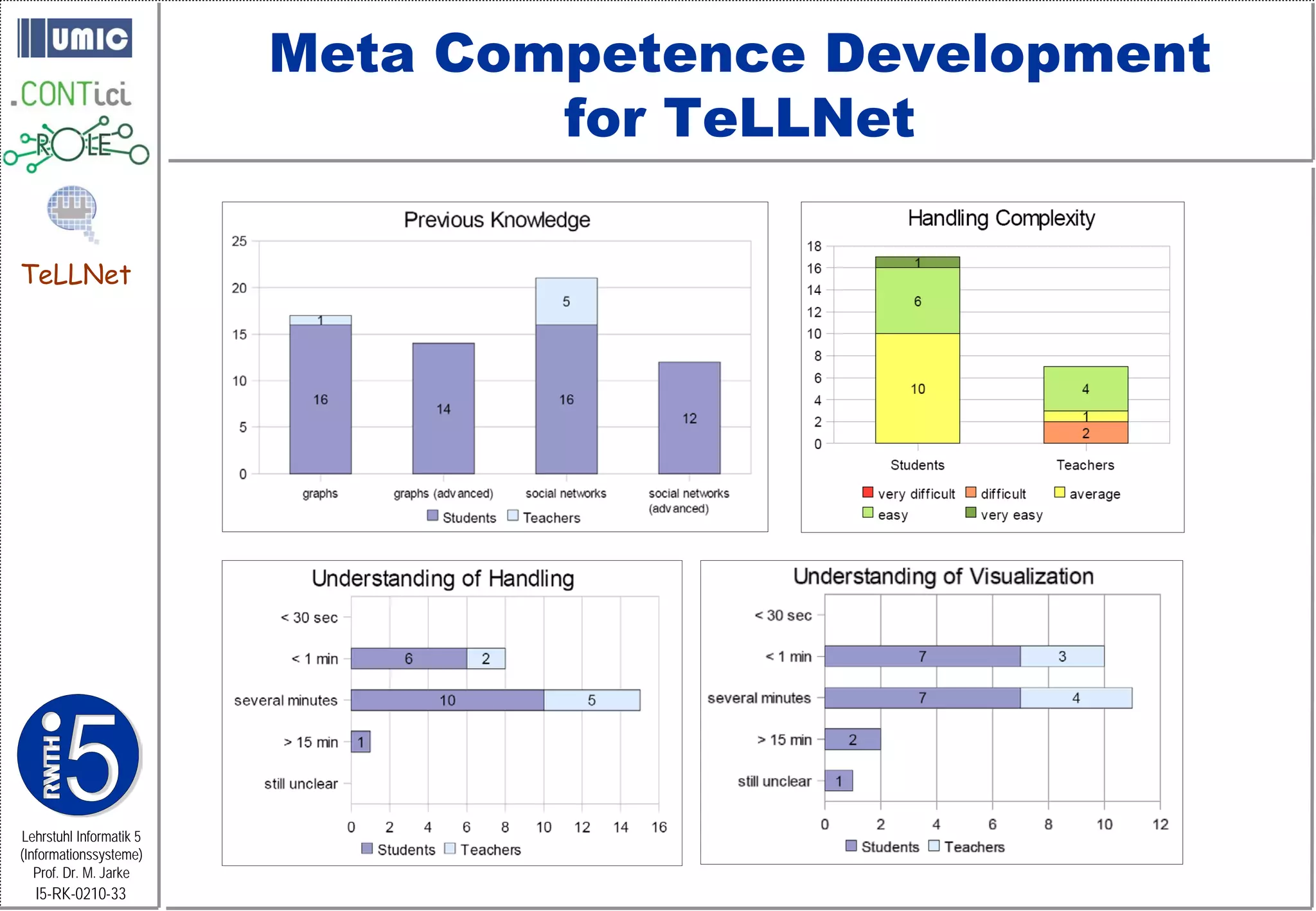
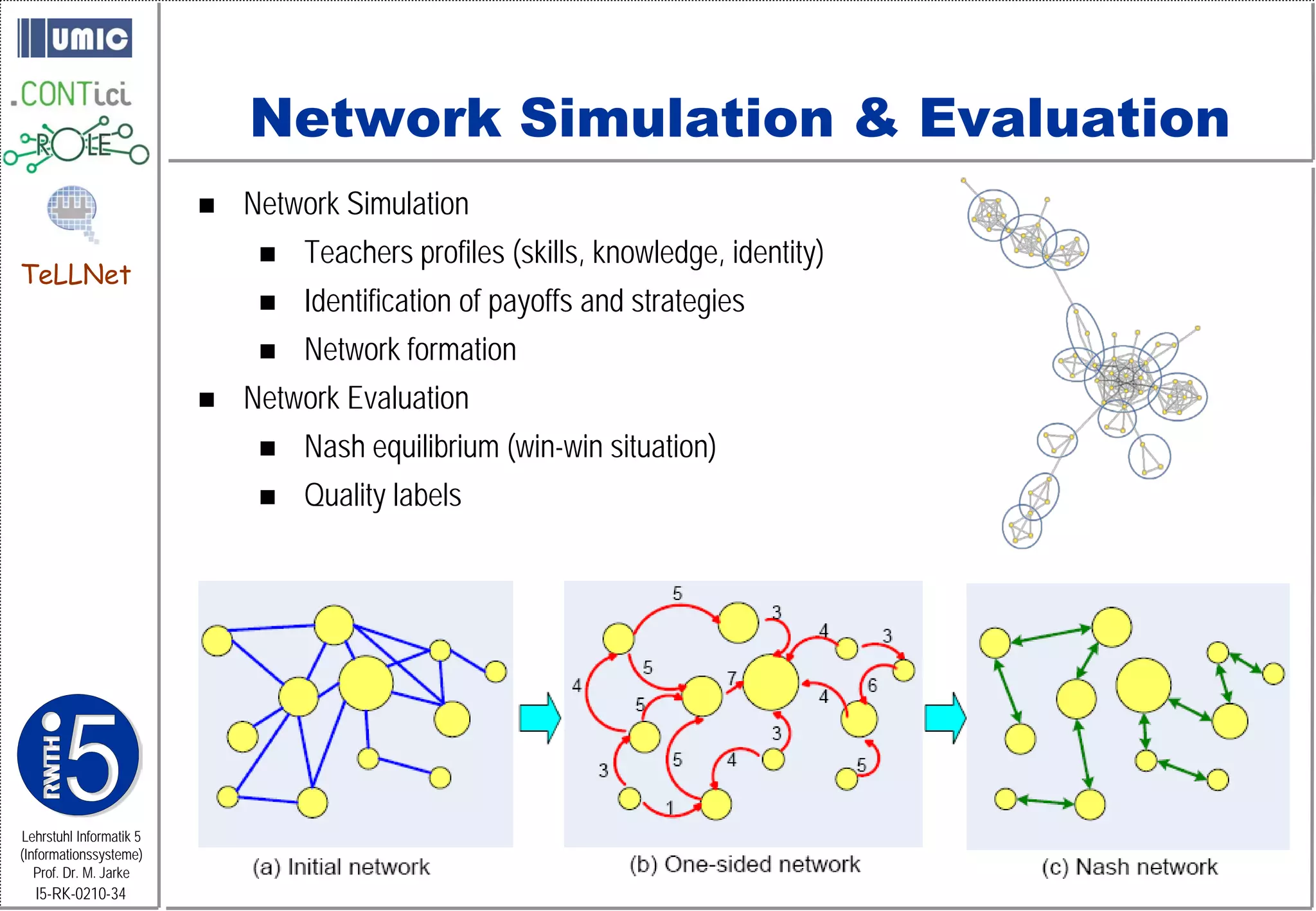
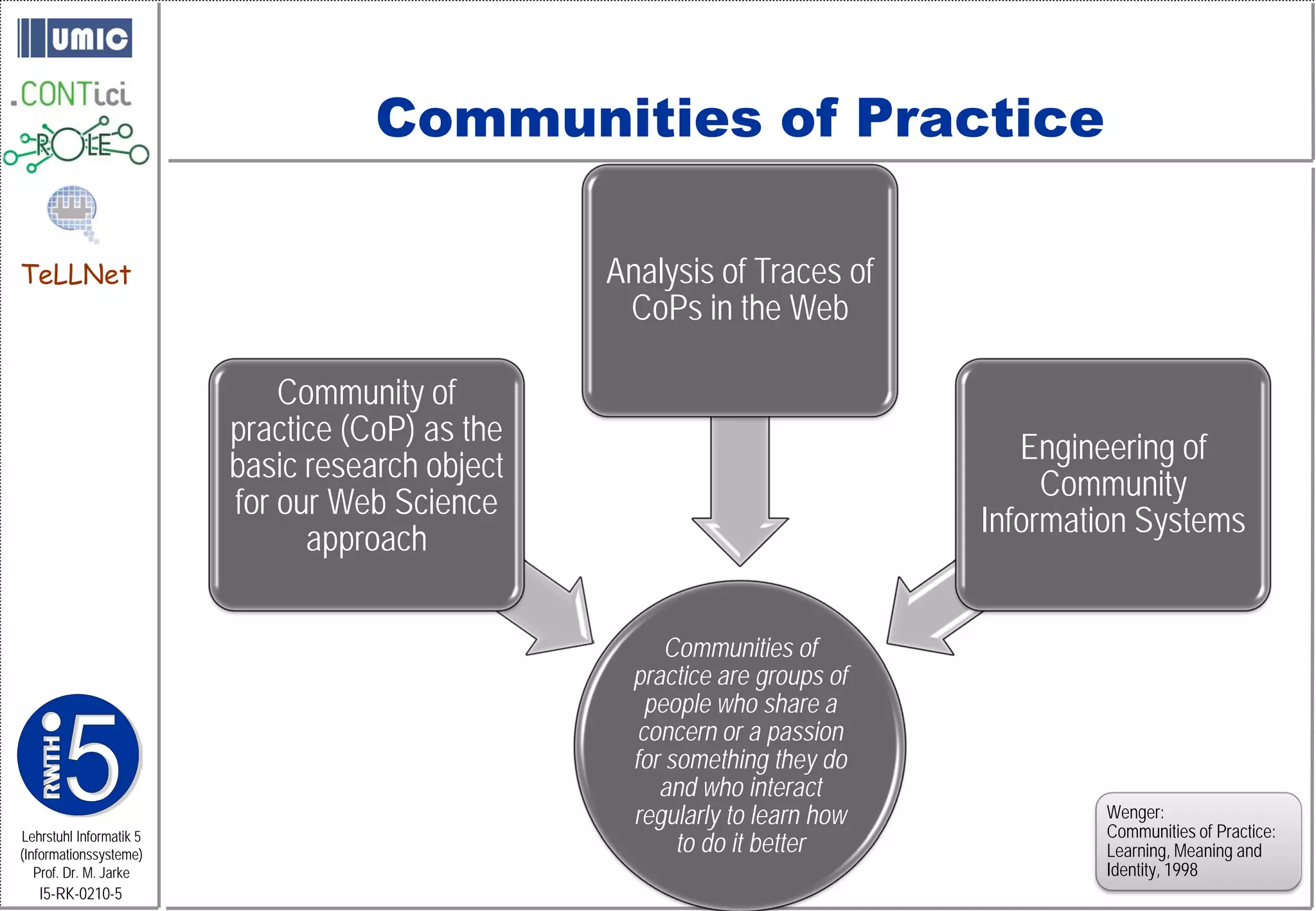
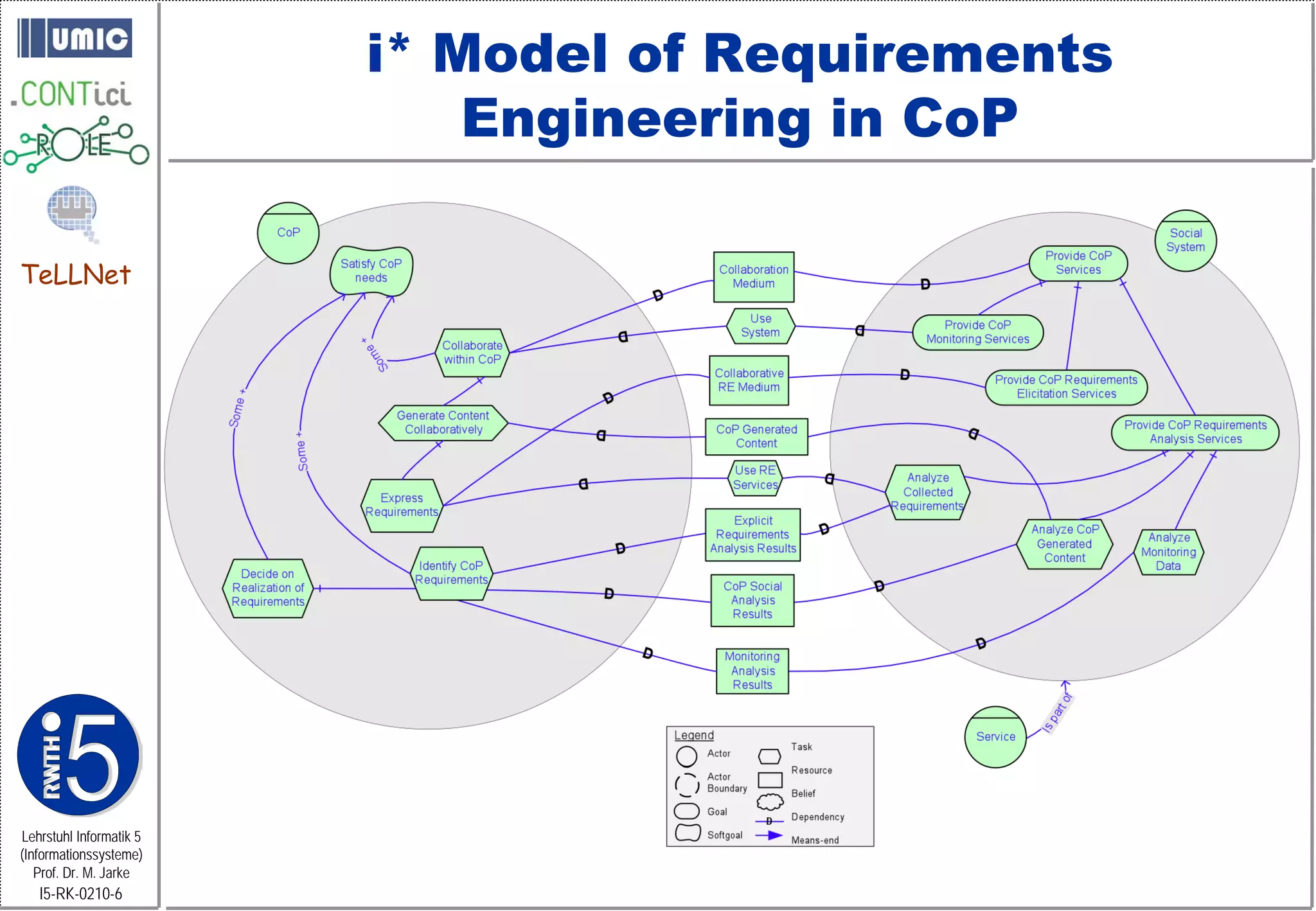
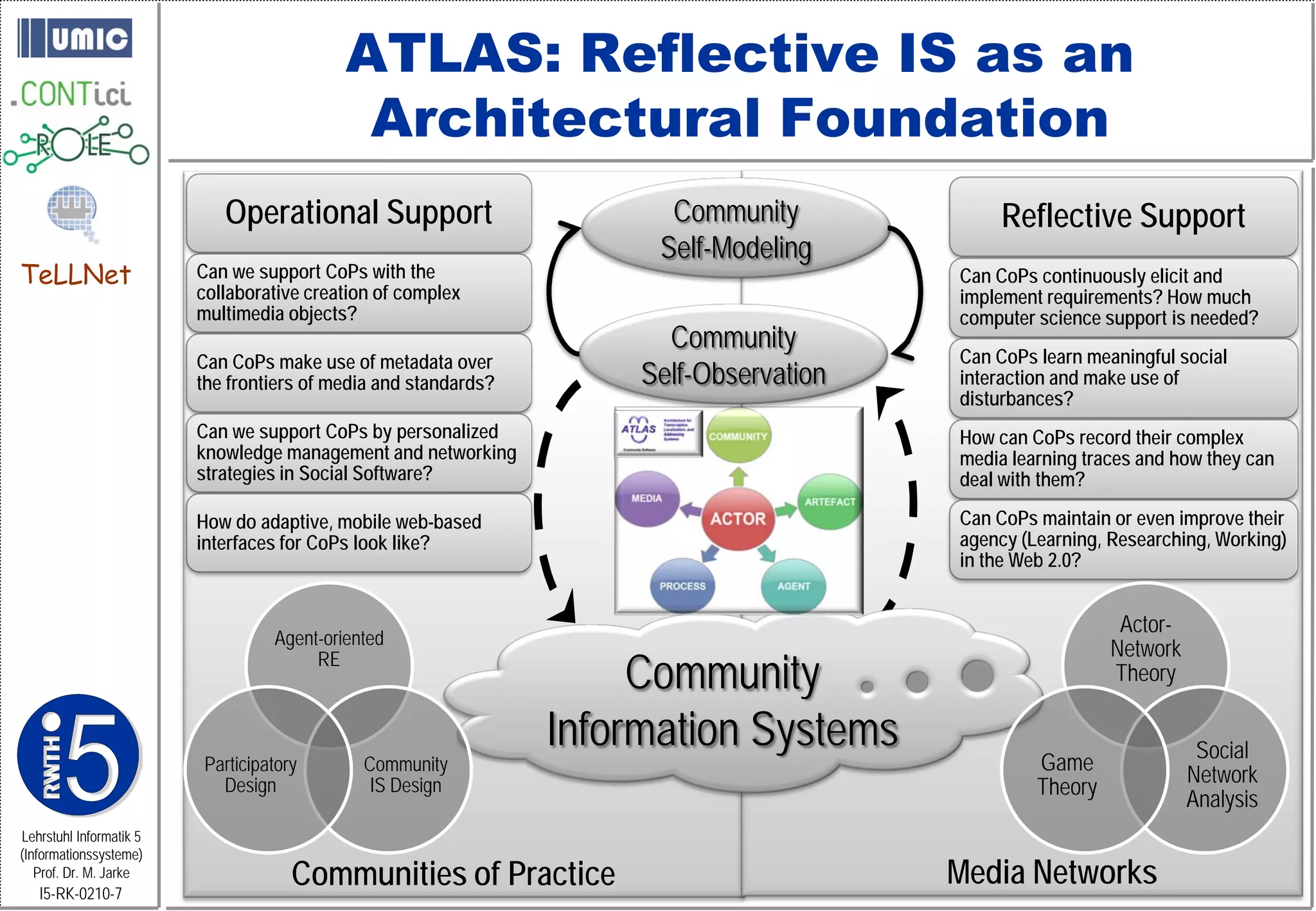
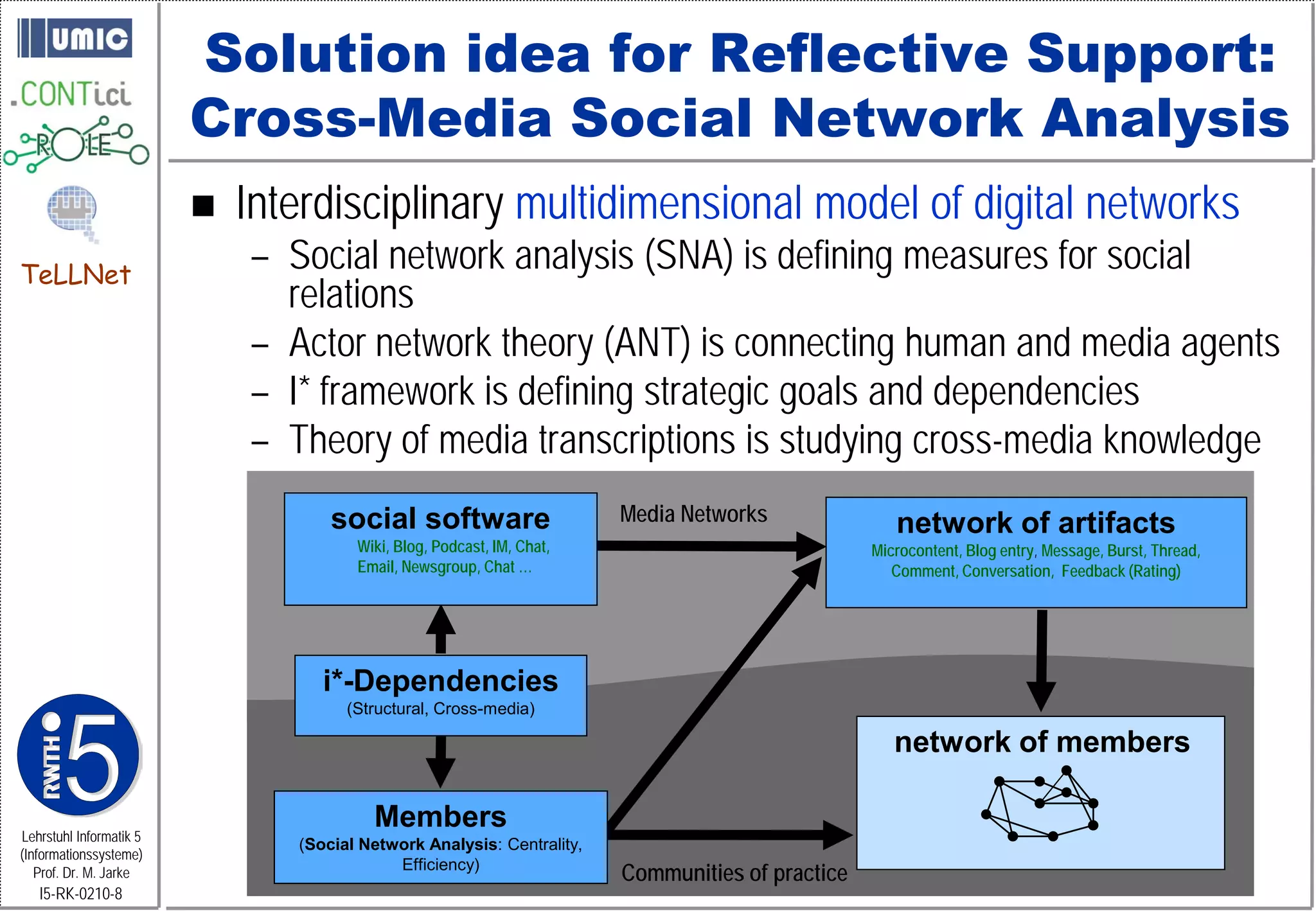
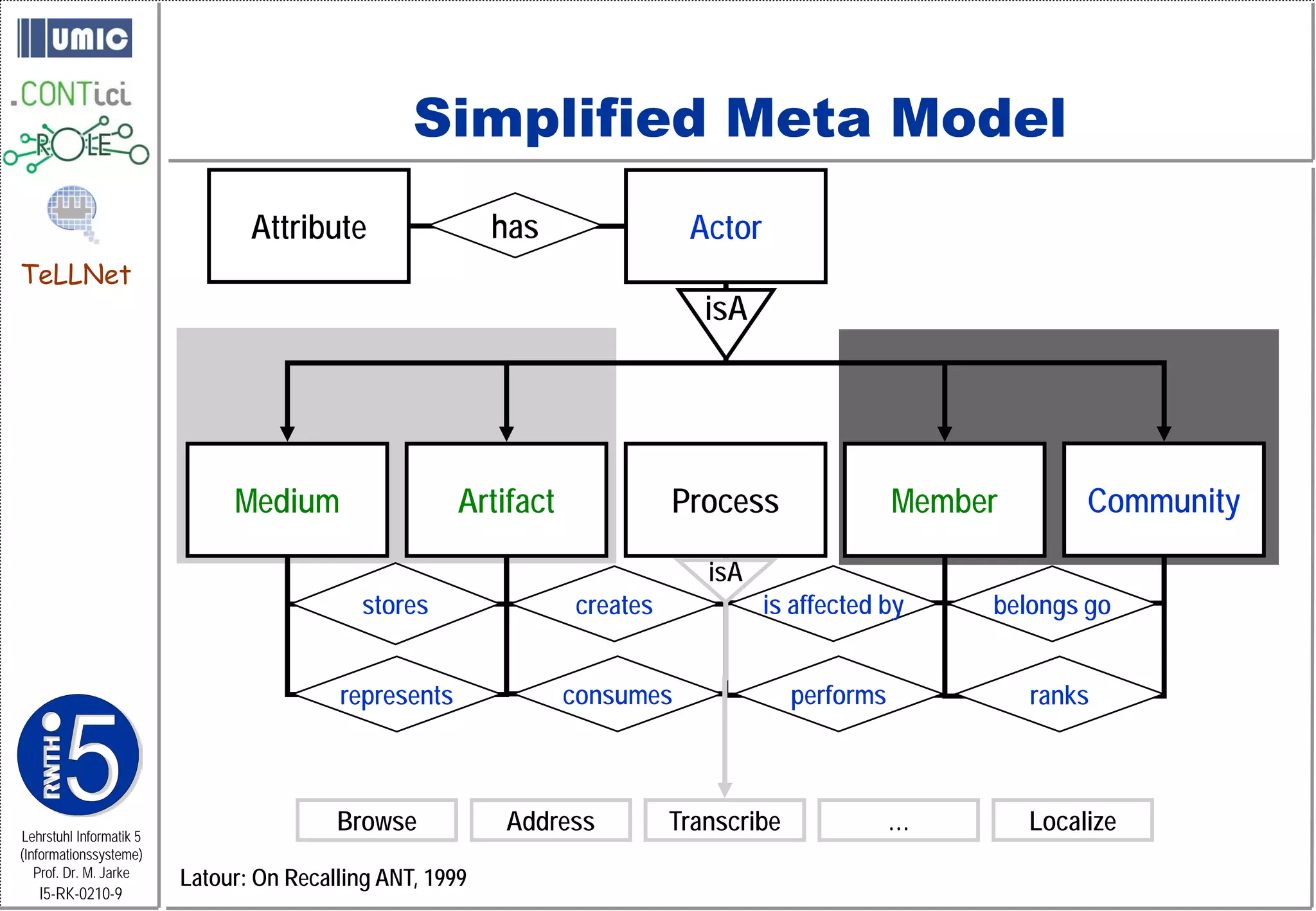
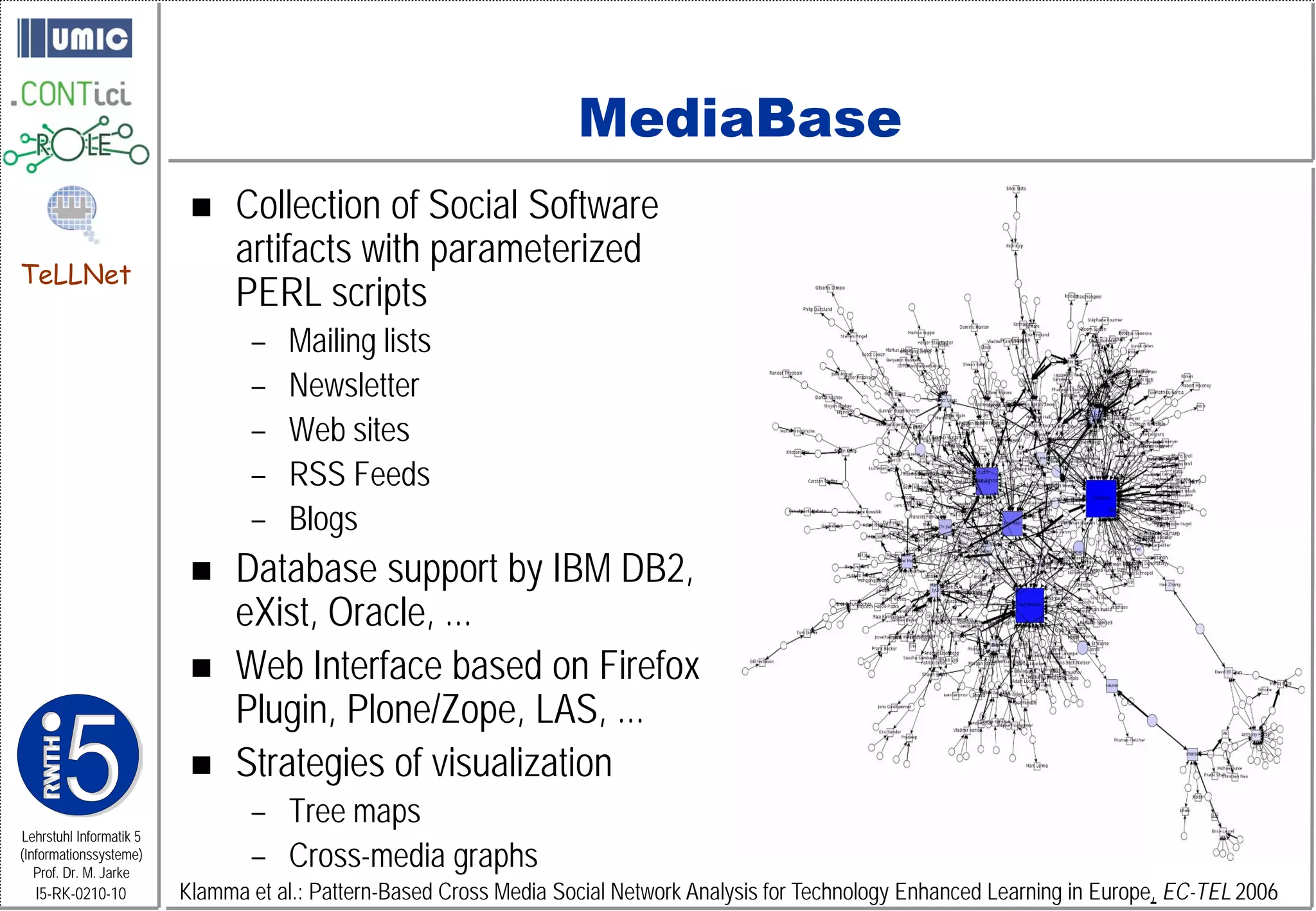
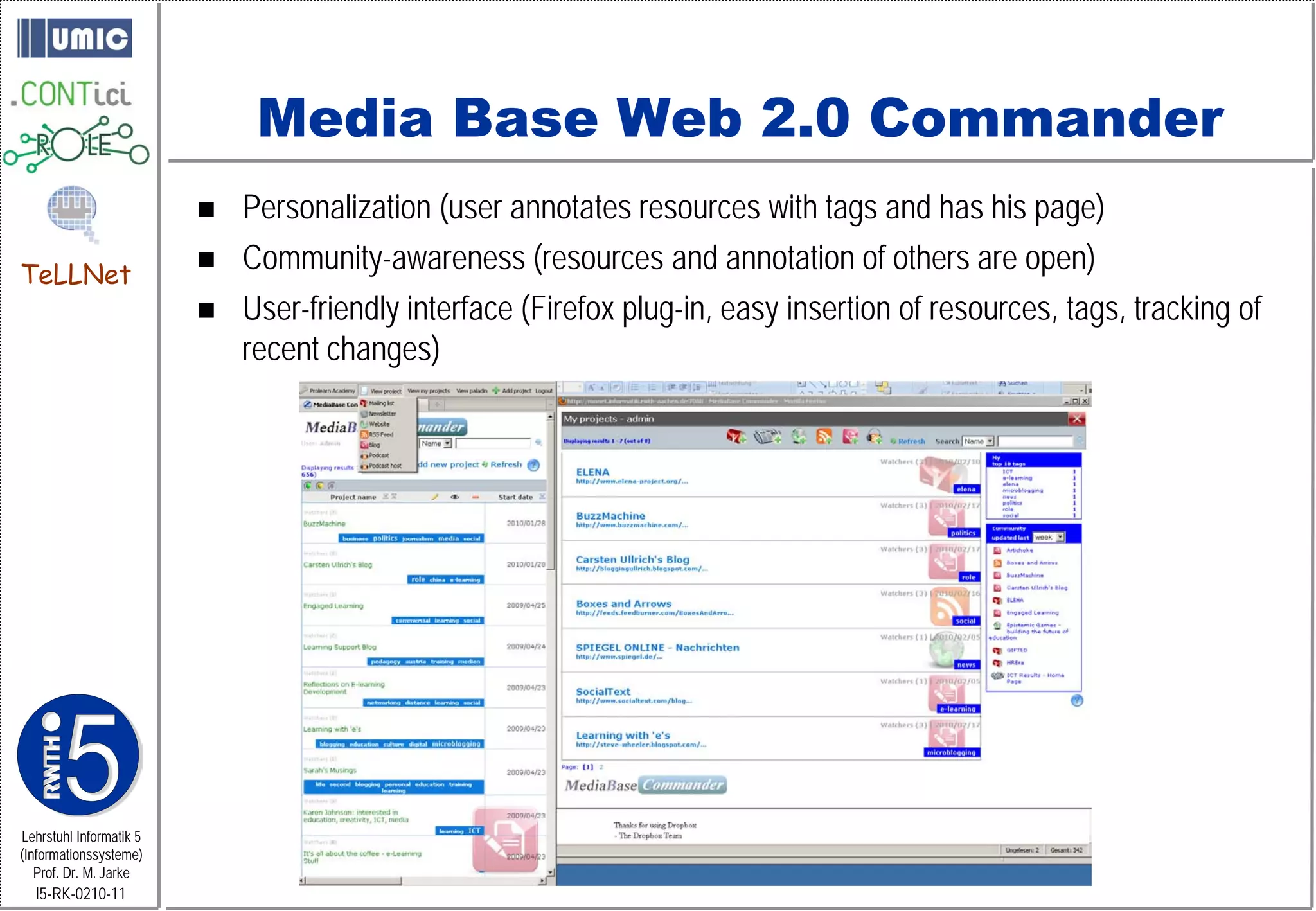
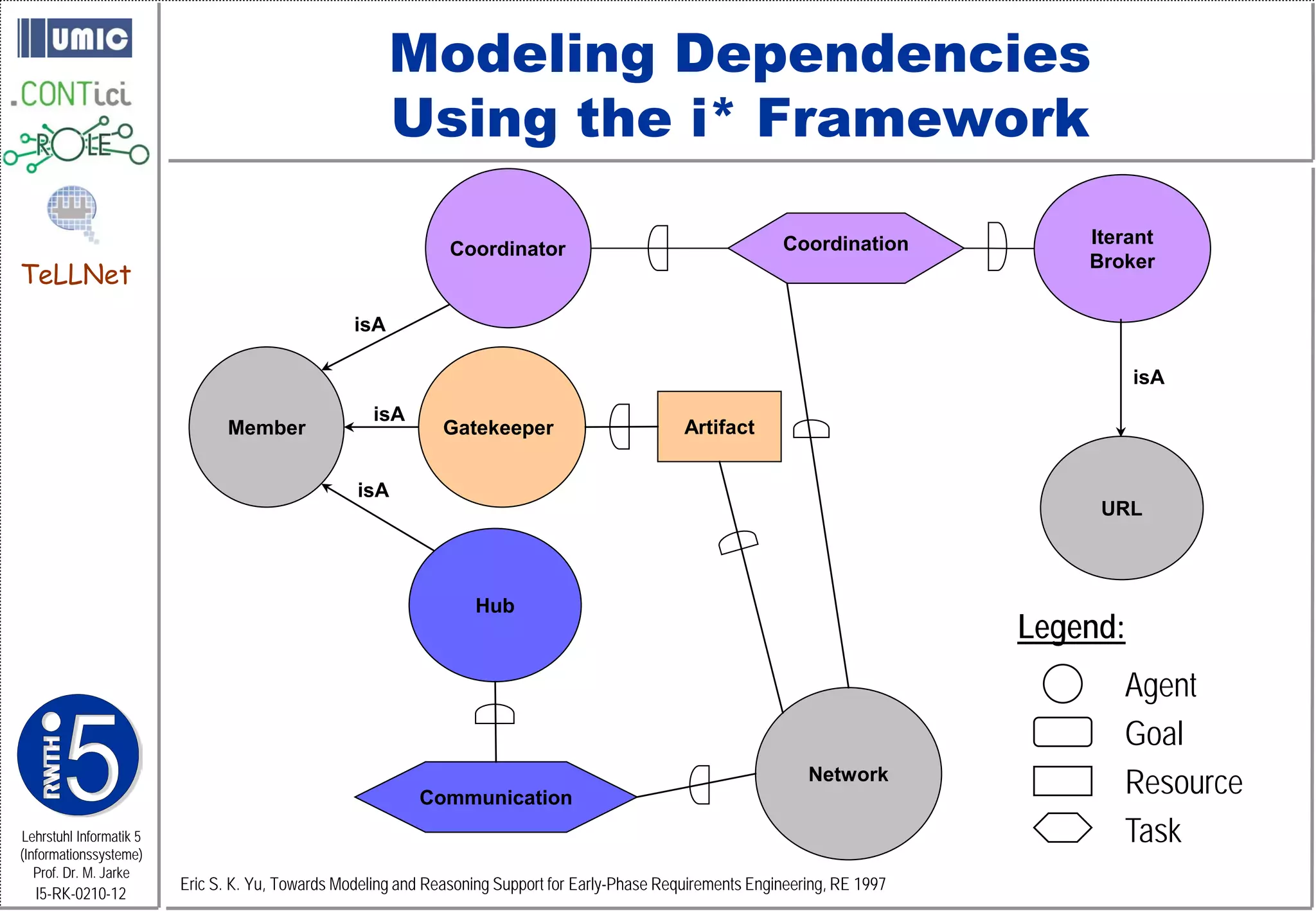
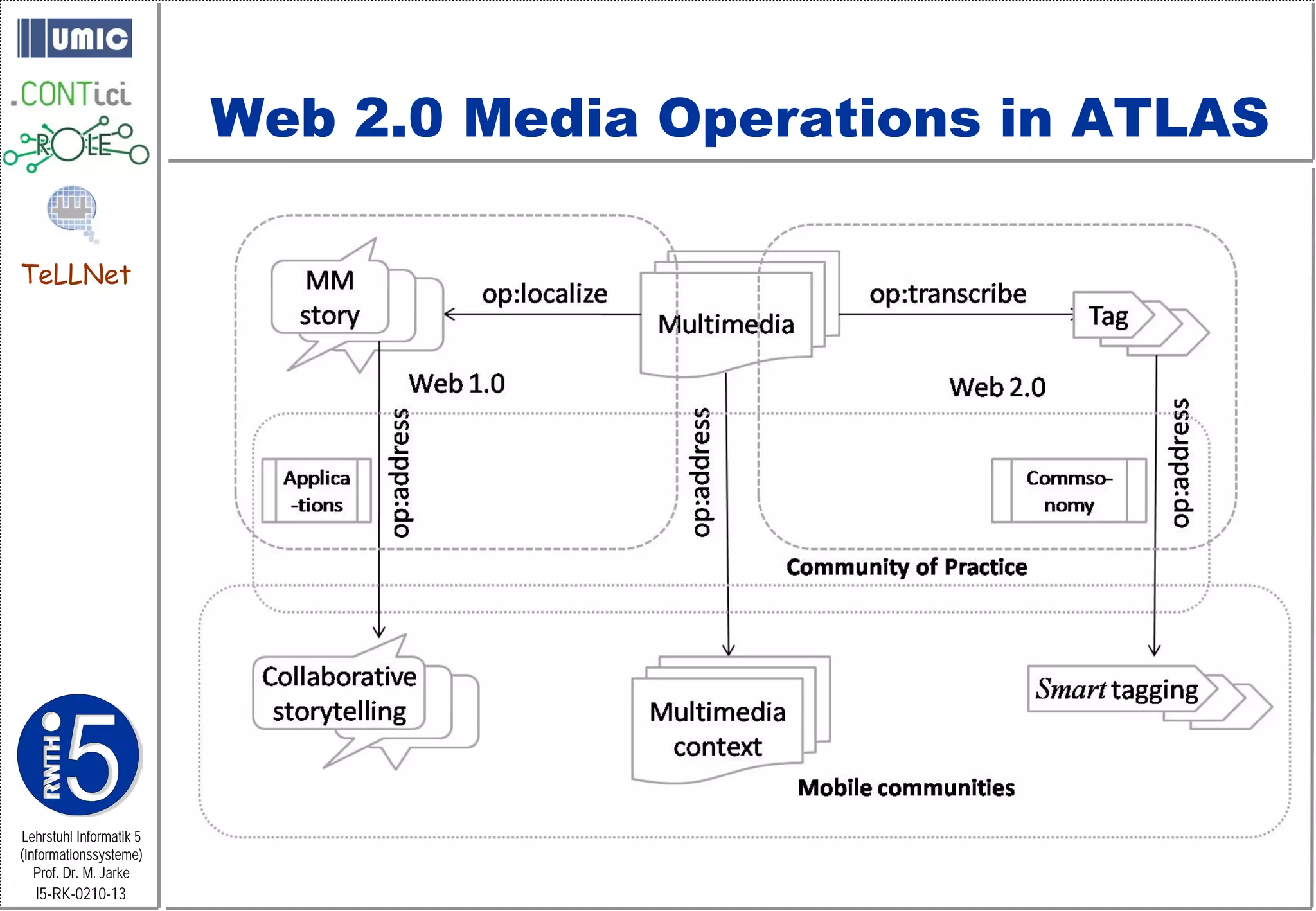
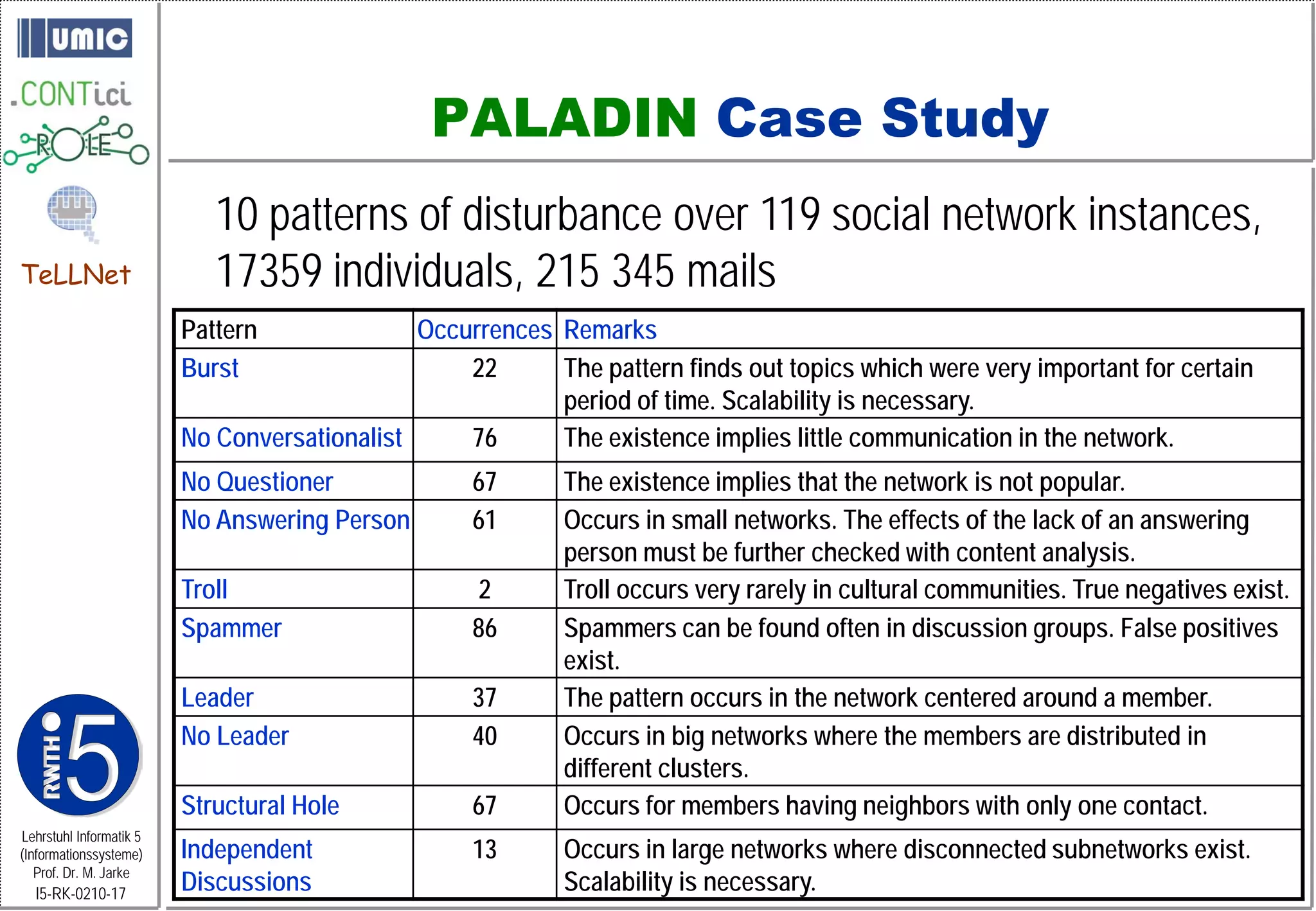
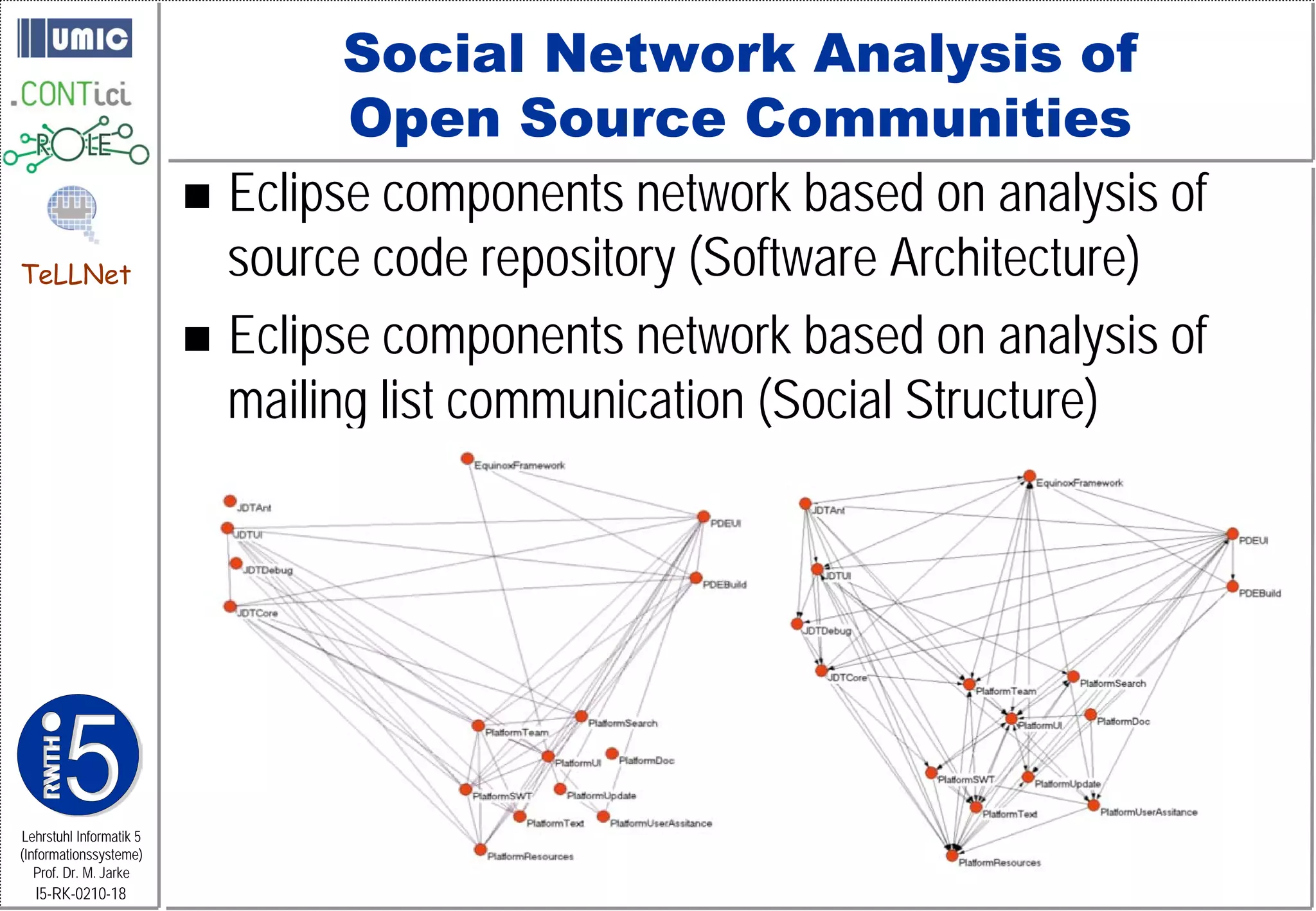
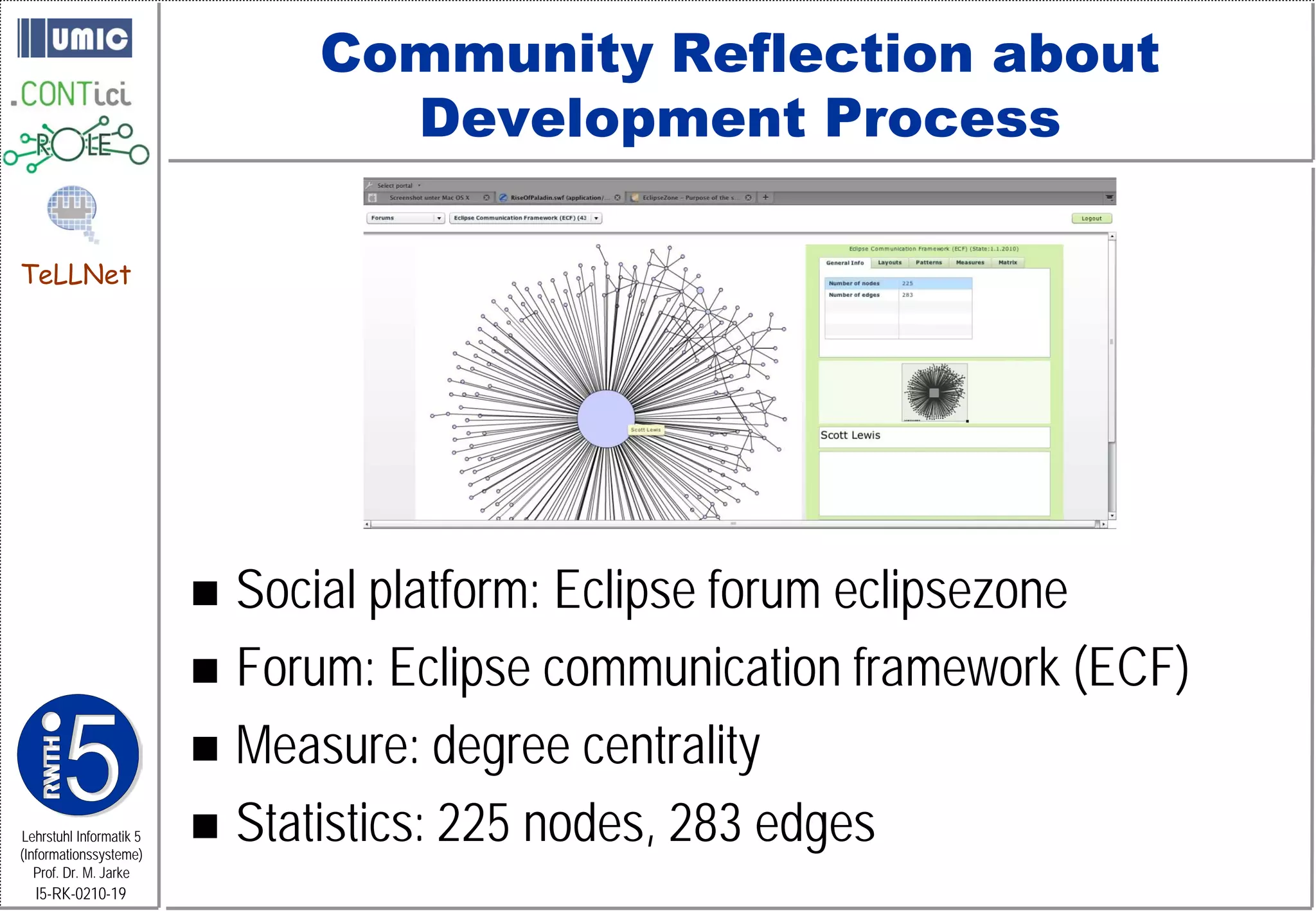
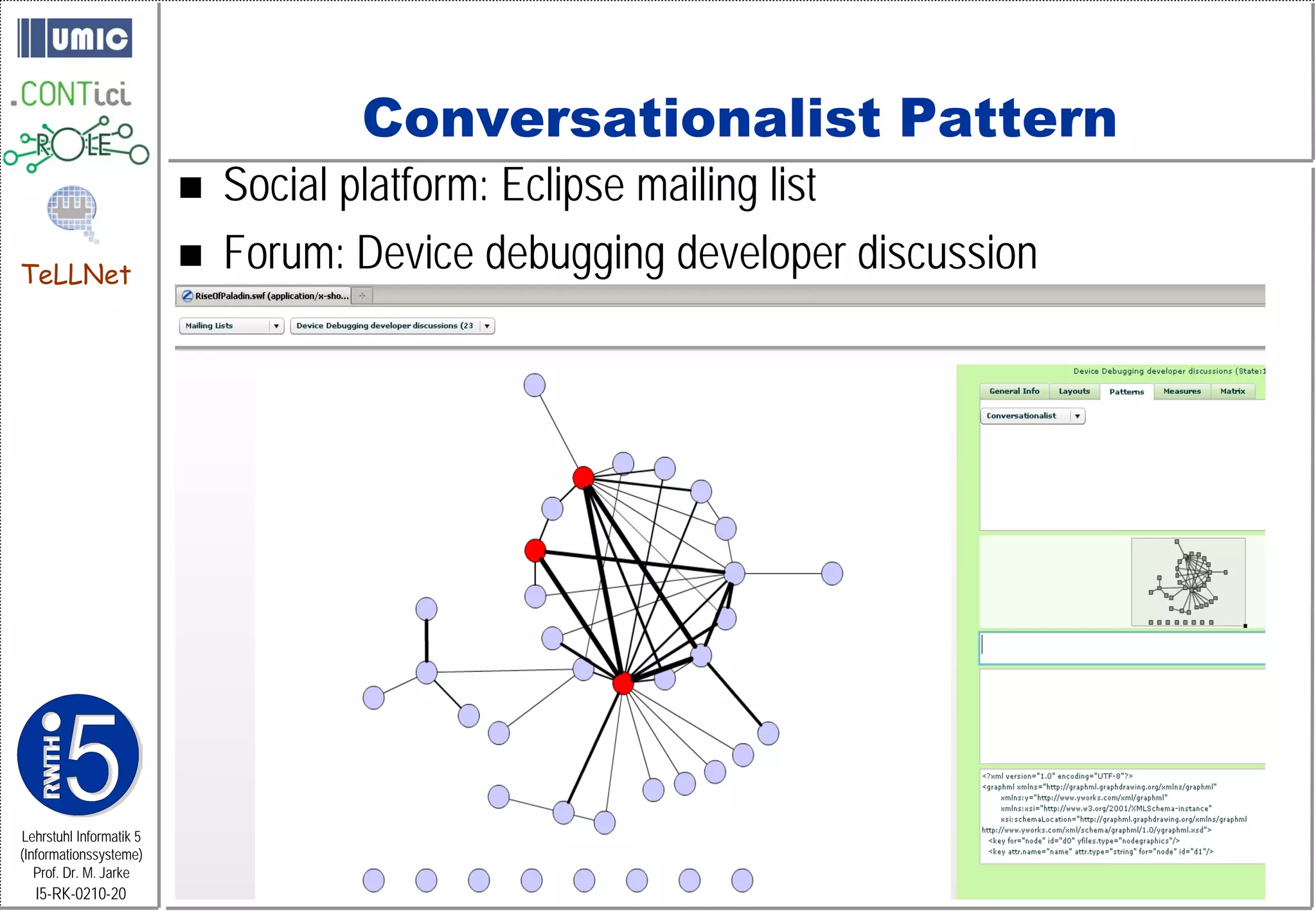
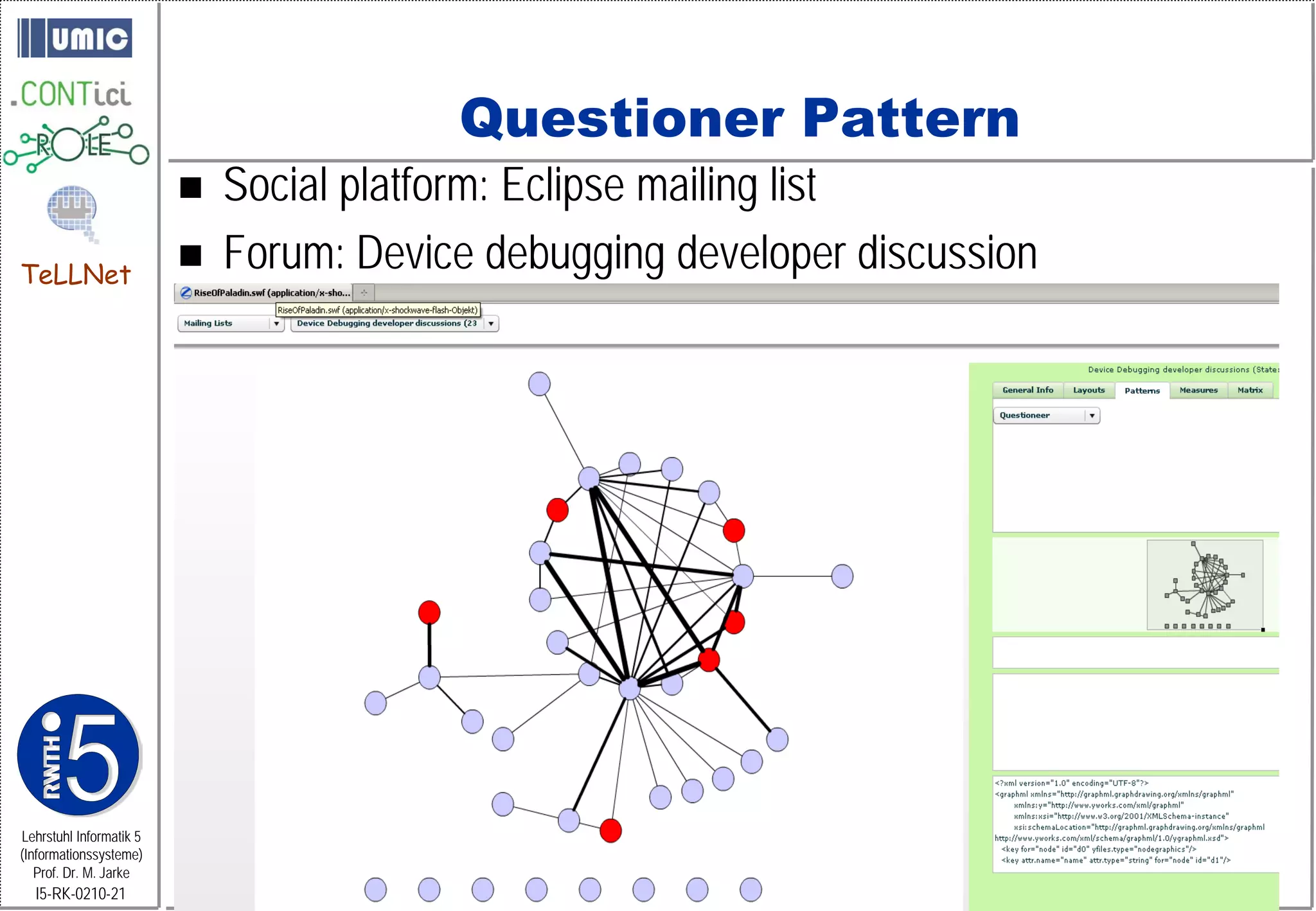
This document describes TeLLNet, a research project that aims to support communities on the web through reflection. It discusses community information systems, modeling community dependencies using the i* framework, analyzing social networks and disturbances in communities, and applying these techniques to case studies of open source software communities and a knowledge network of computer science research. The goal is to help communities better understand themselves and their learning and collaboration processes through reflective social network analysis and visualization tools.



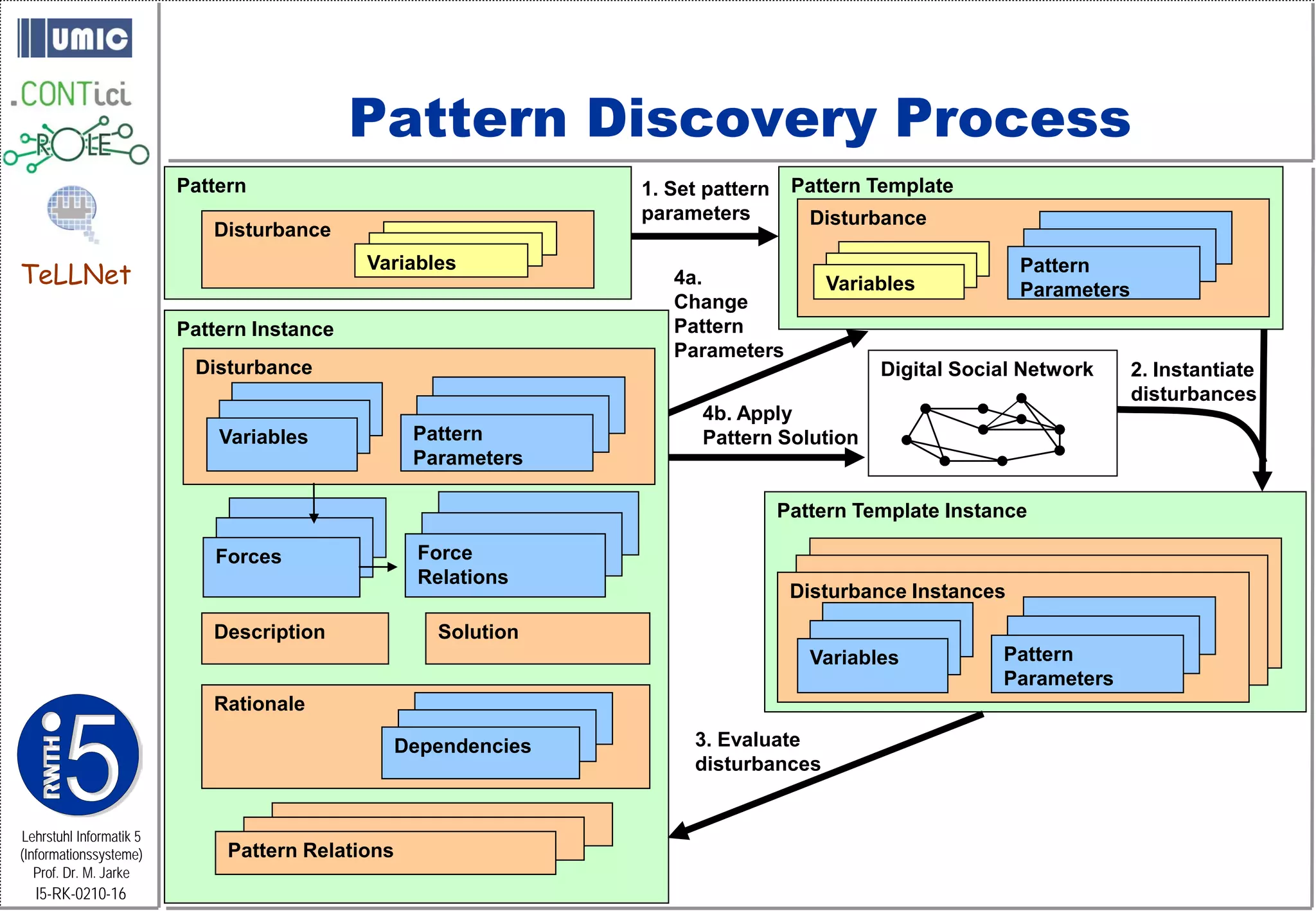
![Pattern Language for PALADIN:
Example Troll
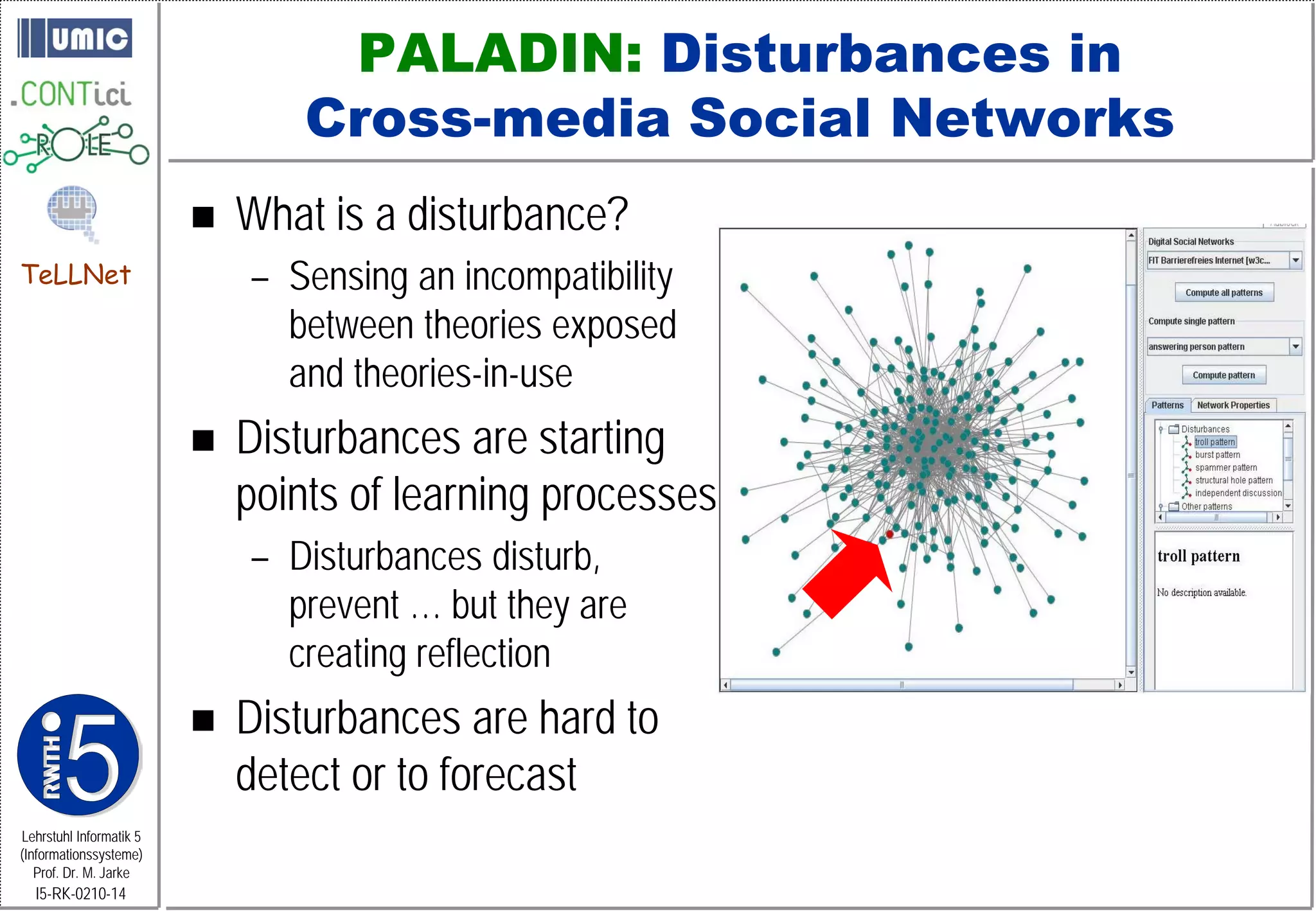
Troll Pattern: This pattern tries to discover the cases when a troll exists in a digital social
network. A troll in the network is considered a disturbance.
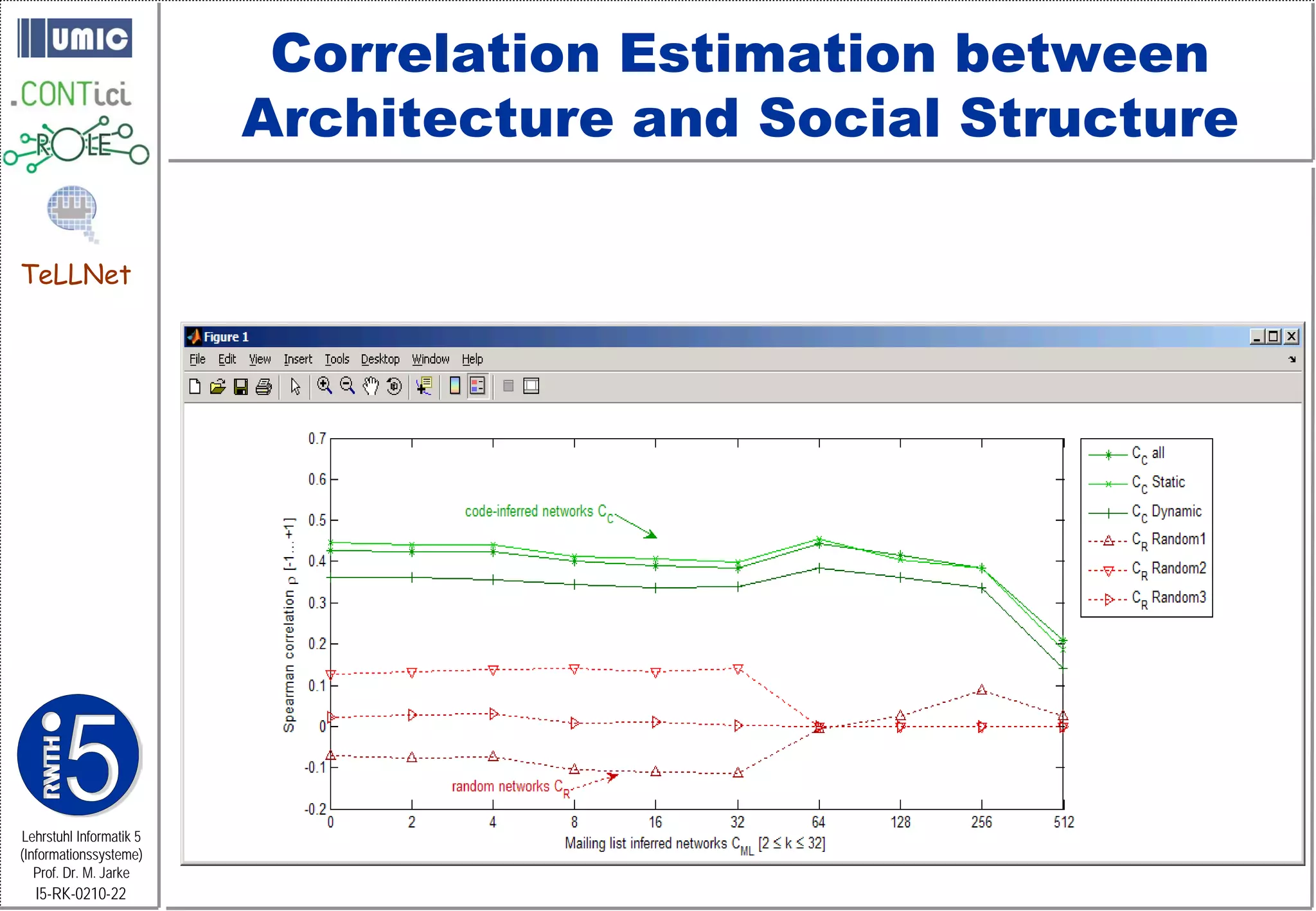
TeLLNet
Disturbance:
(EXISTS [medium | medium.affordance = threadArtefact]) &
(EXISTS [troll |(EXISTS [thread | (thread.author = troll) &
(COUNT [message | (message.author = troll) &
(message.posted = thread)]) > minPosts]) &
(~EXISTS[ thread1, message1| (thread1.author1 != troll) &
(message1.author = troll & message1.posted = thread1 ]))])])
Forces: medium; troll; network; member; thread; message; url
Force Relations: neighbour(troll, member); own thread(troll, thread)
Solution: No attention must be paid to the discussions started by the troll.
Rationale: The troll needs attention to continue its activities. If no attention is paid, he/she
Lehrstuhl Informatik 5
will stop participating in the discussions.
Pattern Relations: Associates Spammer pattern.
(Informationssysteme)
Prof. Dr. M. Jarke
I5-RK-0210-15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/klamma-tudelft-2010-100219143431-phpapp02/75/Reflection-Support-for-Communities-on-the-Web-15-2048.jpg)
![Requirements Reflection Compared
to Community Performance
With increasing number of boundary spanners it becomes
TeLLNet
easier to induce / implement requirements, which can be
evidenced by increased release rates and vice-versa
As most bugs are due to insufficient understanding [NOHI99]
and knowledge creation as well as sharing is supported by
boundary spanners [BDBu07], then increased number of
boundary spanners should be evidenced by decreased bug
rate and vice-versa
Lehrstuhl Informatik 5
(Informationssysteme)
Prof. Dr. M. Jarke
I5-RK-0210-23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/klamma-tudelft-2010-100219143431-phpapp02/75/Reflection-Support-for-Communities-on-the-Web-23-2048.jpg)