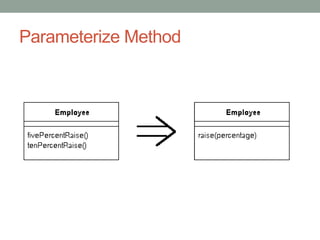
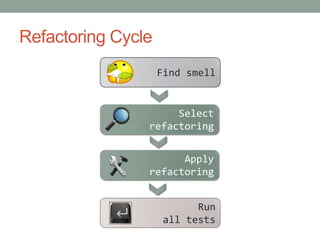
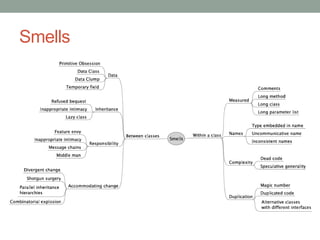
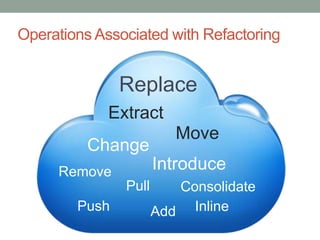
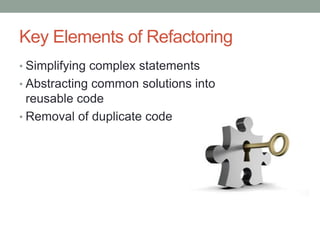
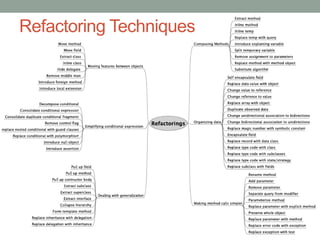
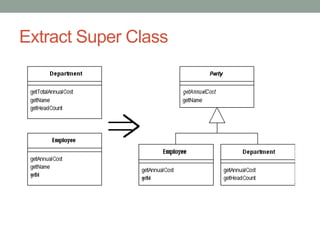
This document discusses refactoring code to improve its structure and design without changing its external behavior. Refactoring involves applying small, incremental changes through techniques like extracting methods, replacing conditionals, and parameterizing methods. It improves code quality by making it more readable, reusable, maintainable and less error-prone. The key is to refactor in small steps through practices like testing and code reviews to pay off technical debt over time.


















![Replace Exception with Testdouble getValueForPeriod (int period) { try { return values[period]; } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { return 0; }}double getValueForPeriod (int period) { return period >= values.length ? 0 : values[period];}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part3-refactoring-110828072917-phpapp01/85/Refactoring-26-320.jpg)