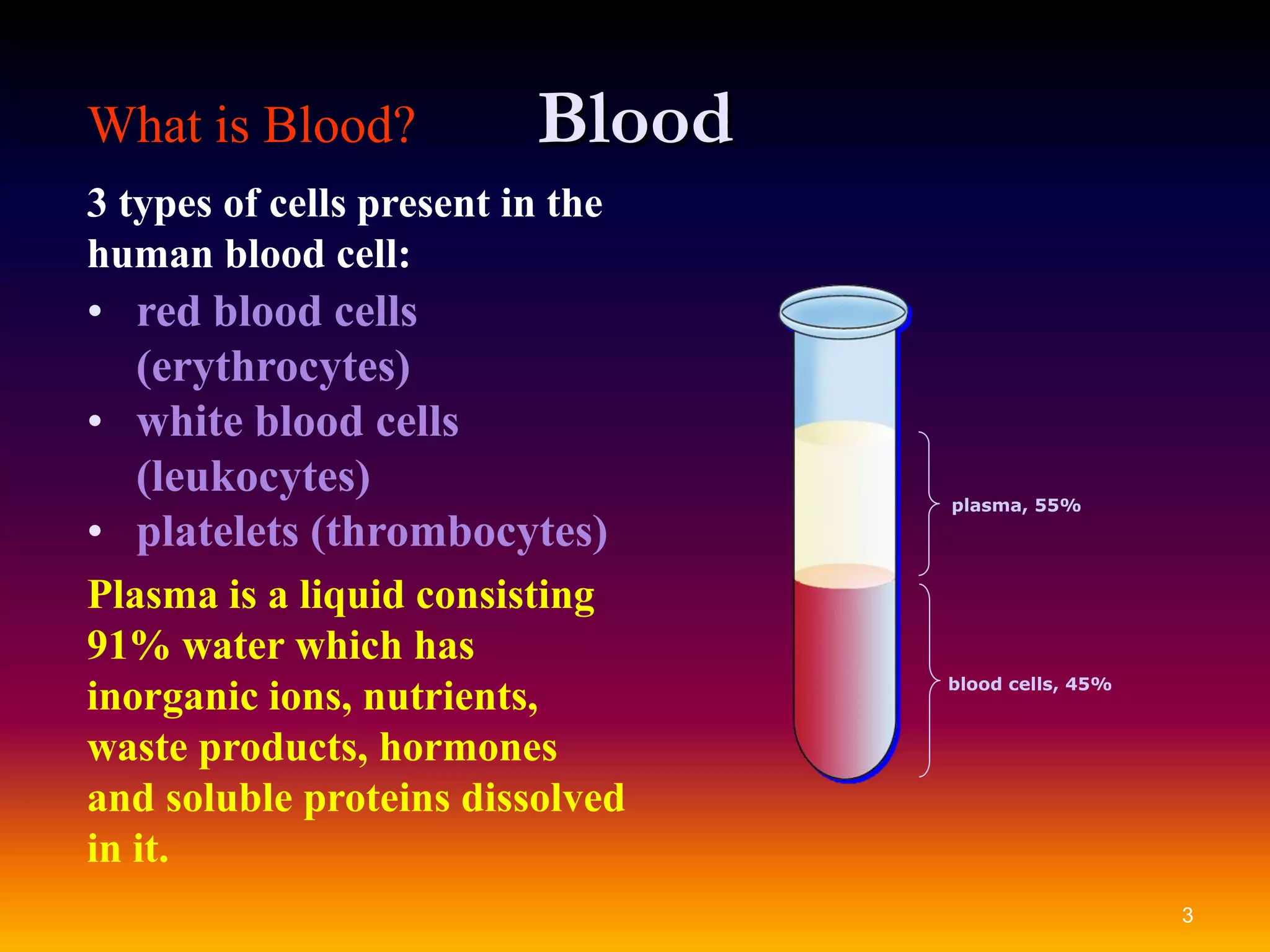
The document discusses the functions of blood and its components. It states that blood has three main cell types - red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin and transport oxygen, white blood cells aid in immunity, and platelets help with clotting. The document also explains that plasma transports nutrients, waste, hormones, and dissolved proteins throughout the body. It provides details on how red blood cells pick up oxygen in the lungs and release it to tissues, as well as transporting carbon dioxide to the lungs to be released.