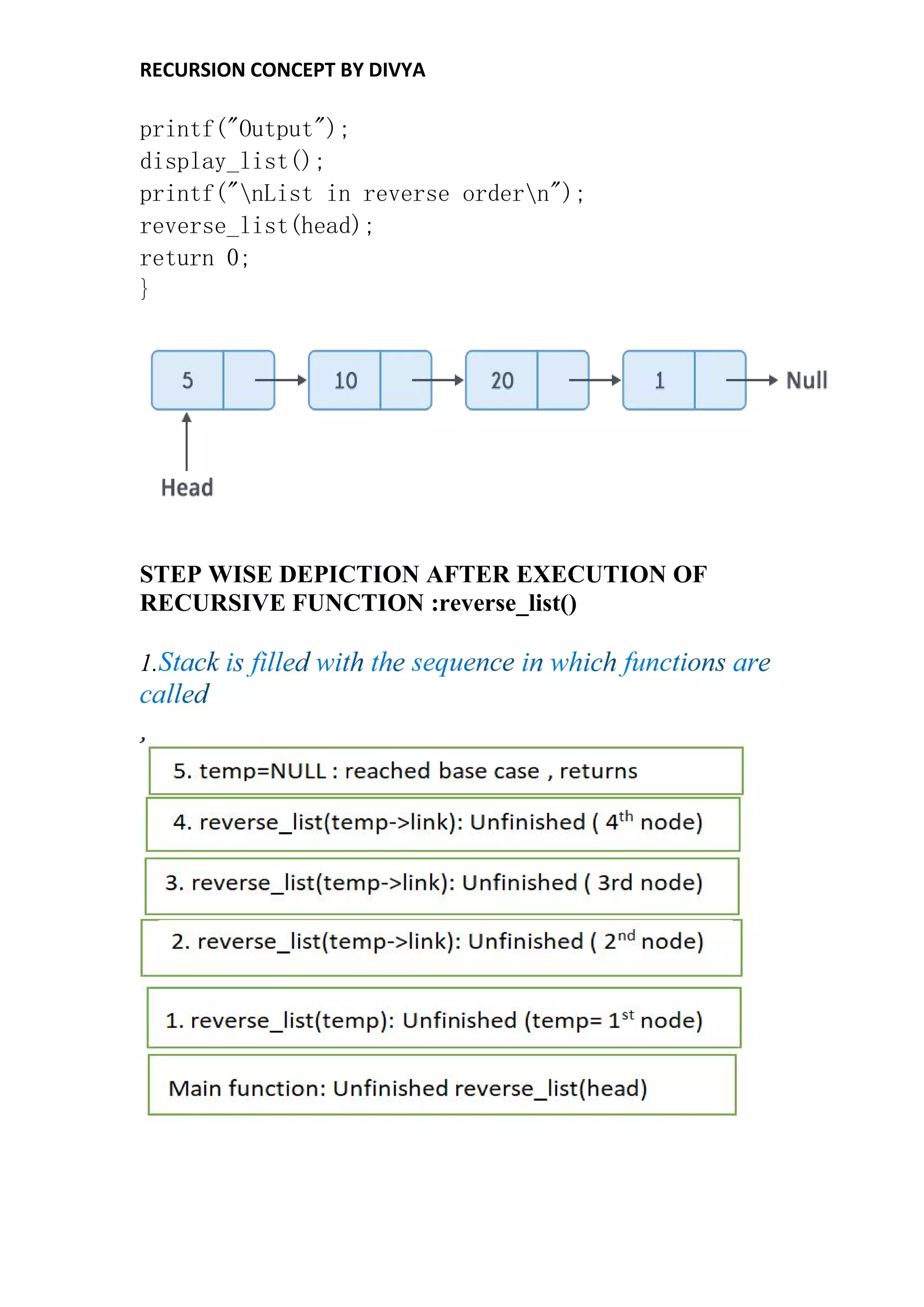
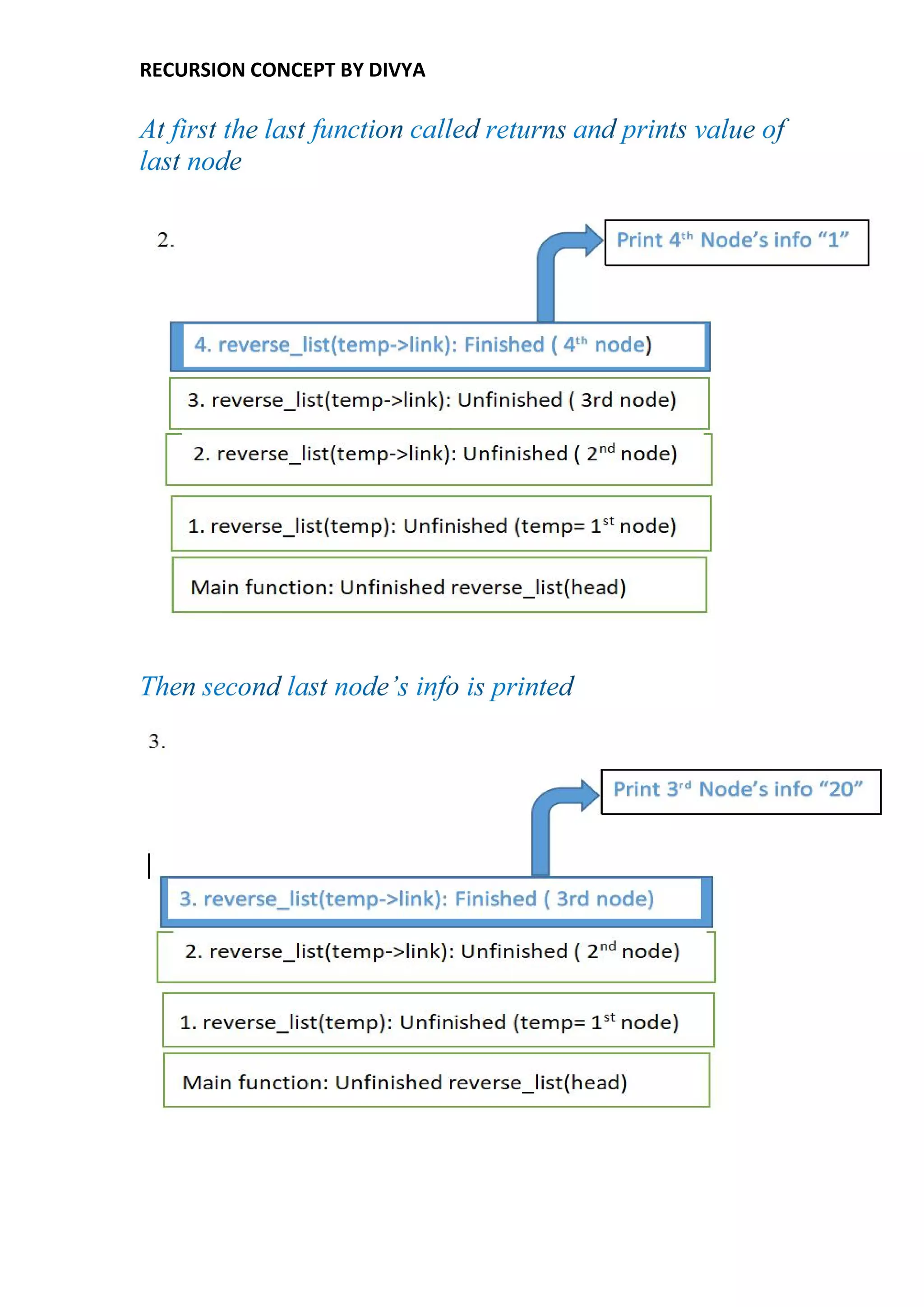
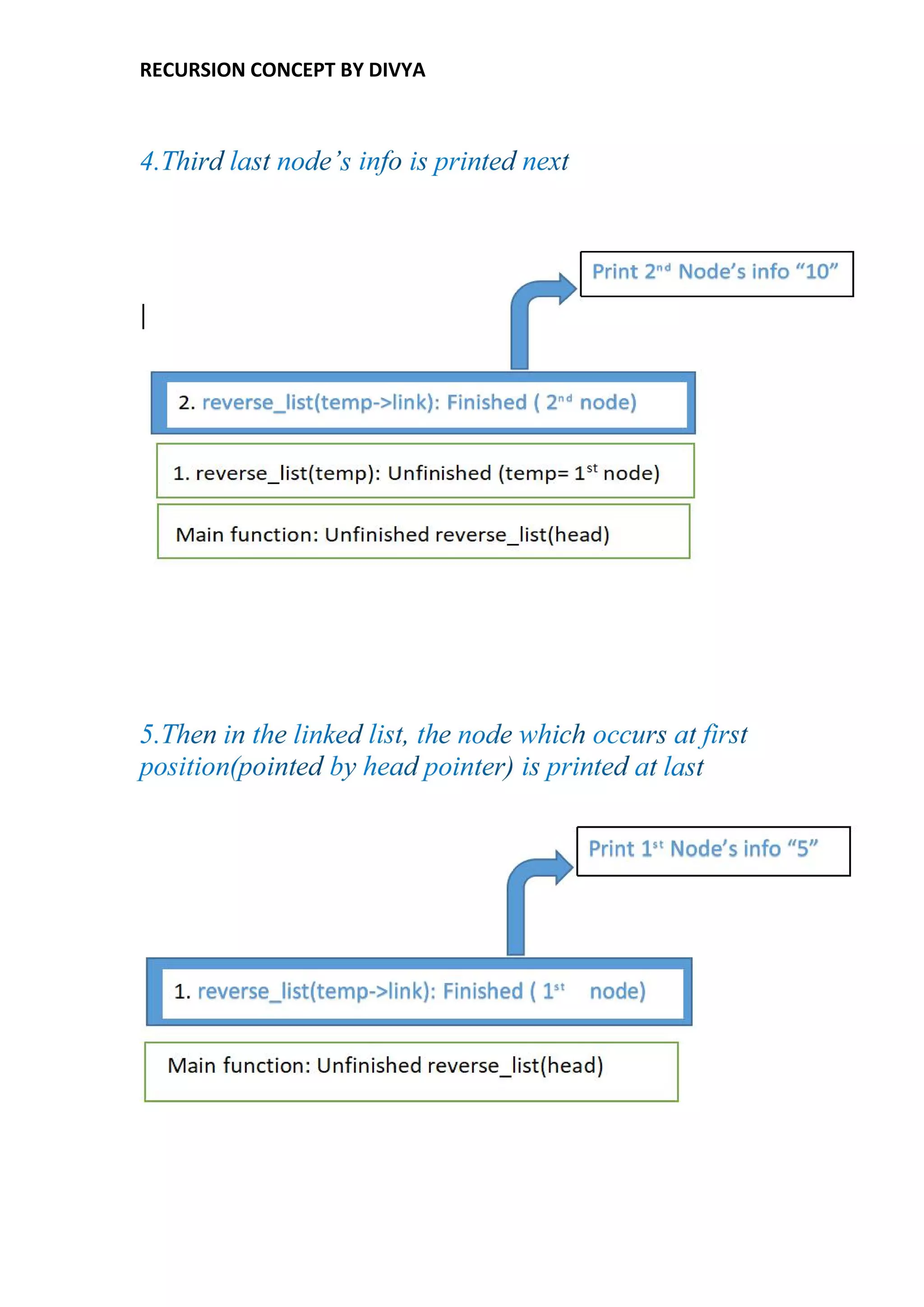
Recursion is a process of solving a problem where the solution depends on solutions to smaller instances of the same problem. Some examples that use recursion include calculating factorials, generating Fibonacci numbers, reversing a linked list, and traversing trees. A recursive function calls itself directly or indirectly. To terminate the recursion, a base case is used. The memory for each function call is allocated on the stack, with each recursive call using new memory on top of the previous call. When the base case is reached, the function returns values up the call stack and memory is de-allocated.