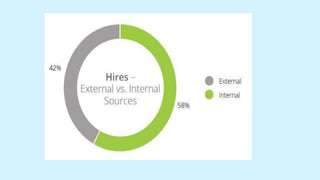
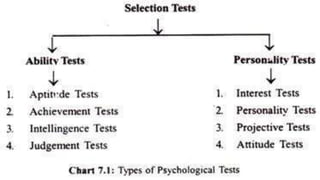
The document discusses the recruitment and selection process in organizations. It begins by outlining the importance of recruitment and selection for filling vacancies and achieving organizational strategies. It then describes the various internal and external sources used for recruitment, such as promotions, referrals, advertisements, employment agencies. The selection process involves initial screening, application forms, tests, interviews, background checks, conditional offers, and medical examinations to evaluate candidates and select the most suitable one. The key steps in the recruitment and selection process are also outlined.