1. John Langley first postulated the concept of drug receptors in 1878 based on his experiments showing that nicotine and curare analogues interacted specifically with muscle cells to cause contraction or relaxation.
2. Paul Ehrlich further developed the drug receptor concept in the early 1900s, demonstrating that the stereochemical structure of a drug was important for its binding and interaction with receptors.
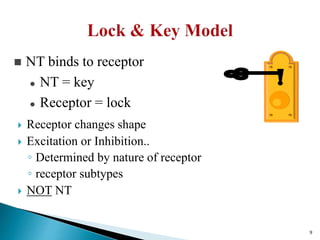
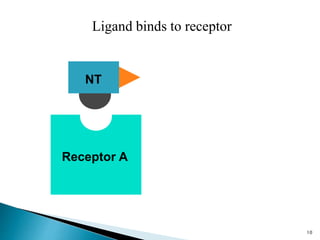
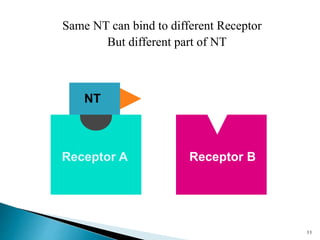
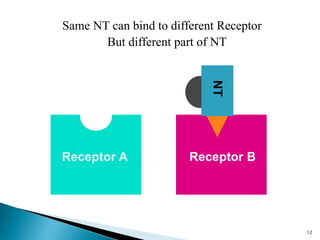
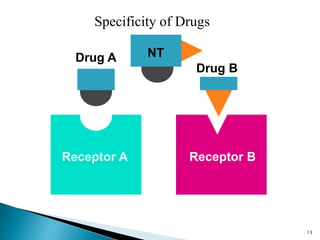
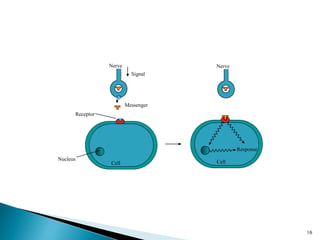
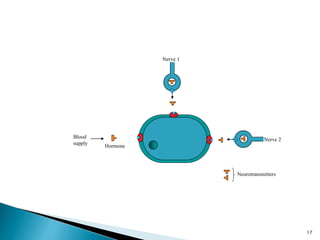
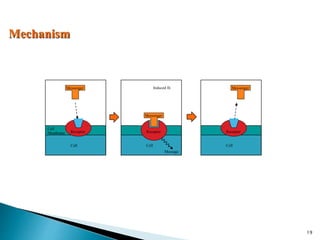
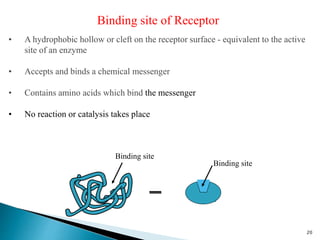
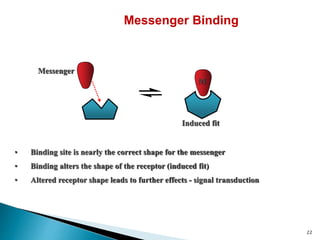
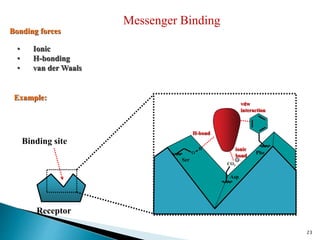
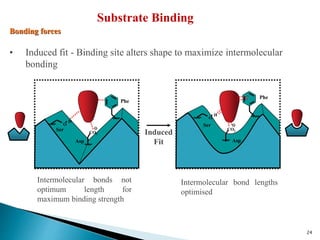
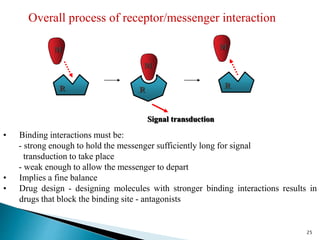
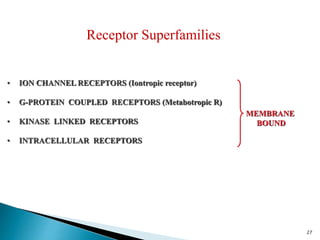
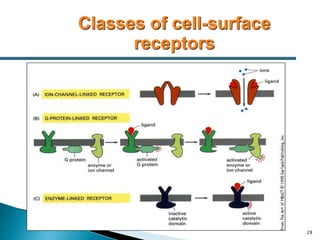
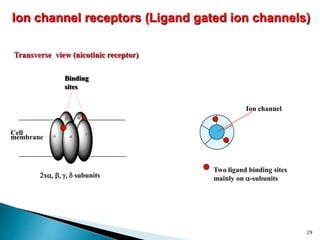
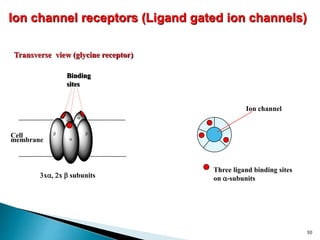
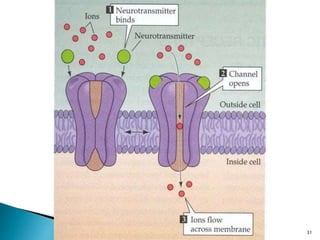
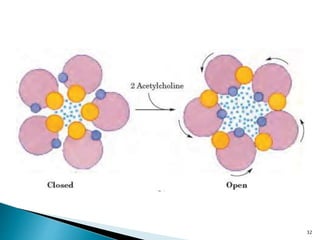
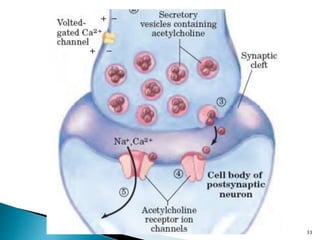
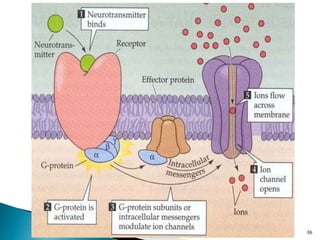
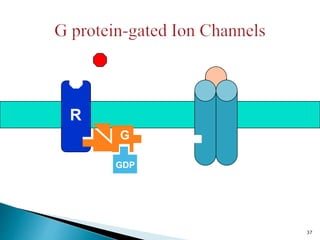
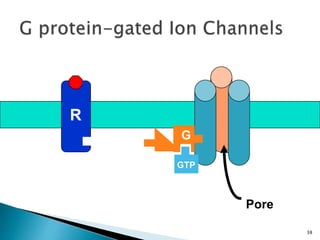
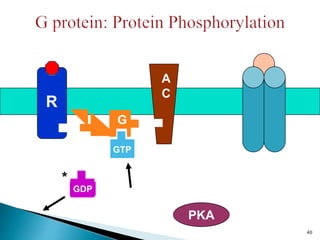
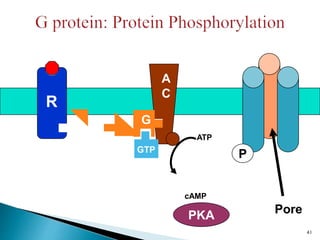
3. Receptors are specific binding sites, usually protein molecules, located on cells or within cells that drugs and neurotransmitters interact with to produce their effects. The binding of a drug or neurotransmitter to its receptor triggers signal transduction pathways that mediate the drug's ultimate physiological or pharmacological response.