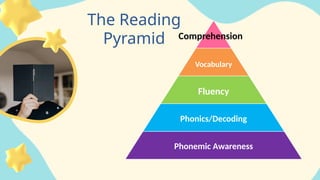
The document outlines the 'reading pyramid,' which consists of phonemic awareness, phonics/decoding, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension as essential components for developing strong literacy skills in children. It emphasizes the importance of systematic instruction in these areas, particularly for struggling readers, and discusses strategies to promote effective reading and comprehension. Ultimately, the goal is to build a solid foundation that enables learners to achieve mastery in reading.