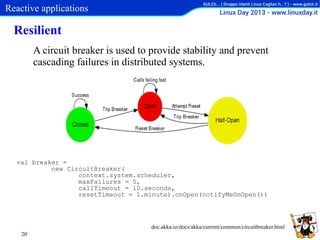
This document discusses reactive applications and the tools used to build them. Reactive applications are event-driven, scalable, resilient, and responsive. They react quickly to events, failures, loads, and through user interfaces. Key tools for building reactive applications include actors, agents, futures, and functional reactive programming. Actors communicate asynchronously through message passing. Agents are reactive memory cells that update asynchronously. Futures allow non-blocking composition. Functional reactive programming uses streams to model events over time.
























![Reactive applications
Promise
Writeable, single-assignment container, which completes a
Future
import scala.concurrent.{ future, promise }
val p = promise[T]
val f = p.future
val producer = future {
val r = produceSomething()
p success r
ContinueDoingSomethingUnrelated()}
val consumer = future {
startDoingSomething()
f onSuccess {
case r => doSomethingWithResult()
}
28
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxday2013massimilianodessireactiveapplications-131105152740-phpapp01/85/Reactive-applications-Linux-Day-2013-28-320.jpg)



