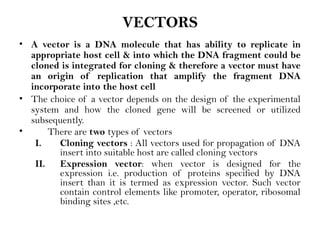
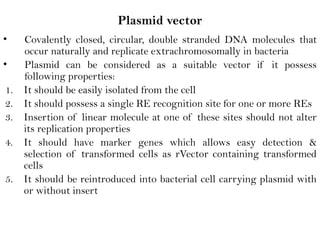
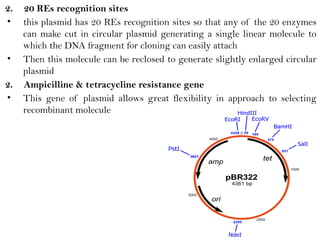
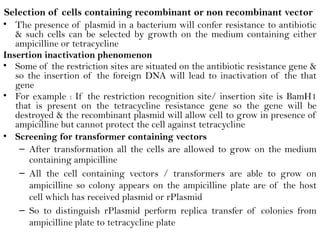
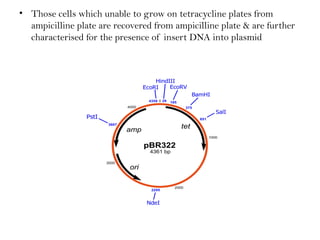
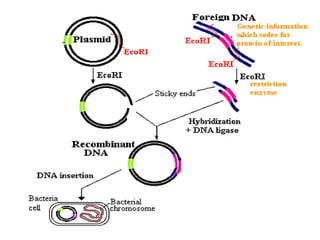
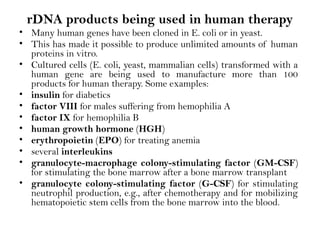
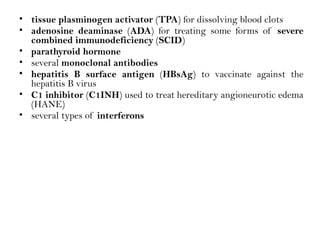
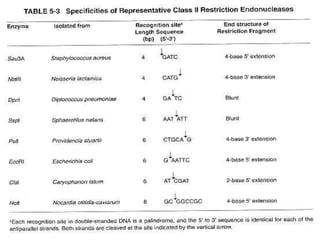
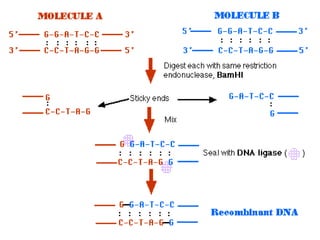
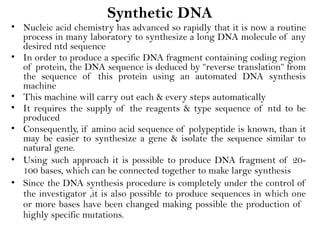
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves editing DNA to create new synthetic molecules through gene cloning and has historical roots from the early 1970s. Key milestones include the foundational work of Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer, and the development of techniques enabling the cloning and expression of genes for human therapy, such as insulin and growth hormones. The technology relies on various tools and methods including restriction endonucleases and vectors for effective gene cloning and manipulation.










![• Calculation shows that for 10 kbs of fragments, 1.5x103
colonies
are needed for E.coli genome & 2x106
for Homo sapience .
• In later case, number of colonies required are unmanageable &
therefore much larger fragments about 40 kbs in size must be
cloned, but the large fragment require special vector for cloning.
• Inevitably the gene will come from only as a small part of entire
genome [approximately 0.03% in case of E.coli & 0.03x10-3 in case
of mammalian gene] so a way must be found to identify the gene &
pull it out from the other part of genome either before or after
cloning
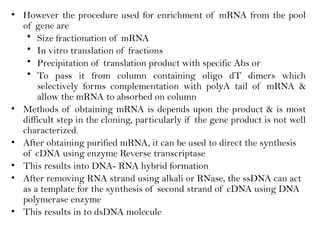
• This job is much easier if the corresponding mRNA will be
available in the fairly pure form
• If the protein for which it codes is the major product of the cell,
then mRNA will already be enriched for desired species](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rdnatechnology1238765-240822165619-018ef48f/85/rDNA-Technology_1238765467765321489-pptx-17-320.jpg)


![HYBRIDIZATION METHOD
• This method depends on the principle that mRNA forms complex
with cDNA segment from which it has been transcribed
• This method is possible if protein encoding genes do not have
introns
• First the total DNA from organism is isolated, than this dsDNA is
treated with alkali or heat & converted into ssDNA by denaturation
• This strands are mixed with the mRNA transcribed by that genes.
• this complex is isolated & DNA is separated from RNA by RNase
treatment
• the ssDNA thus obtained is converted into dsDNA by using DNA
pol I enzyme
• this method is most suitable for isolating genes which exist in
multiple copies
• mRNA pairs with cDNA protein to form DNA-RNA complex
[hybrid]
• for ex: ribosomal genes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rdnatechnology1238765-240822165619-018ef48f/85/rDNA-Technology_1238765467765321489-pptx-22-320.jpg)