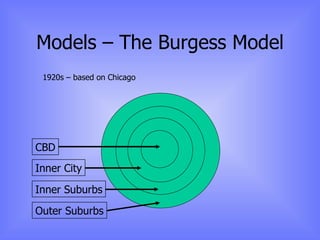
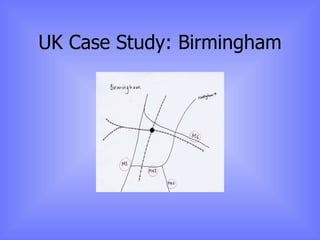
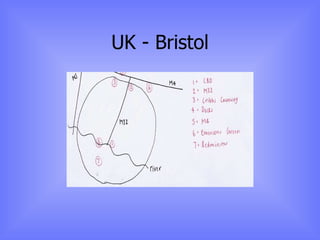
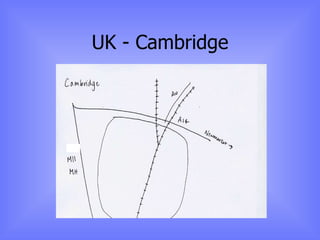
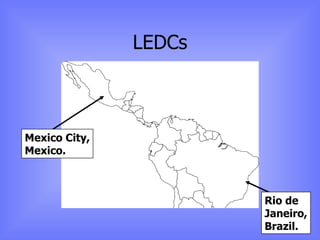
The document discusses models of urban growth and change, including the Burgess and Hoyt models. It provides terminology to describe urban structures, such as CBD, inner city, and outer suburbs. Factors that influence urban growth patterns are also examined, such as transportation, industry, retail, and population changes. Case studies are presented on cities in the UK and Europe to illustrate how urban areas have developed and changed over time.