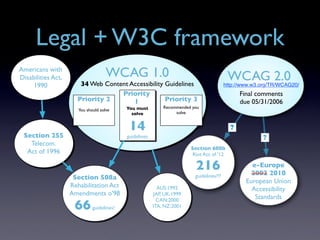
This document discusses universal design, accessibility, and usability in web development. It begins with definitions of universal design and accessibility, noting they aim to make products usable by the widest range of people. It then covers accessibility guidelines and principles like perceivable, operable, understandable and robust content. The document also discusses usability factors and evaluation methods. It emphasizes that accessibility without usability is incomplete, and usability without accessibility excludes users. The key message is that web developers should use inclusive, progressive design principles to build applications that are accessible and usable for all.