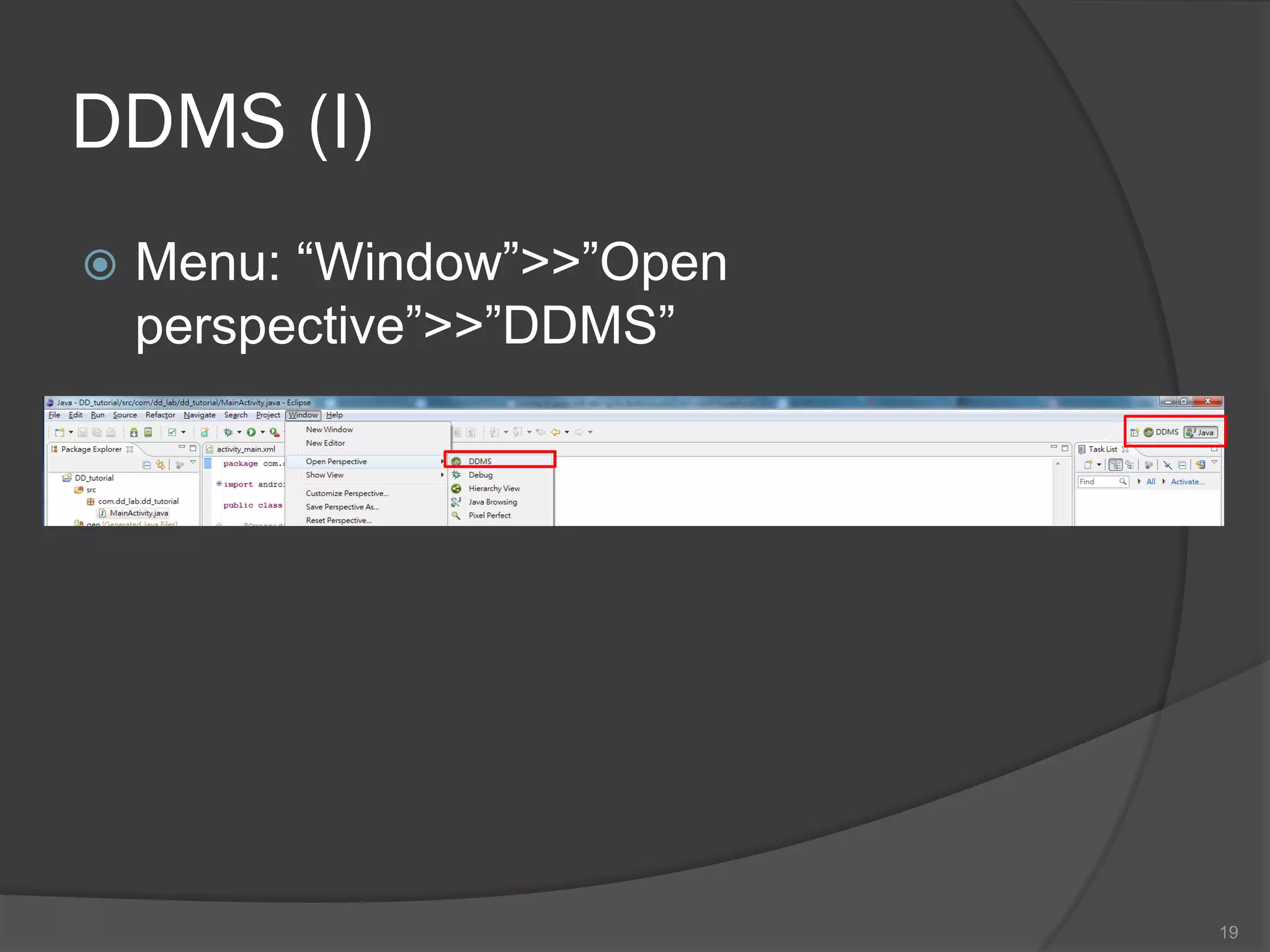
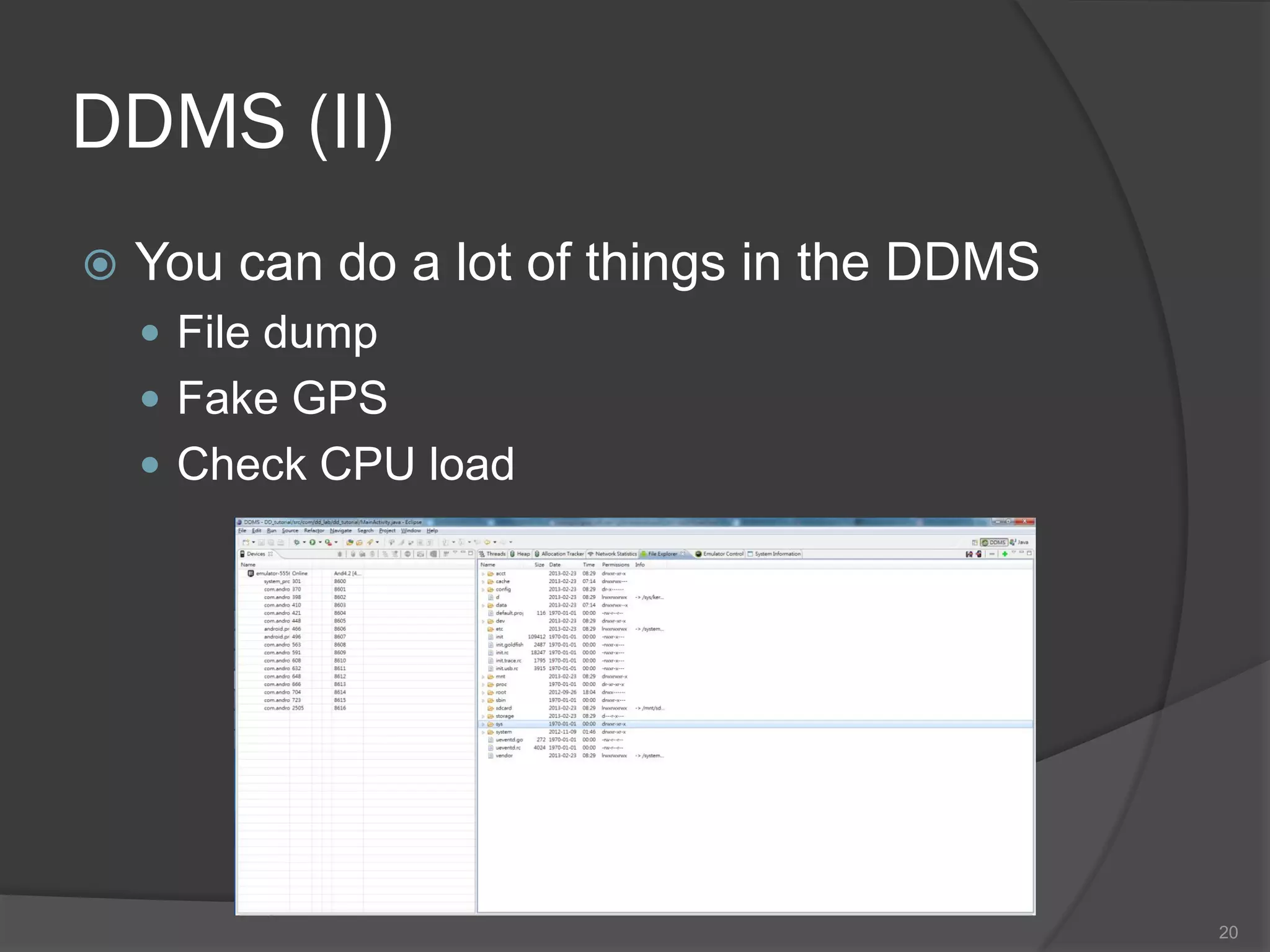
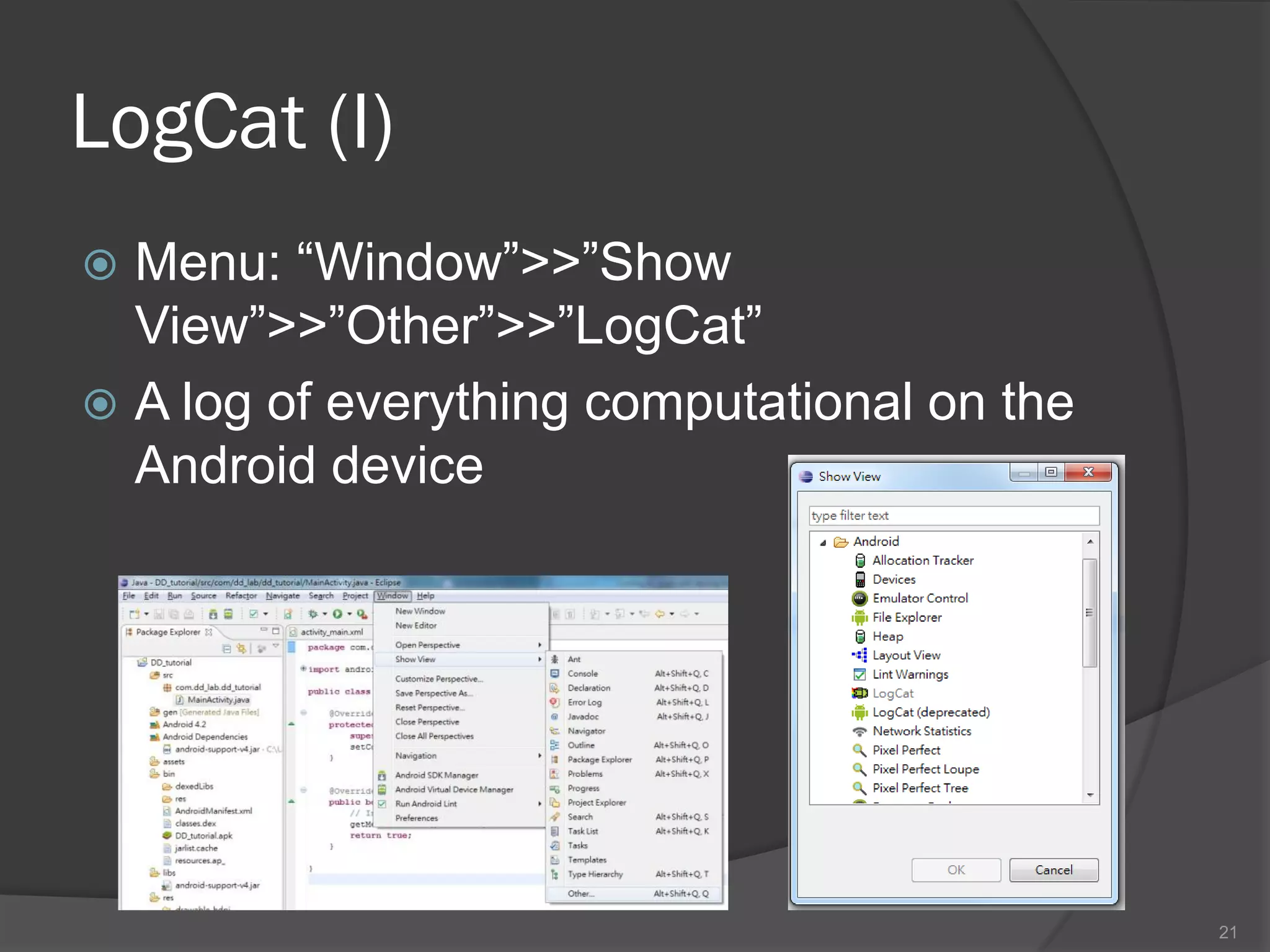
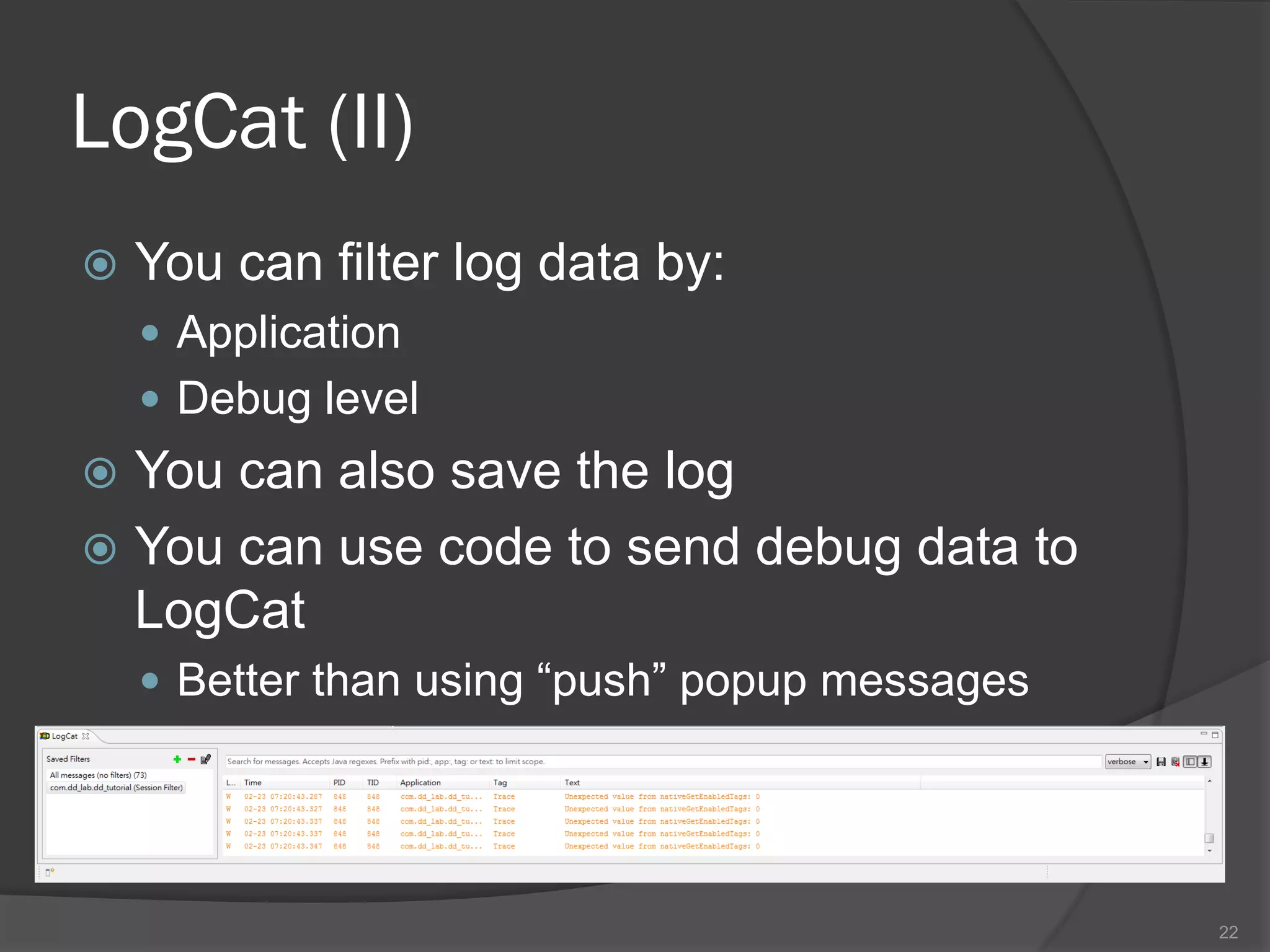
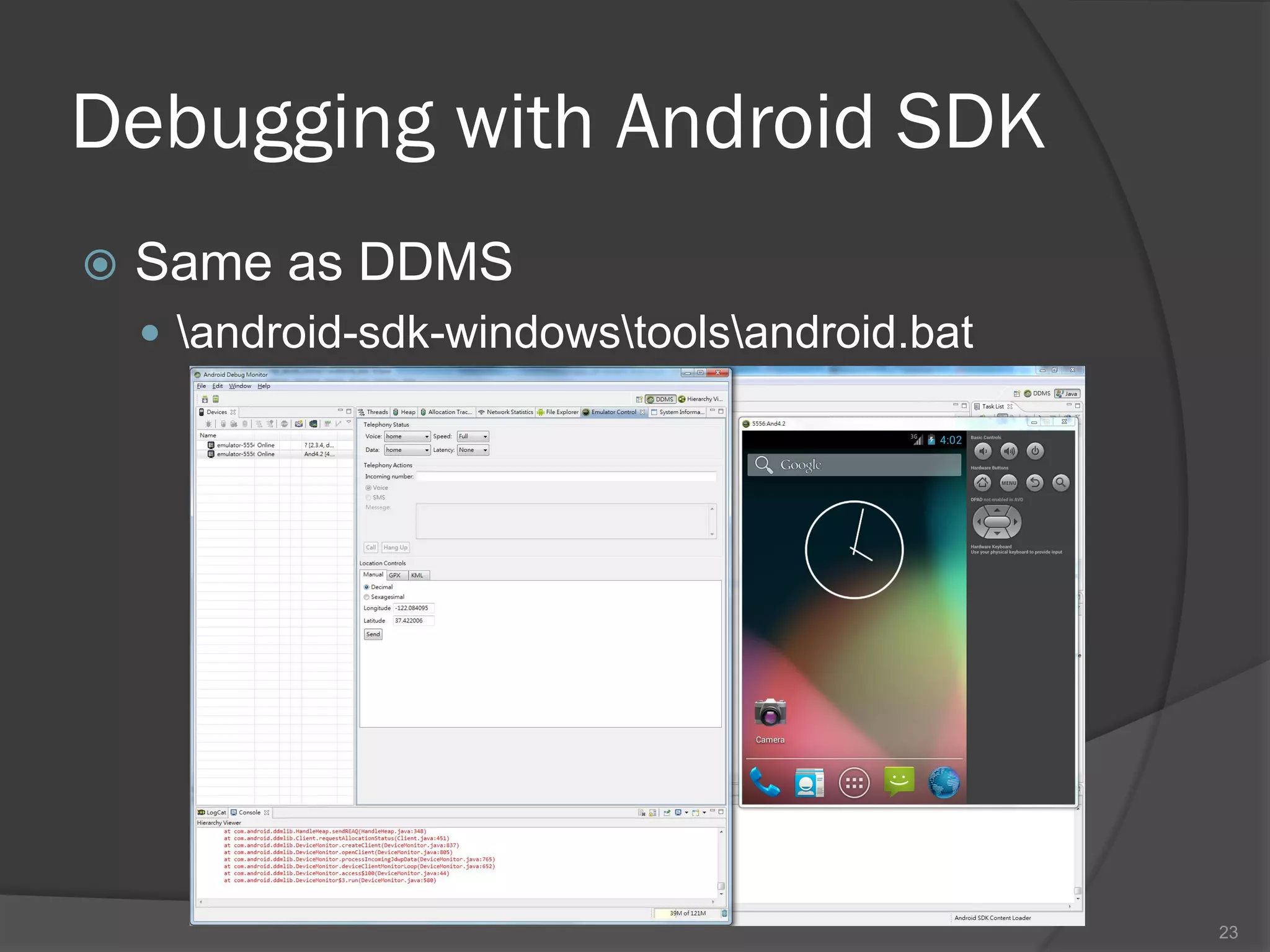
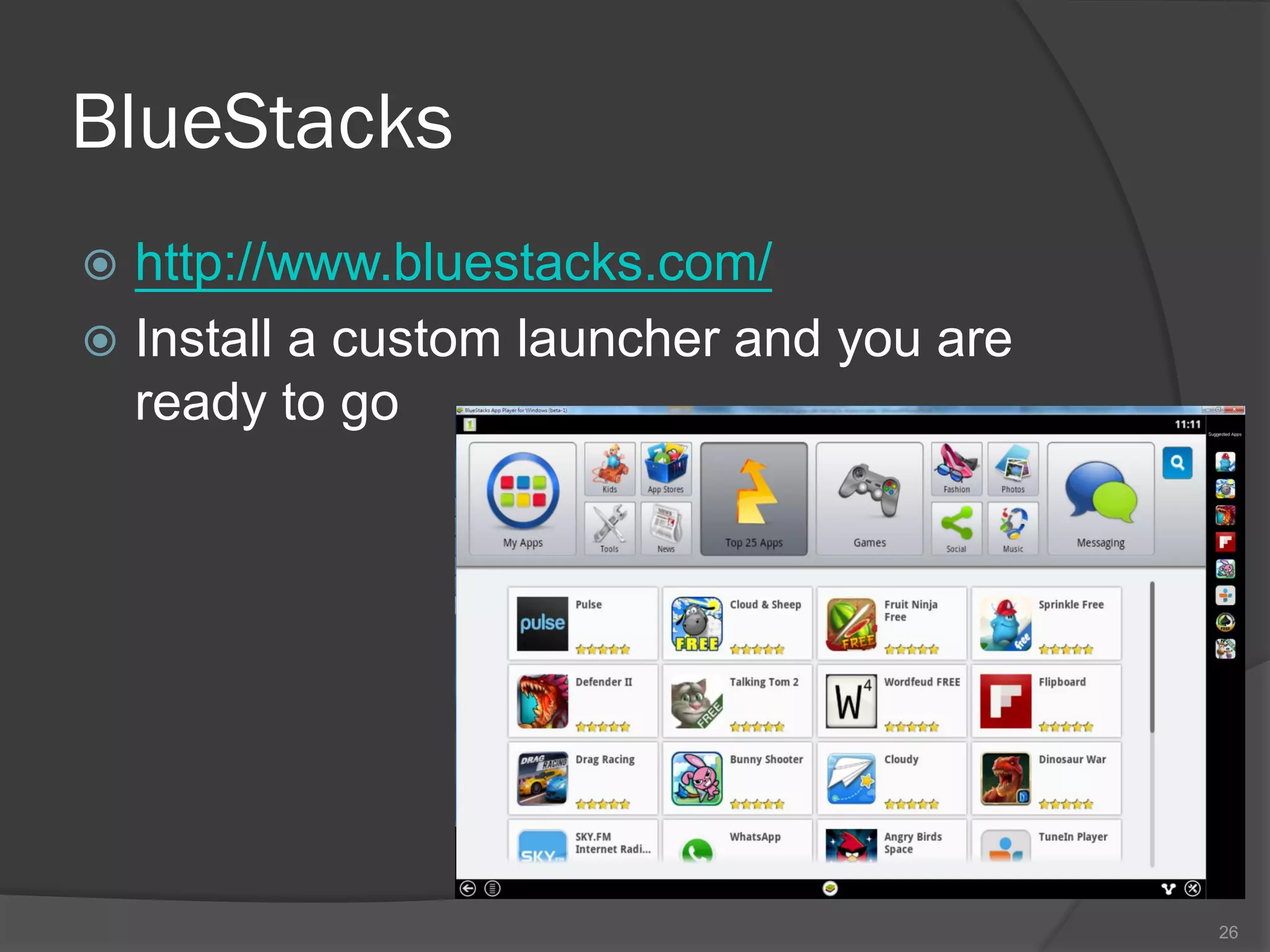
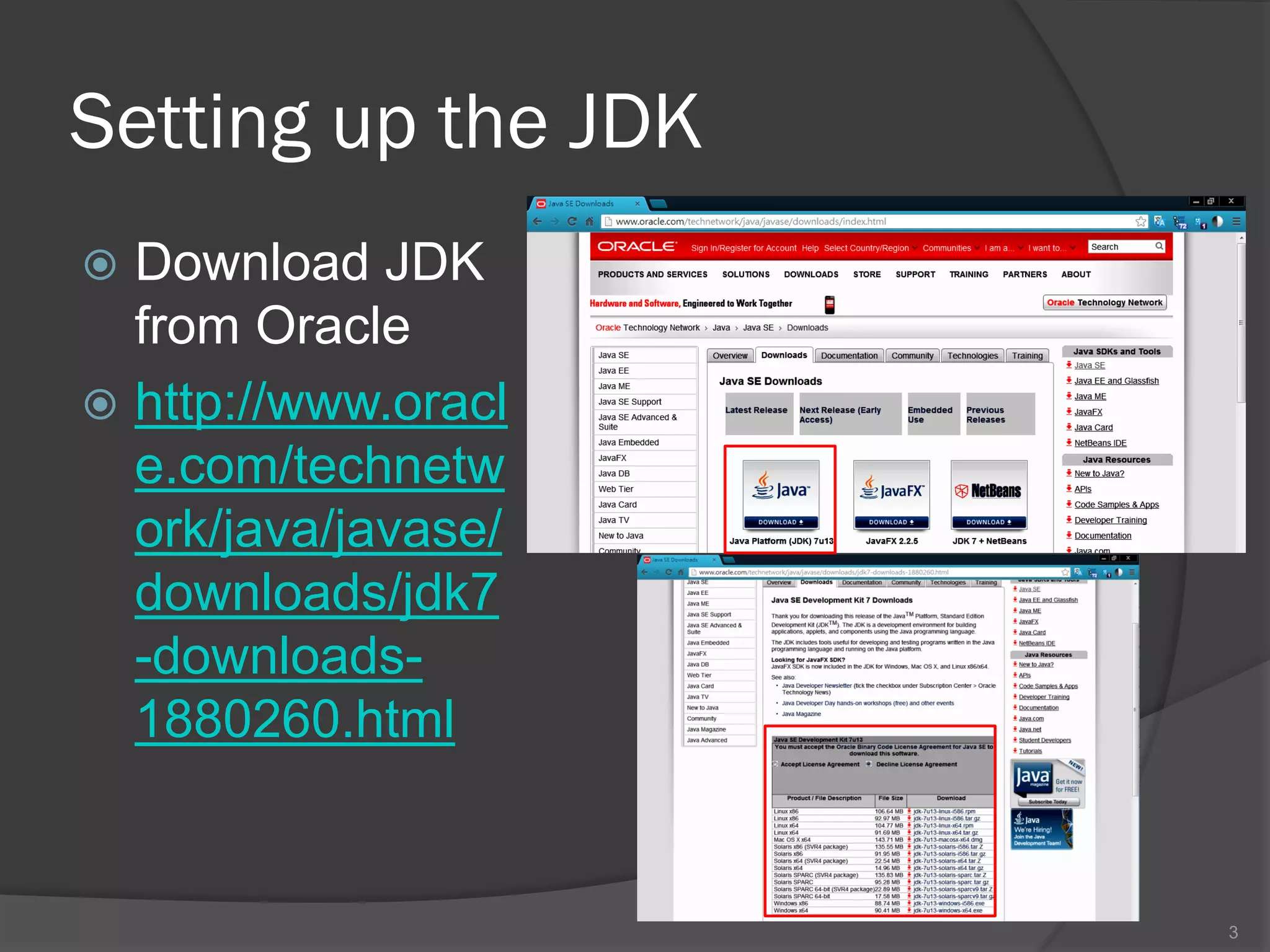
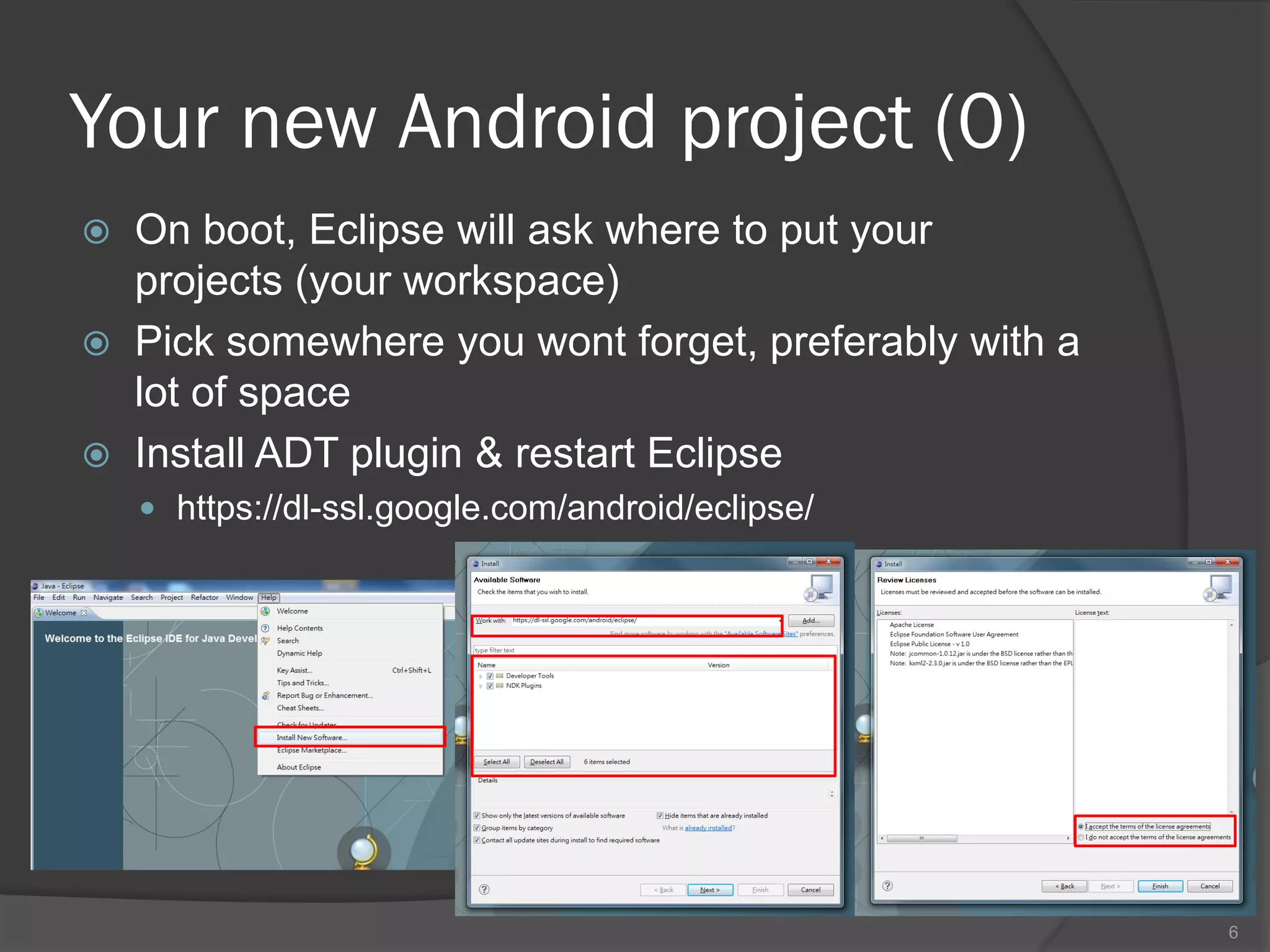
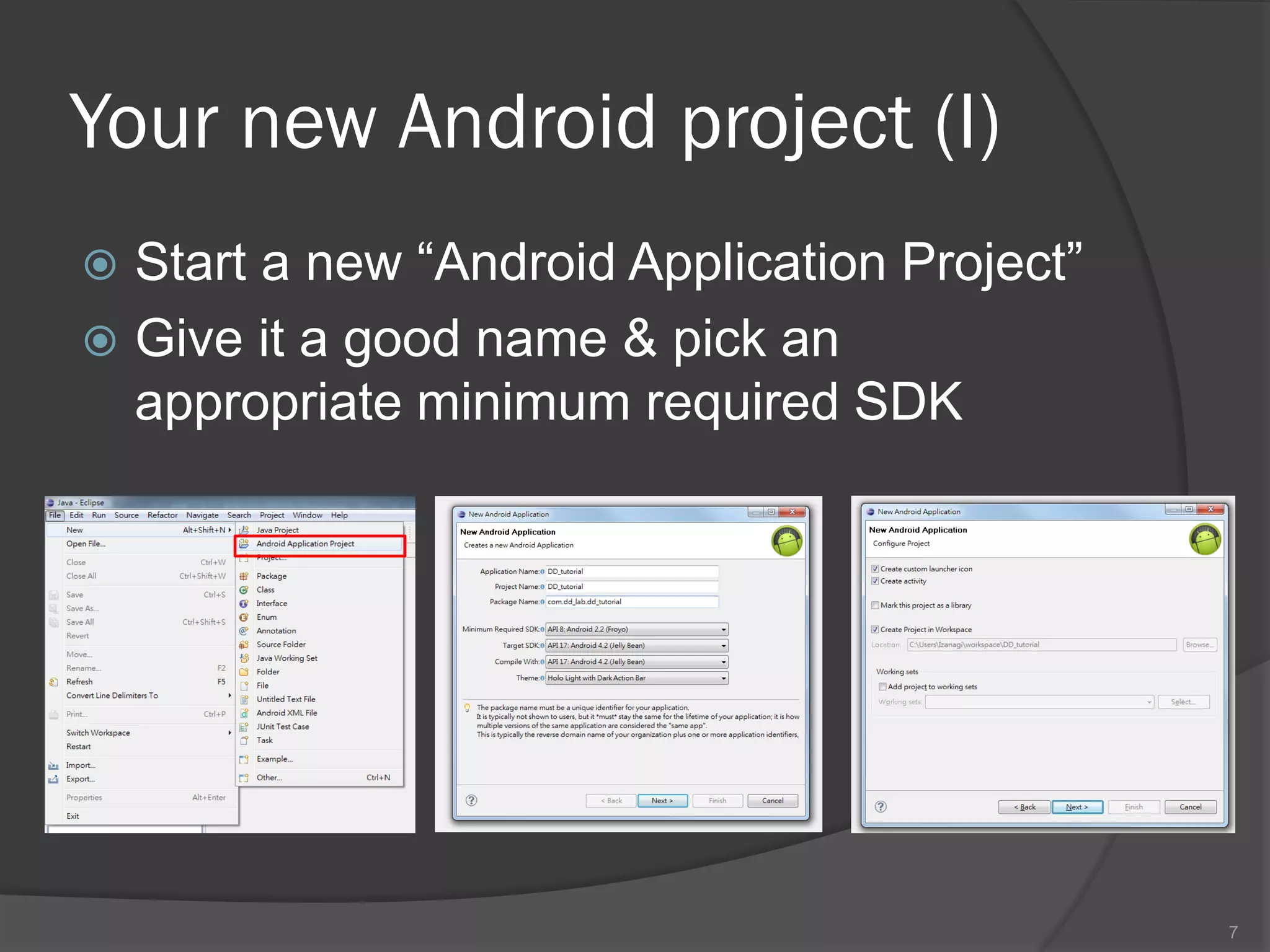
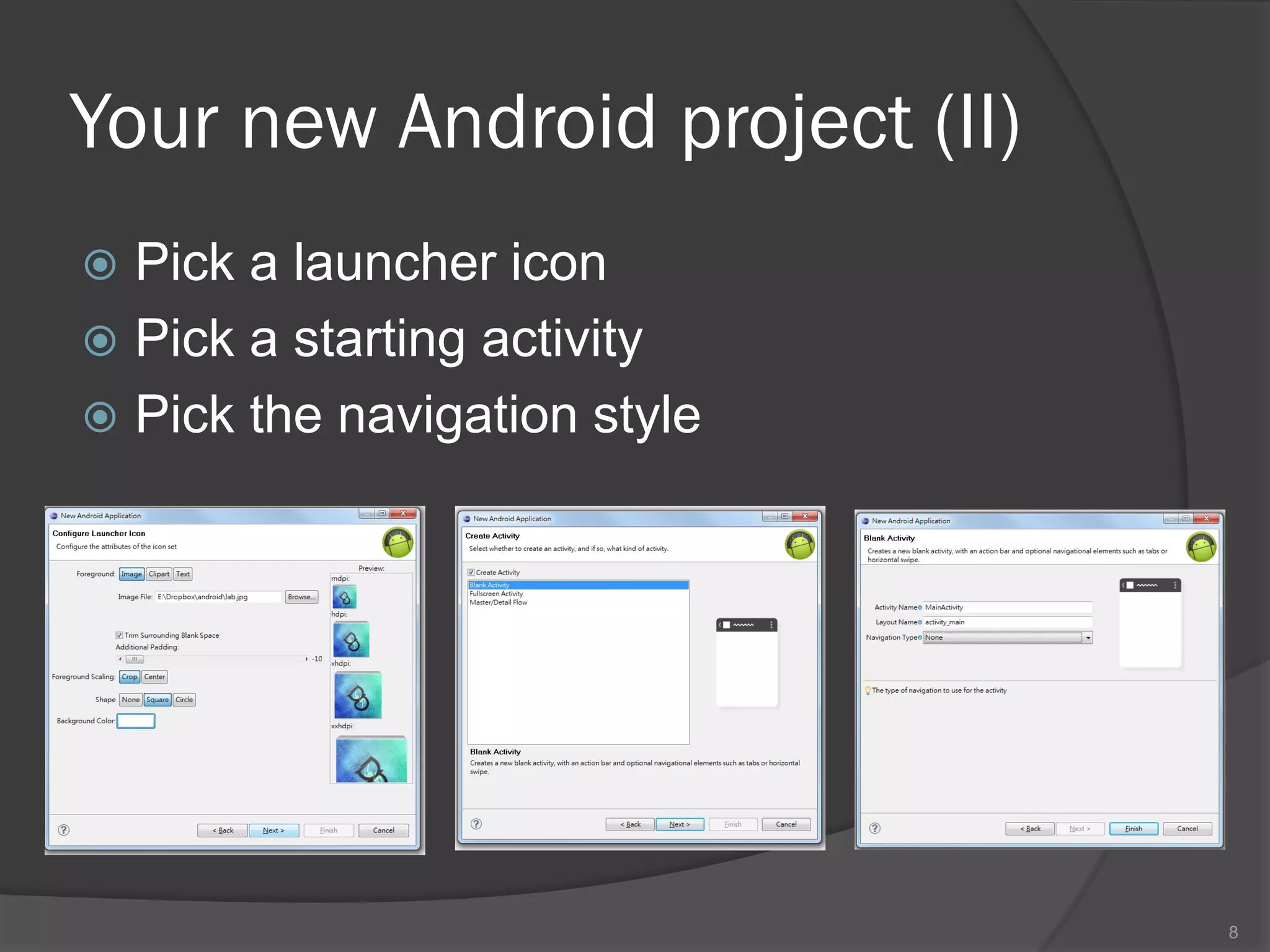
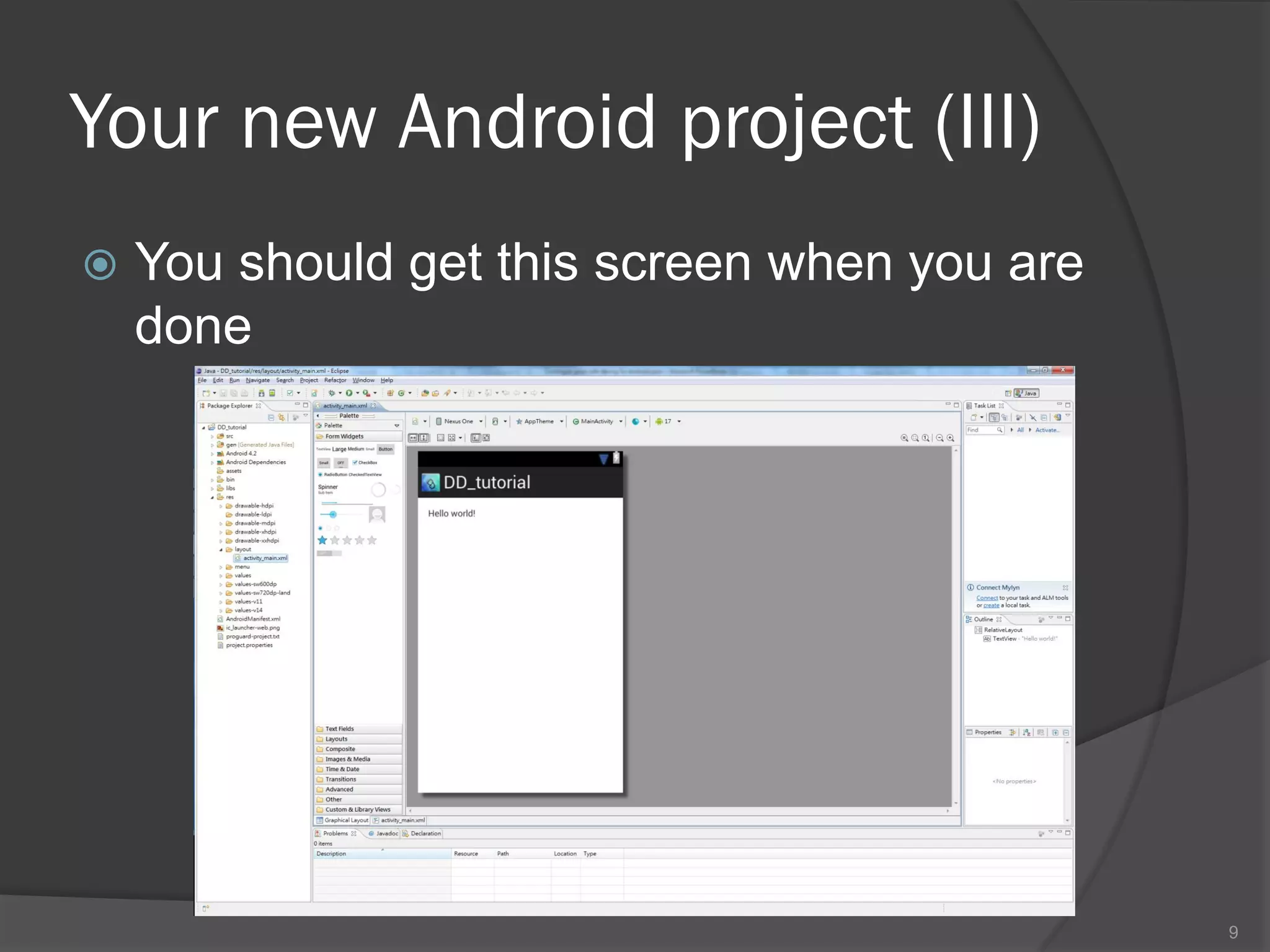
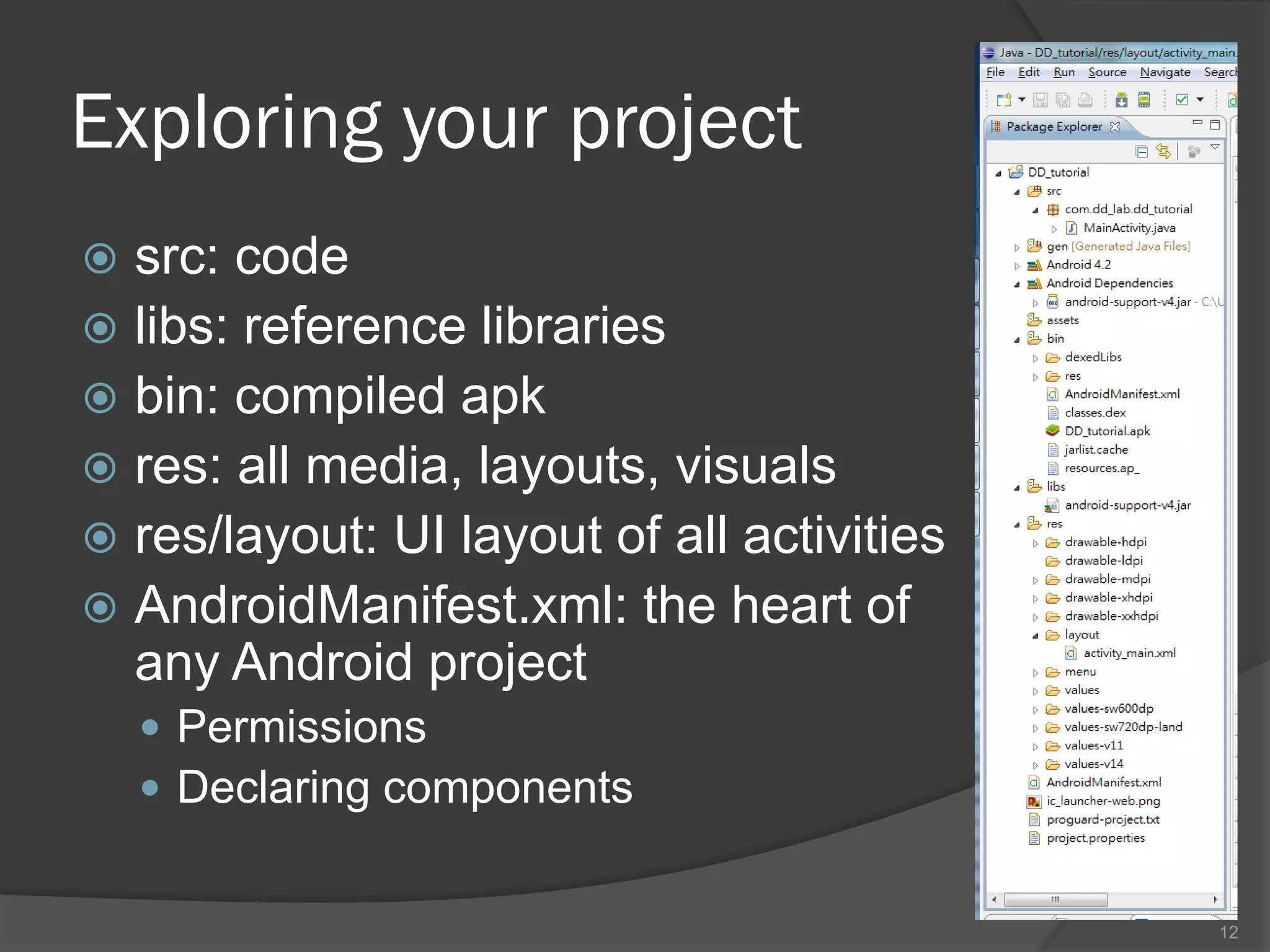
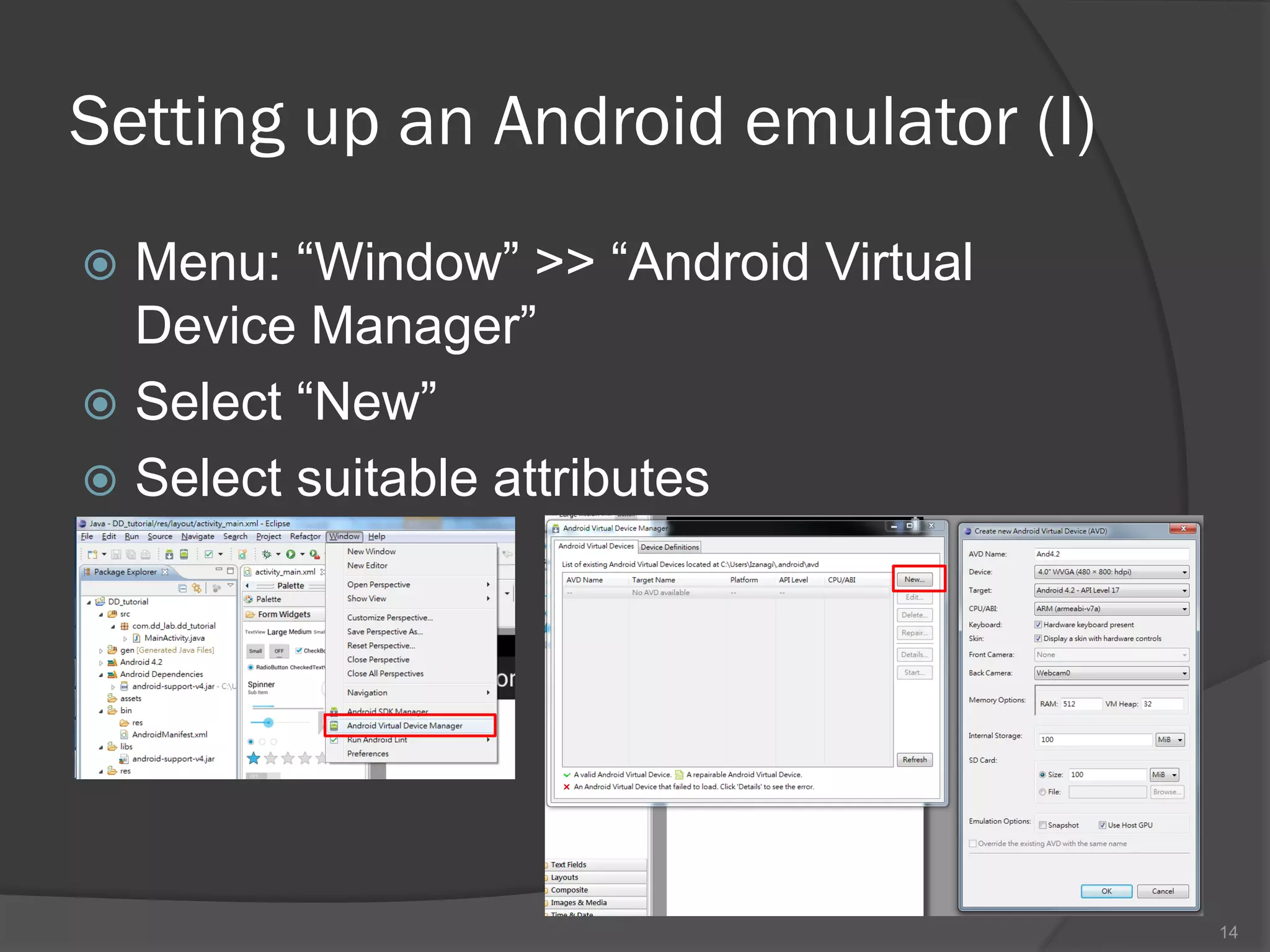
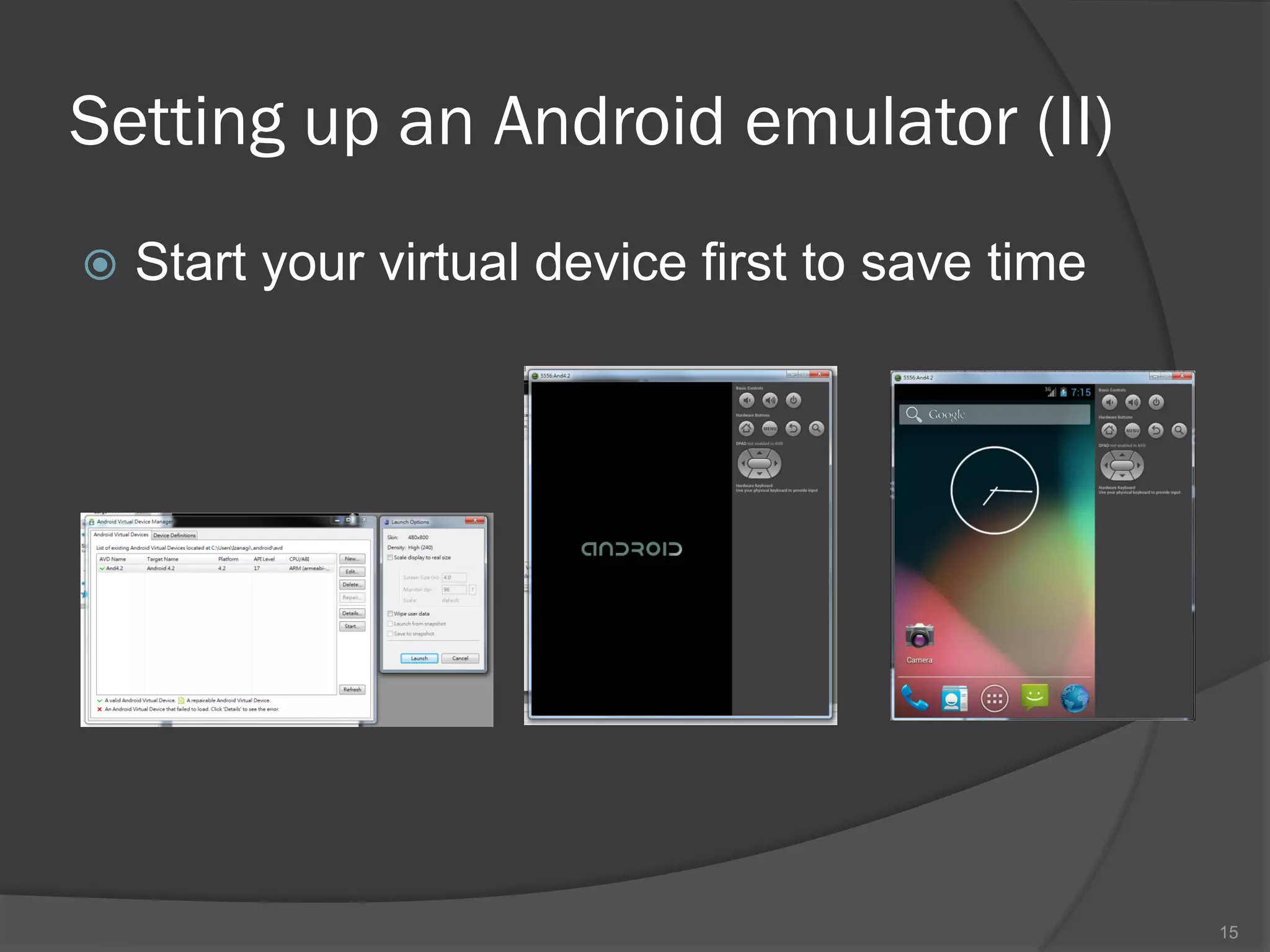
The document outlines the steps to set up a development environment for Android applications, including installing the JDK, Android SDK, and Eclipse IDE. It details creating a new Android project, debugging procedures, and testing applications on various devices. Additionally, it provides information on publishing apps and best practices for development and debugging.







![Emulating your Android
application
Select one of your source
files
Select the green “Run
[your program name]
button
First run only:
Select run as “Android
Applicaiton”
Say “Yes” to LogCat, nyan~!
Viola!!
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comingtogripswithdevingforandroid-130225111259-phpapp02/75/CCDD2013w-Coming-to-grips-with-deving-for-android-by-16-2048.jpg)