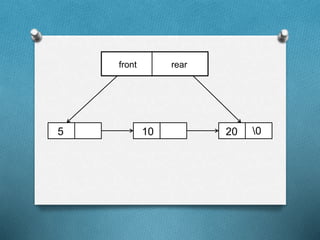
The document discusses queues, which are first-in first-out (FIFO) data structures with a front and rear end where insertion occurs at the rear and deletion occurs at the front. It describes queue operations like creation, insertion, deletion, checking for emptiness/fullness. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. Applications of queues include accessing files from disk systems, CPU scheduling in operating systems, and ticket reservation systems.