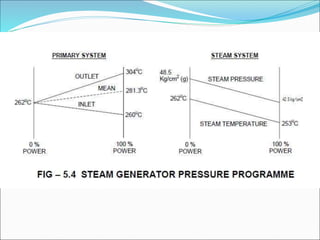
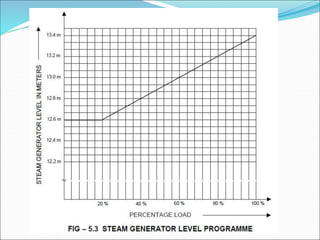
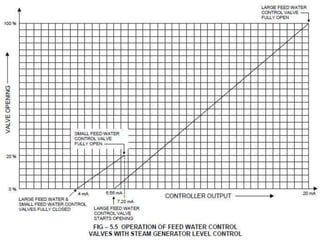
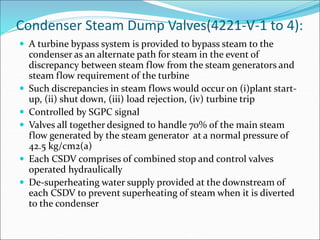
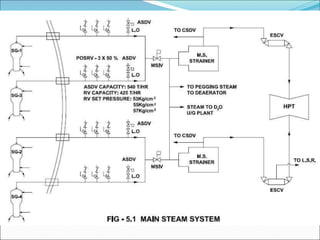
The document outlines the function and system description of steam generators in a reactor, detailing the production of dry steam, safety mechanisms, and emergency supply protocols. It includes specifications for various components like steam lines, safety relief valves, and turbine systems, ensuring proper operation under different reactor conditions. The document also emphasizes the importance of maintaining steam quality and addressing potential emergency situations involving feed water loss.