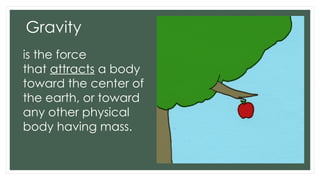
The document discusses the concepts of gravity and friction, including their effects on object movement and various experiments to demonstrate these principles. It outlines activities and questions designed to engage learners in understanding gravity's properties and its significance in everyday phenomena. Additionally, it includes assessments and thought-provoking questions related to the principles of gravity.