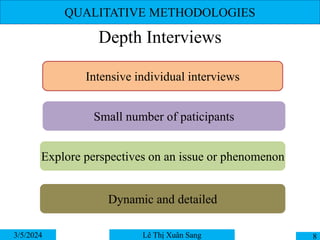
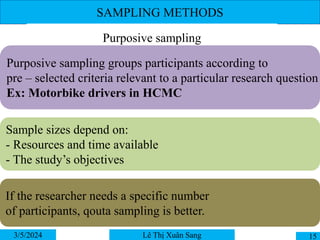
This document discusses qualitative and quantitative research methodologies. It explains that qualitative research allows understanding of a phenomenon from the perspectives of people involved and seeks to provide a rich understanding of an issue. The most common qualitative methods are described as participant observation, depth interviews, and focus groups. It also covers sampling methods for qualitative research, including purposive sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling.