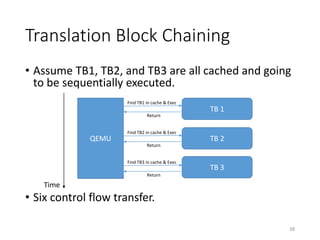
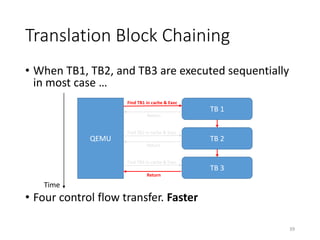
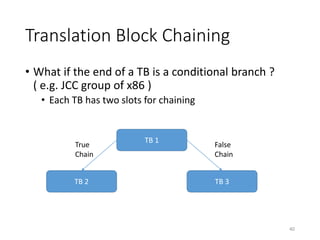
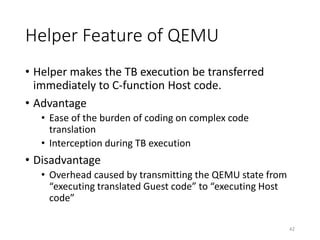
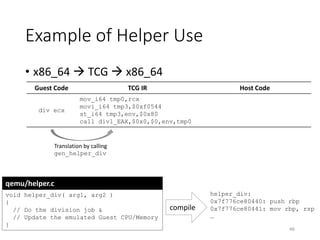
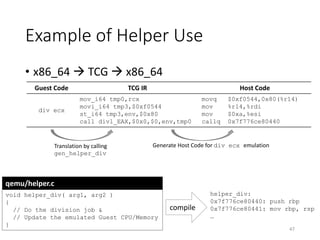
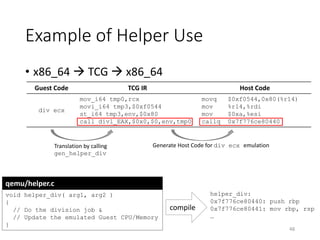
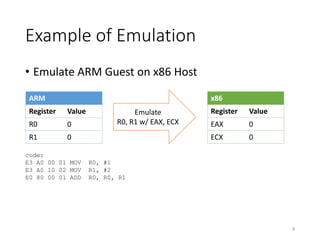
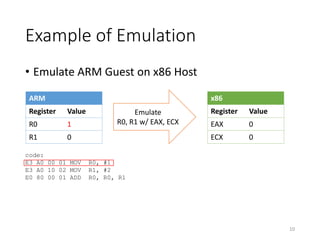
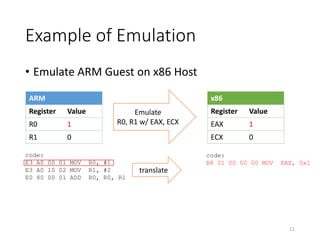
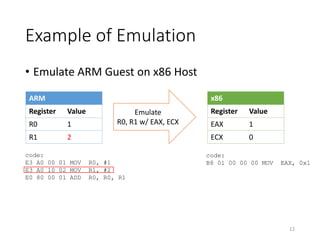
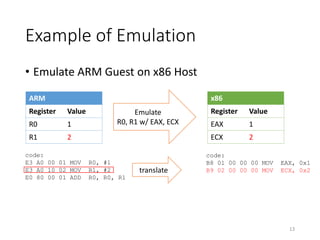
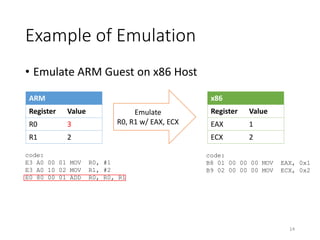
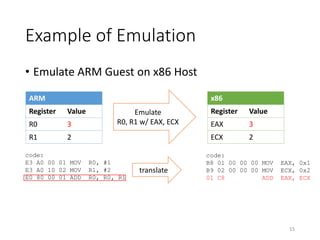
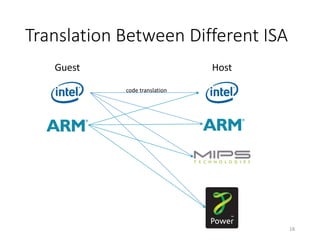
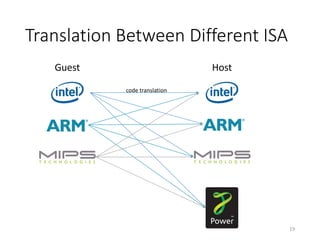
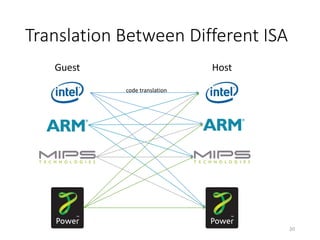
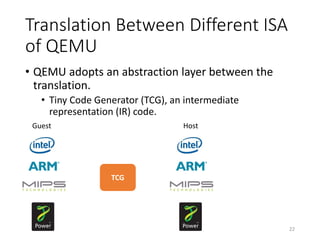
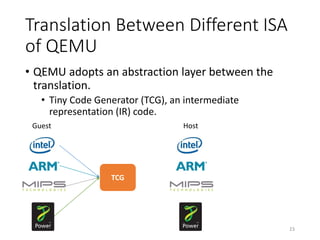
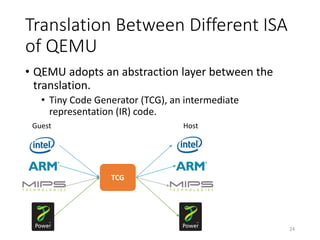
QEMU is an emulator that uses dynamic translation to emulate one instruction set architecture (ISA) on another host ISA. It translates guest instructions to an intermediate representation (TCG IR) code, and then compiles the IR code to native host instructions. QEMU employs techniques like translation block caching and chaining to improve the performance of dynamic translation. It also uses helper functions to offload complex operations during translation to improve efficiency.







![Example of
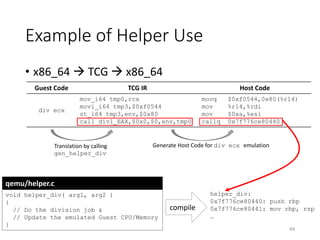
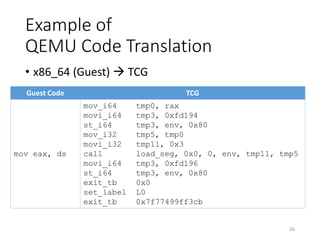
QEMU Code Translation
TCG Host Code
mov_i64 tmp0, rax
movi_i64 tmp3, 0xfd194
st_i64 tmp3, env, 0x80
mov_i32 tmp5, tmp0
movi_i32 tmp11, 0x3
call load_seg, 0x0, 0, env, tmp11, tmp5
movi_i64 tmp3, 0xfd196
st_i64 tmp3, env, 0x80
exit_tb 0x0
set_label L0
exit_tb 0x7f77499ff3cb
mov rax, 0x3
mov [0x7f779478f008], rax
mov [r14 + 0x80], 0xfd194
mov rdi, r14
mov esi, 0x3
mov edx, 0x10
call 0x7f776ce8e500
mov [r14 + 0x80], 0xfd196
xor eax, eax
jmp 0x7f776a9fec16
lea rax, [rip – 0x110005ed]
jmp 0x7f776a9fec16
• TCG x86_64 (Host)
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemuintro-151105065404-lva1-app6892/85/Qemu-Introduction-27-320.jpg)
![Example of
QEMU Code Translation
TCG Host Code
mov_i64 tmp0, rax
movi_i64 tmp3, 0xfd194
st_i64 tmp3, env, 0x80
mov_i32 tmp5, tmp0
movi_i32 tmp11, 0x3
call load_seg, 0x0, 0, env, tmp11, tmp5
movi_i64 tmp3, 0xfd196
st_i64 tmp3, env, 0x80
exit_tb 0x0
set_label L0
exit_tb 0x7f77499ff3cb
mov rax, 0x3
mov [0x7f779478f008], rax
mov [r14 + 0x80], 0xfd194
mov rdi, r14
mov esi, 0x3
mov edx, 0x10
call 0x7f776ce8e500
mov [r14 + 0x80], 0xfd196
xor eax, eax
jmp 0x7f776a9fec16
lea rax, [rip – 0x110005ed]
jmp 0x7f776a9fec16
• TCG x86_64 (Host)
28
I just wanna execute
mov eax, ds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemuintro-151105065404-lva1-app6892/85/Qemu-Introduction-28-320.jpg)

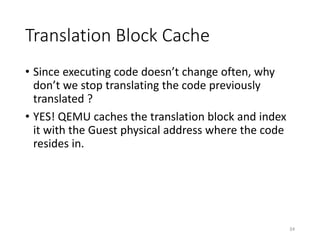
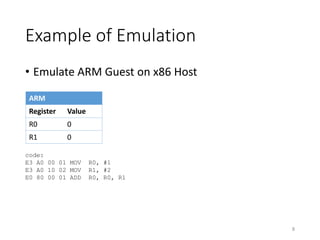
![Translation Block Cache
• Workflow
35
main:
mov dword ptr [esp+18], 0
mov dword ptr [esp+14], 80
mov dword ptr [esp+10], 1
mov dword ptr [esp+C], 0
mov dword ptr [esp+8], 0
mov dword ptr [esp+4], C0000000
mov dword ptr [esp], 00404020
mov eax, dword ptr[00406120]
call eax // f = CreateFileA( … )
sub esp, 1C
mov dword ptr[ebp-C], eax
cmp dword ptr[ebp-C], -1
jnz short 00401557 // if(f == -1)
mov eax, -1
jmp short 0040156C // return -1
mov eax, dword ptr [ebp-C]
mov dword ptr [esp], eax
mov eax, dword ptr[0040611C]
call eax // CloseHandle( f )
sub esp, 4
mov eax, 0
mov ecx, dword ptr [ebp-4]
leave // return 0
EIP = 0x11223344
GVA = 0x11223344
GPA = 0x5566
Is TB_cache[GPA]
Valid ?
Execute the TB
Code Translation
mov dword ptr [esp+18], 0
mov dword ptr [esp+14], 80
mov dword ptr [esp+10], 1
mov dword ptr [esp+C], 0
mov dword ptr [esp+8], 0
mov dword ptr [esp+4], C0000000
mov dword ptr [esp], 00404020
mov eax, dword ptr[00406120]
call eax
TB_cache[GPA] = TB
GVA: Guest Virtual Address
GPA: Guest Physical Address
Guest Host
True
False
Lookup the Guest
page table for GVA
TB (Translated code inside)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemuintro-151105065404-lva1-app6892/85/Qemu-Introduction-35-320.jpg)