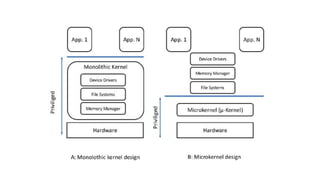
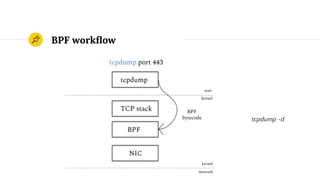
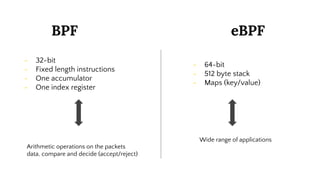
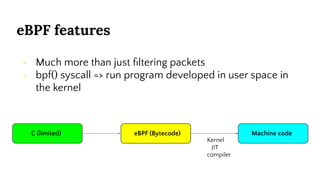
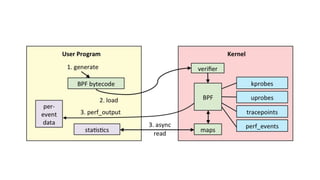
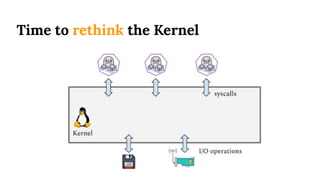
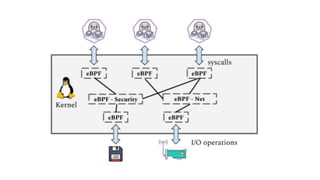
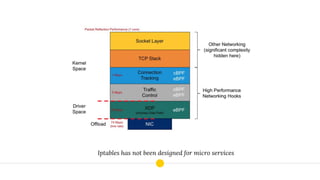
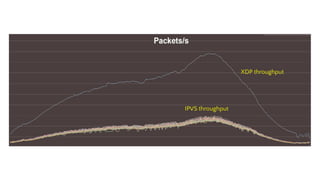
This document provides an introduction to eBPF (Extended Berkeley Packet Filter), which allows running user-space code in the Linux kernel without needing to compile a kernel module. It describes how eBPF avoids unnecessary copying of packets between kernel and user-space for improved performance. Examples are given of using eBPF for networking tasks like SDN configuration, DDoS mitigation, intrusion detection, and load balancing. The document concludes by noting eBPF provides alternatives to iptables that are better suited for microservices architectures.