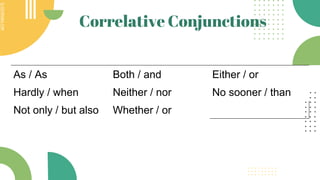
This document discusses different types of connecting words that can be used between clauses in sentences. It describes coordinating conjunctions like and, but, or, nor, so, yet, for which connect two independent clauses of equal importance. Independent marker words like however, moreover, can also connect independent clauses and require a semicolon. Subordinating conjunctions like because, before, when introduce dependent clauses and correlate conjunctions like either/or, neither/nor work in pairs to join equal clauses.