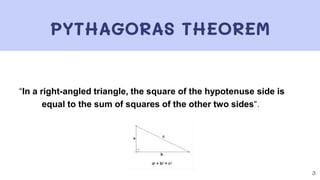
This document provides information about Pythagoras' theorem and its converse. It begins by defining Pythagoras' theorem as "In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides". It then gives an example of applying Pythagoras' theorem to find the distance of the foot of a ladder from the bottom of a wall. Next, it defines the converse of Pythagoras' theorem as "If a triangle, the square on the greatest side is equal to sum of square on the other two sides, then the triangle is right angled triangle". Finally, it provides some practice problems for students to work through.