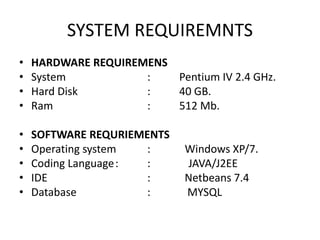
This document proposes a provably secure key-aggregate cryptosystem that allows for efficient online data sharing on the cloud. It allows data owners to encrypt data and delegate decryption rights to users via a single broadcast aggregate key, while retaining the ability to revoke access. The proposed system provides data confidentiality, user revocation, scalability, and prevents collusion. It is proven to be semantically secure and collusion resistant under appropriate security assumptions. Hardware requirements include a Pentium IV 2.4 GHz processor and 512 MB RAM, while software requirements include Windows XP/7, Java/J2EE, Netbeans 7.4, and MySQL database.