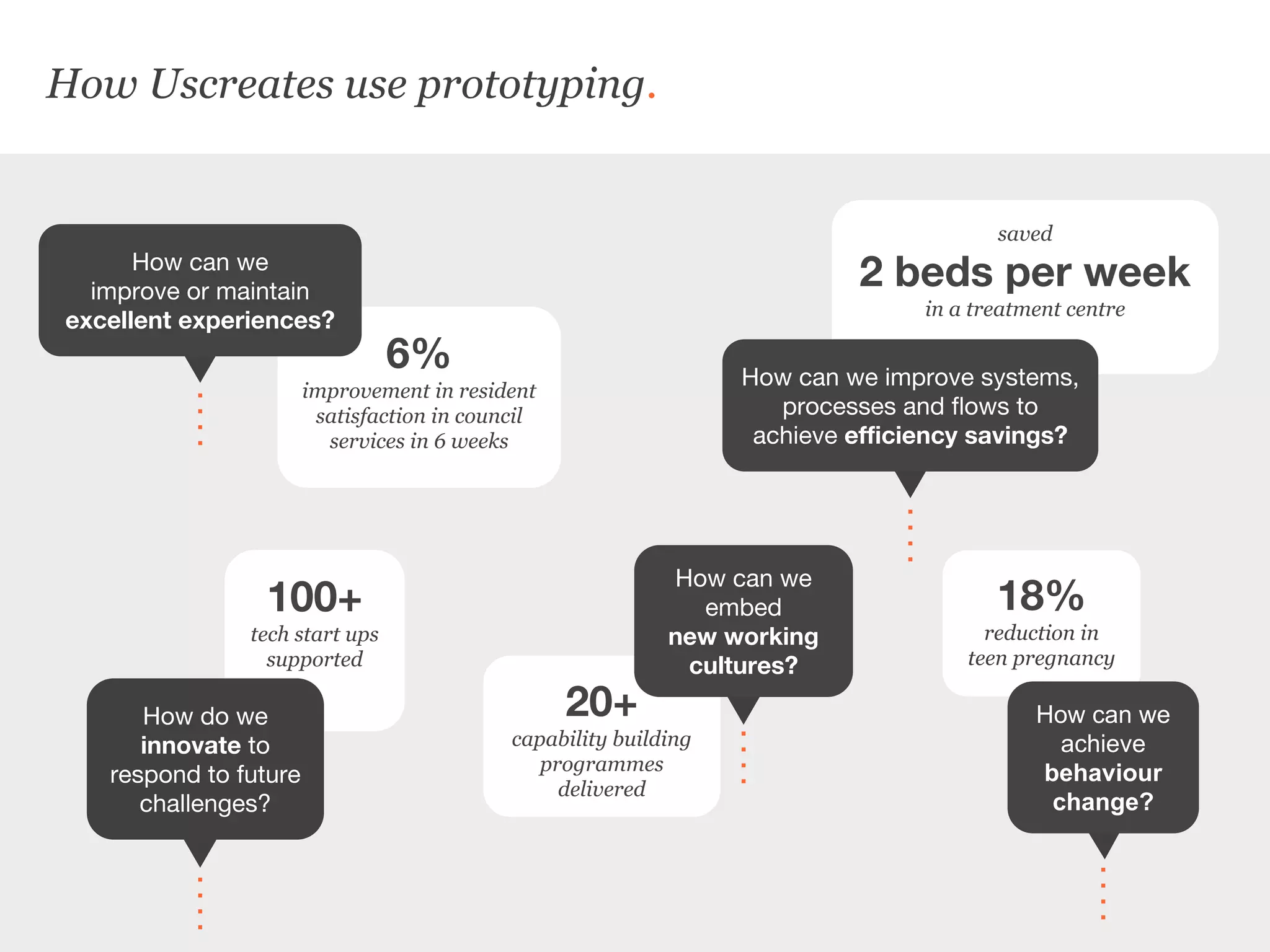
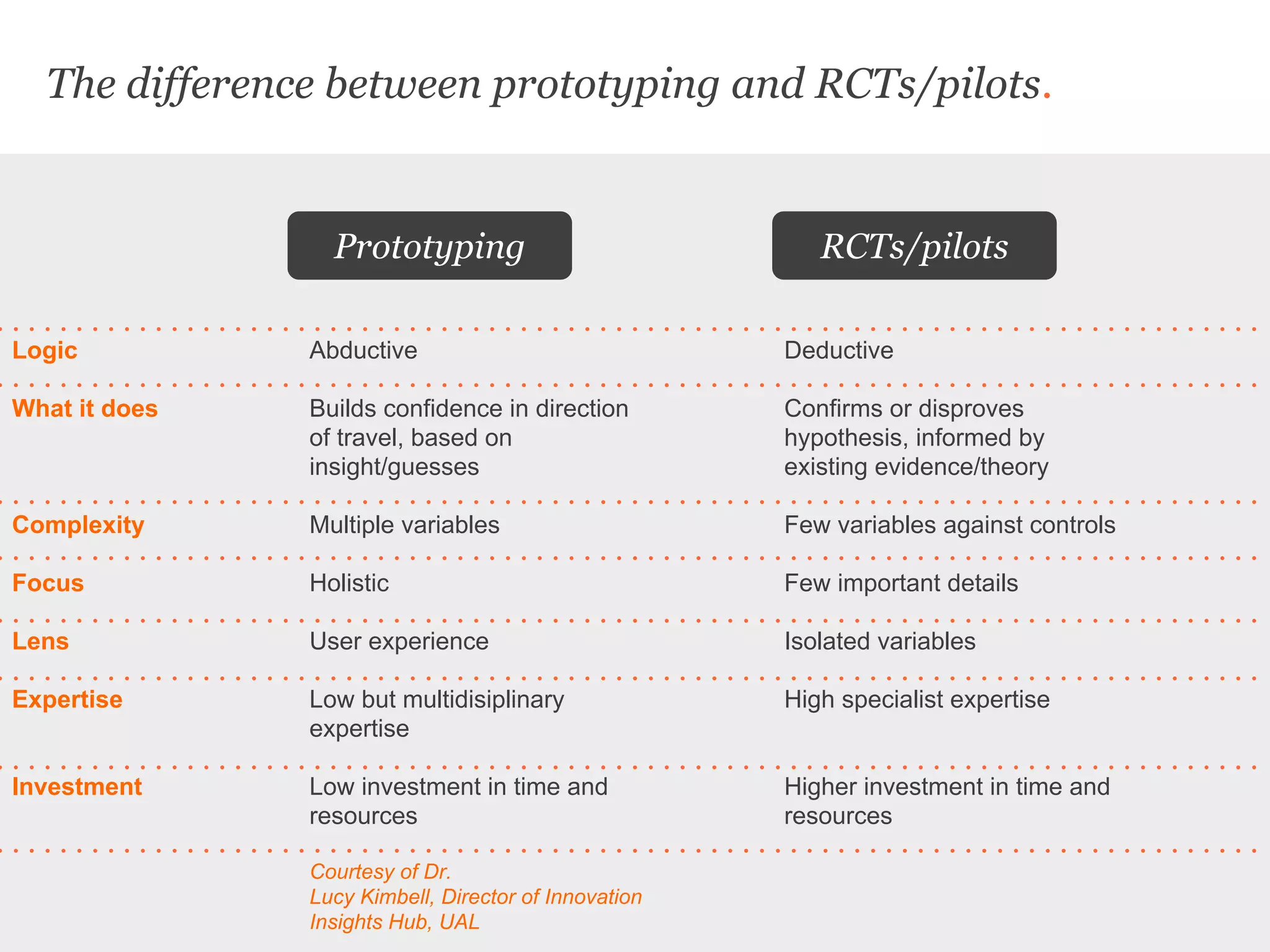
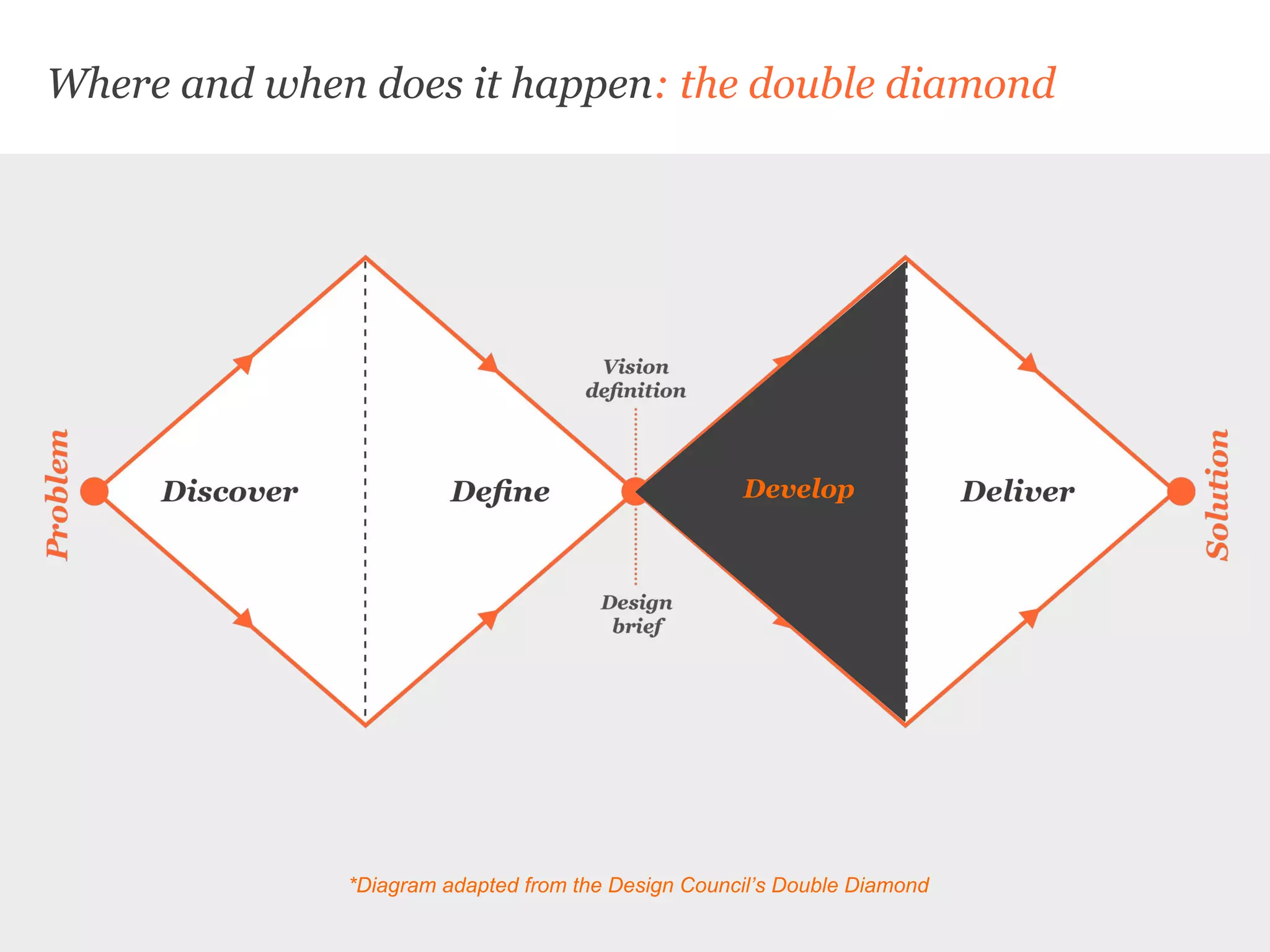
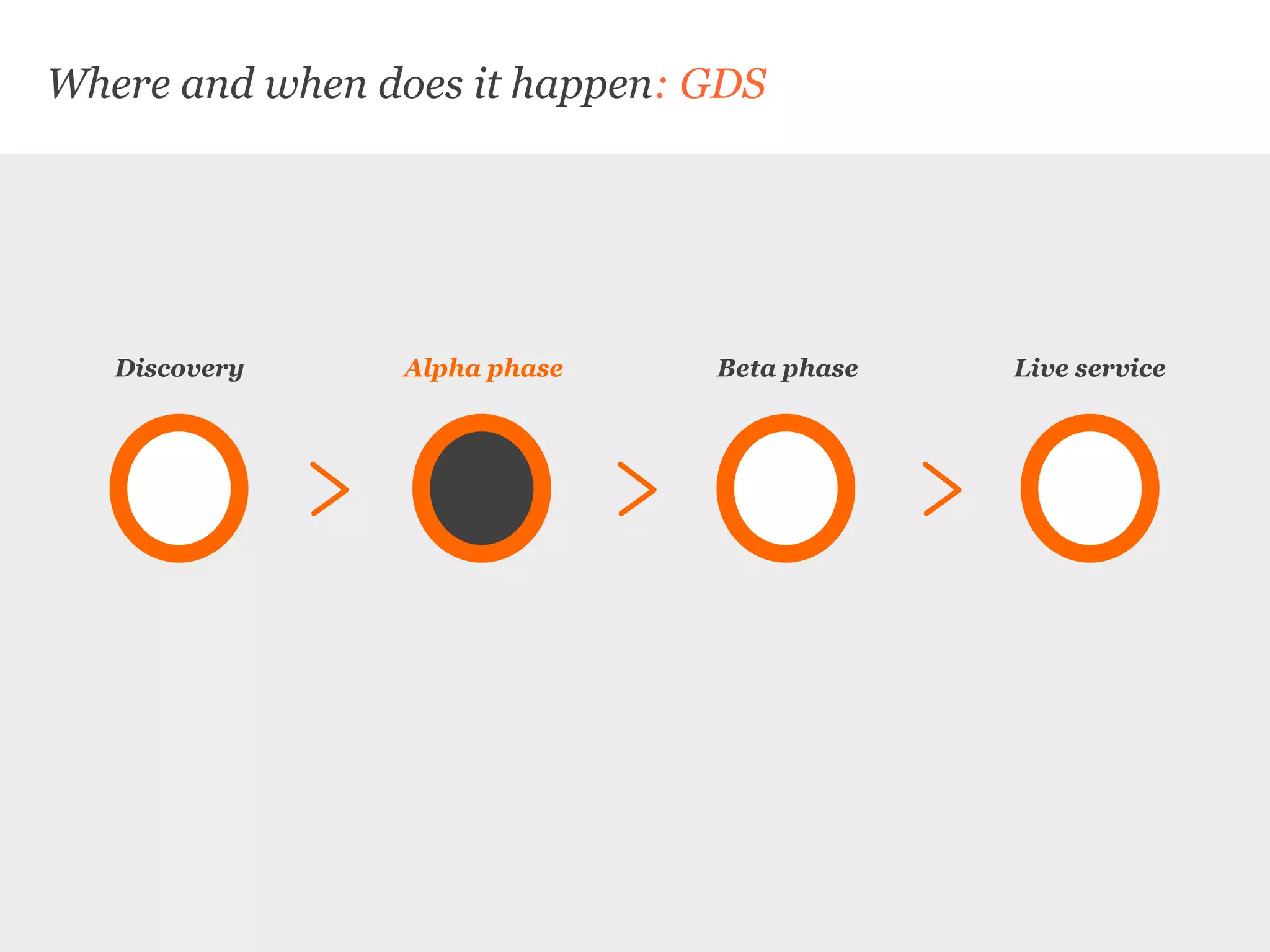
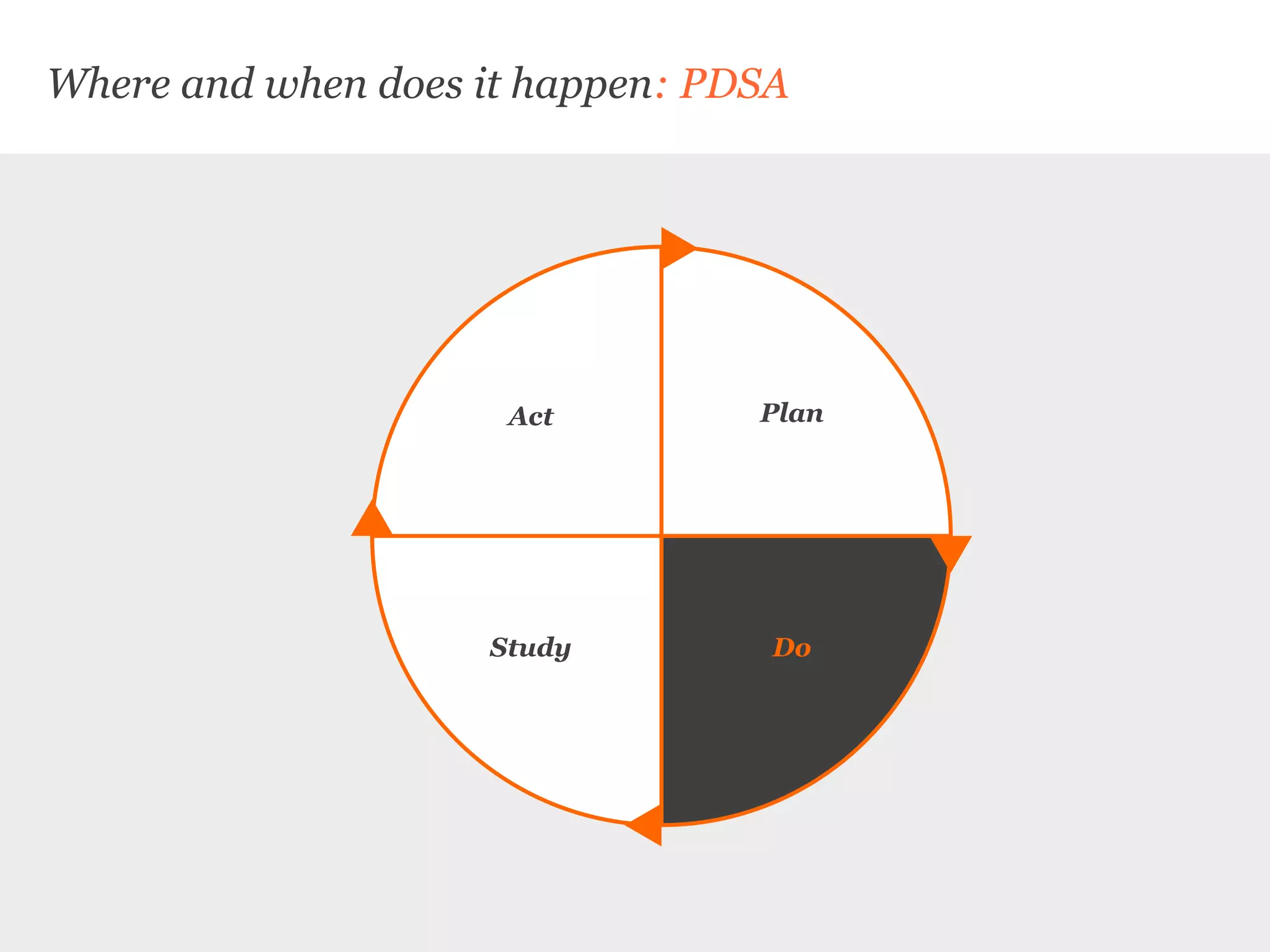
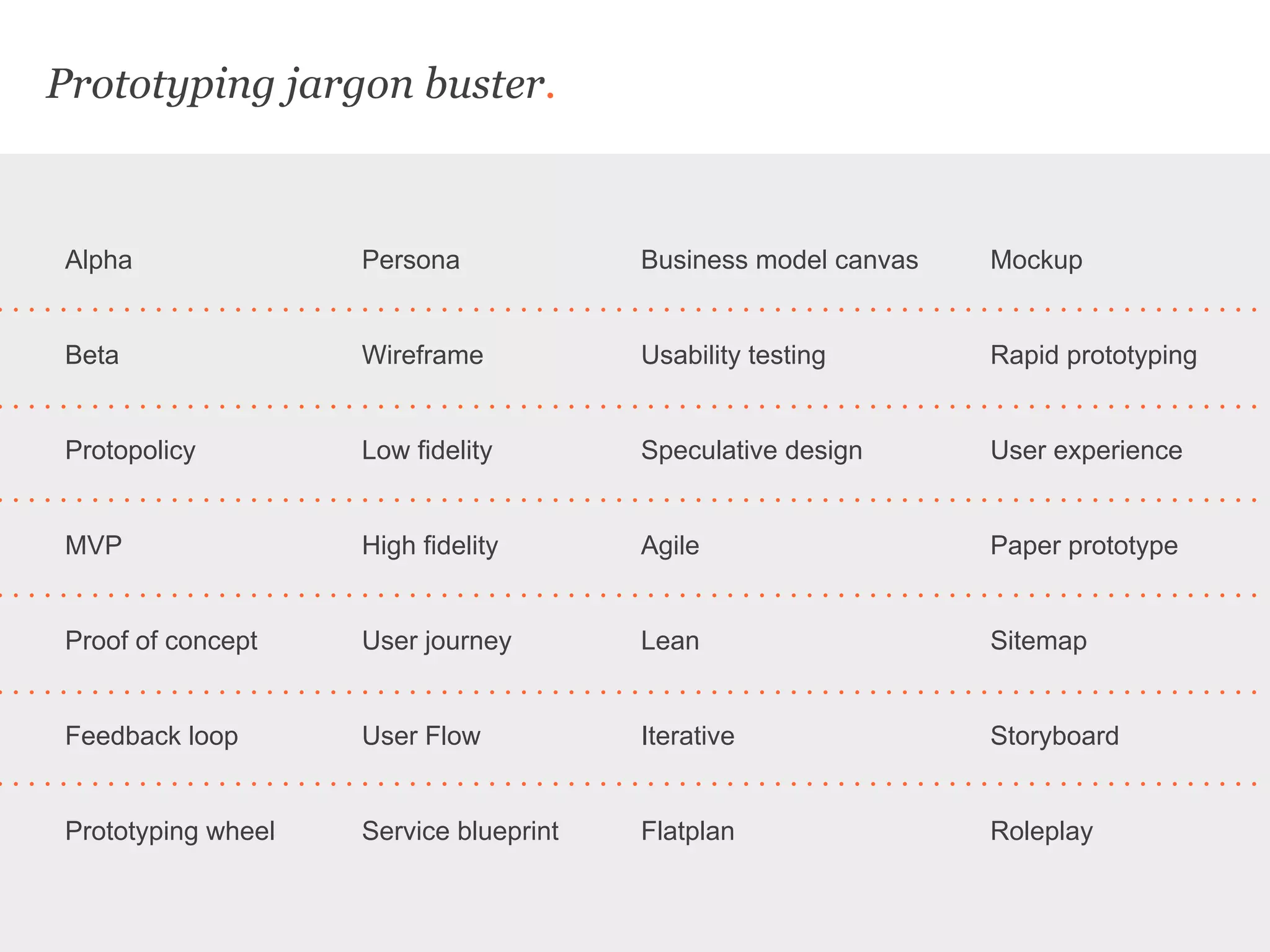
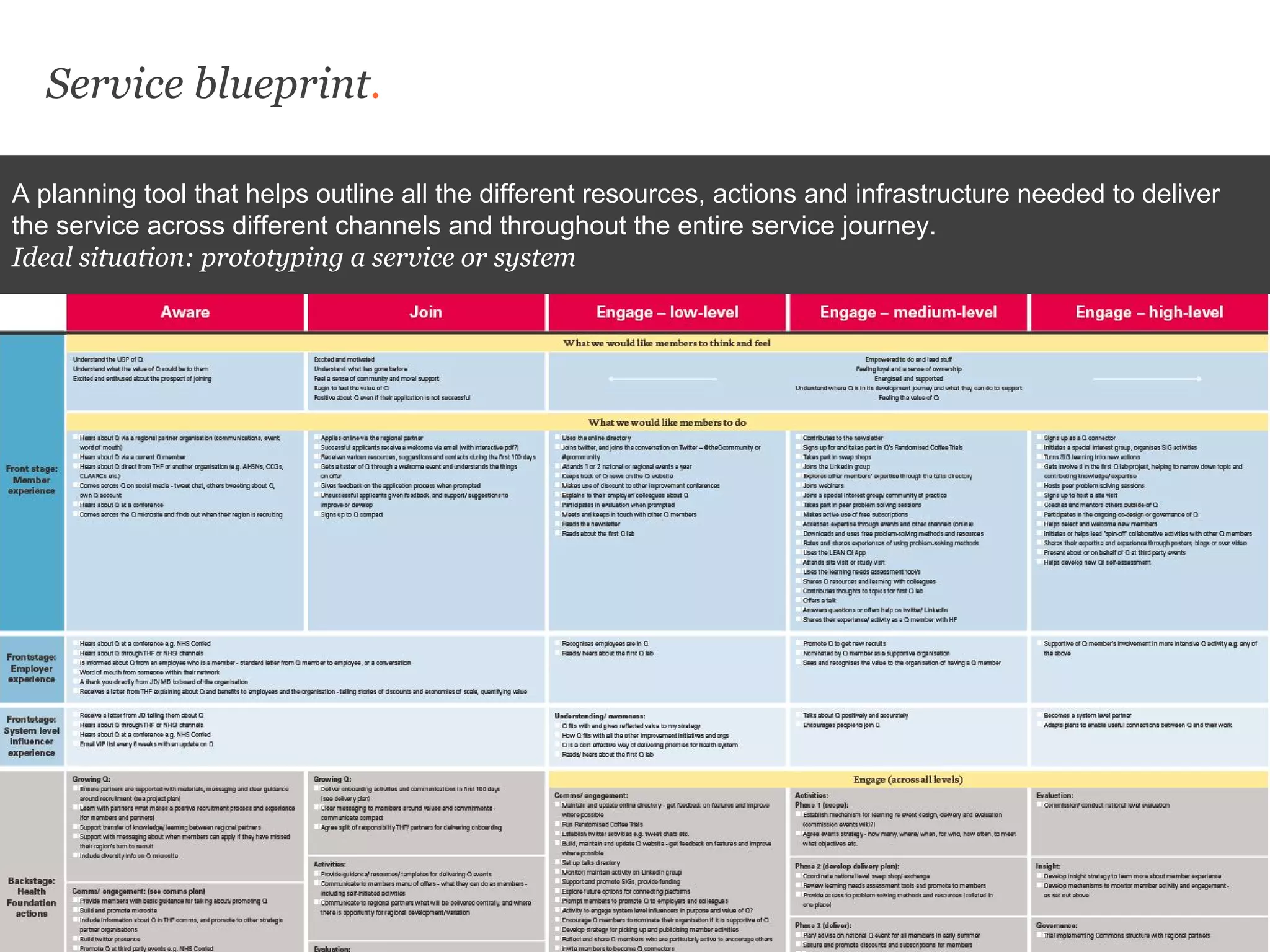
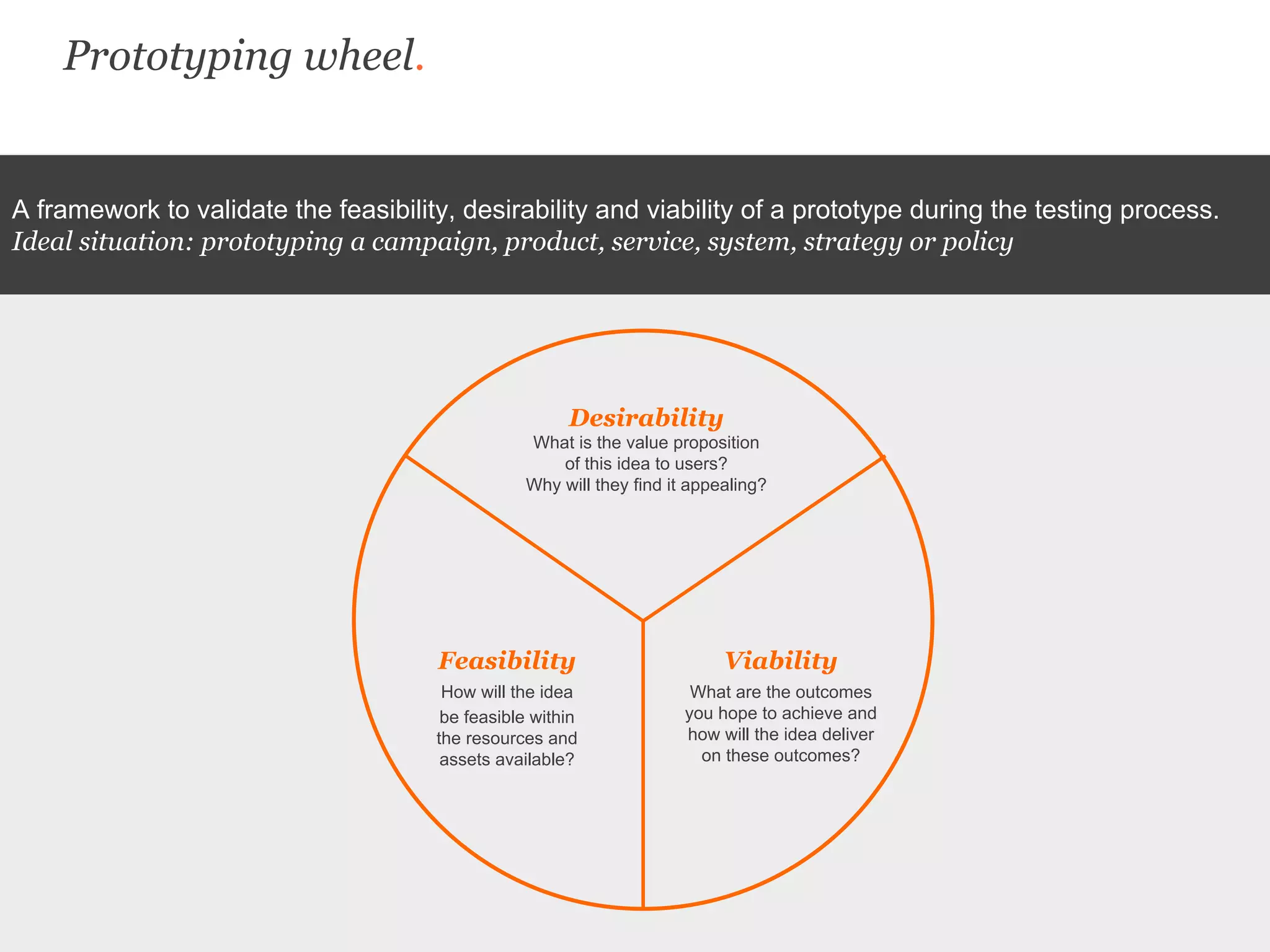
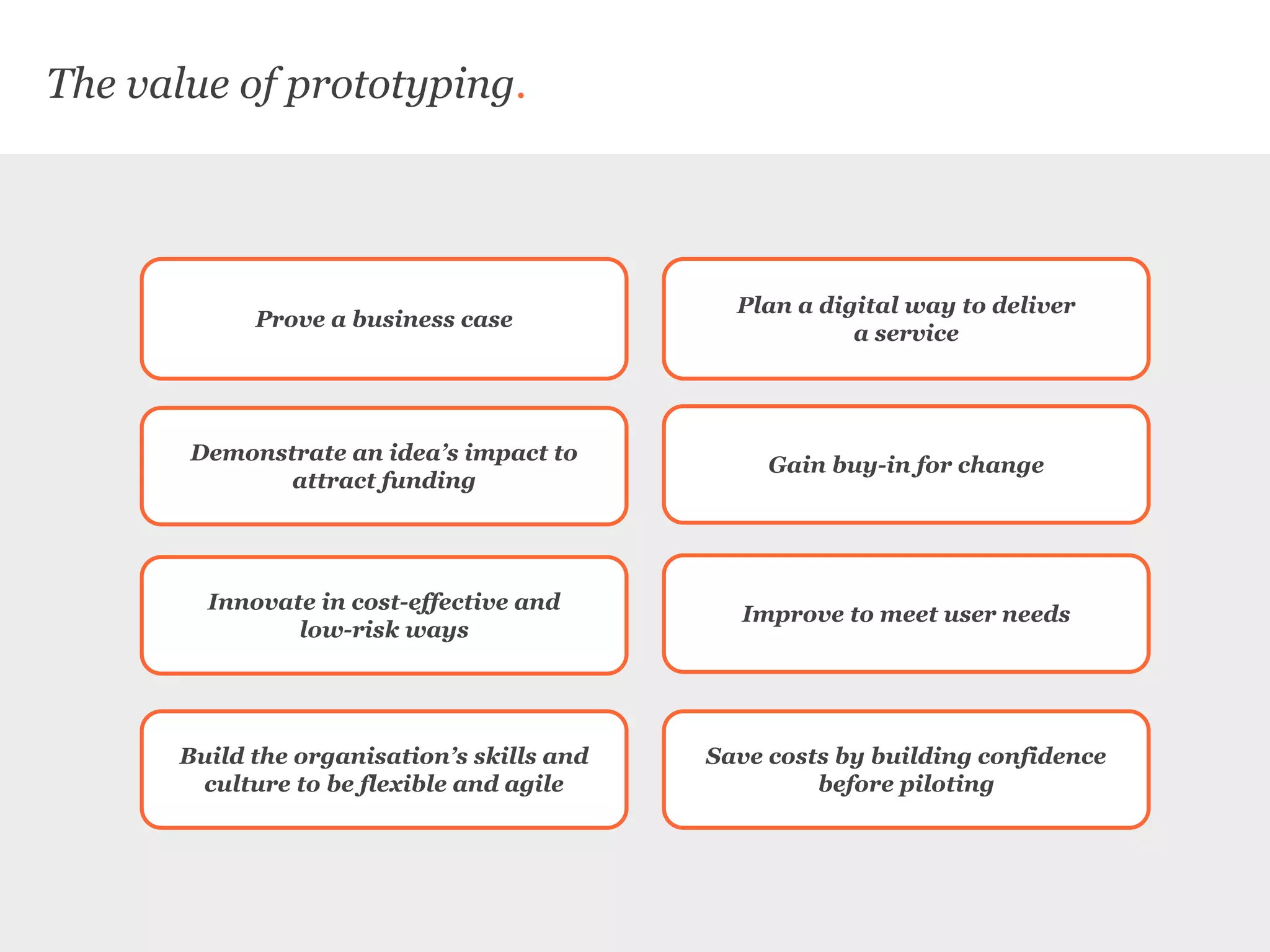
Uscreates is a design agency that uses prototyping to create better health and wellbeing outcomes. Prototyping involves quickly mocking up ideas with minimal resources to assess viability, desirability, and feasibility. It allows testing concepts through methods like paper prototypes, wireframes, roleplays and more before implementing. Prototyping provides benefits like demonstrating impact to attract funding, proving business cases, gaining buy-in for change, and innovating in cost-effective, low-risk ways. It is part of an iterative process to improve ideas and meet user needs.