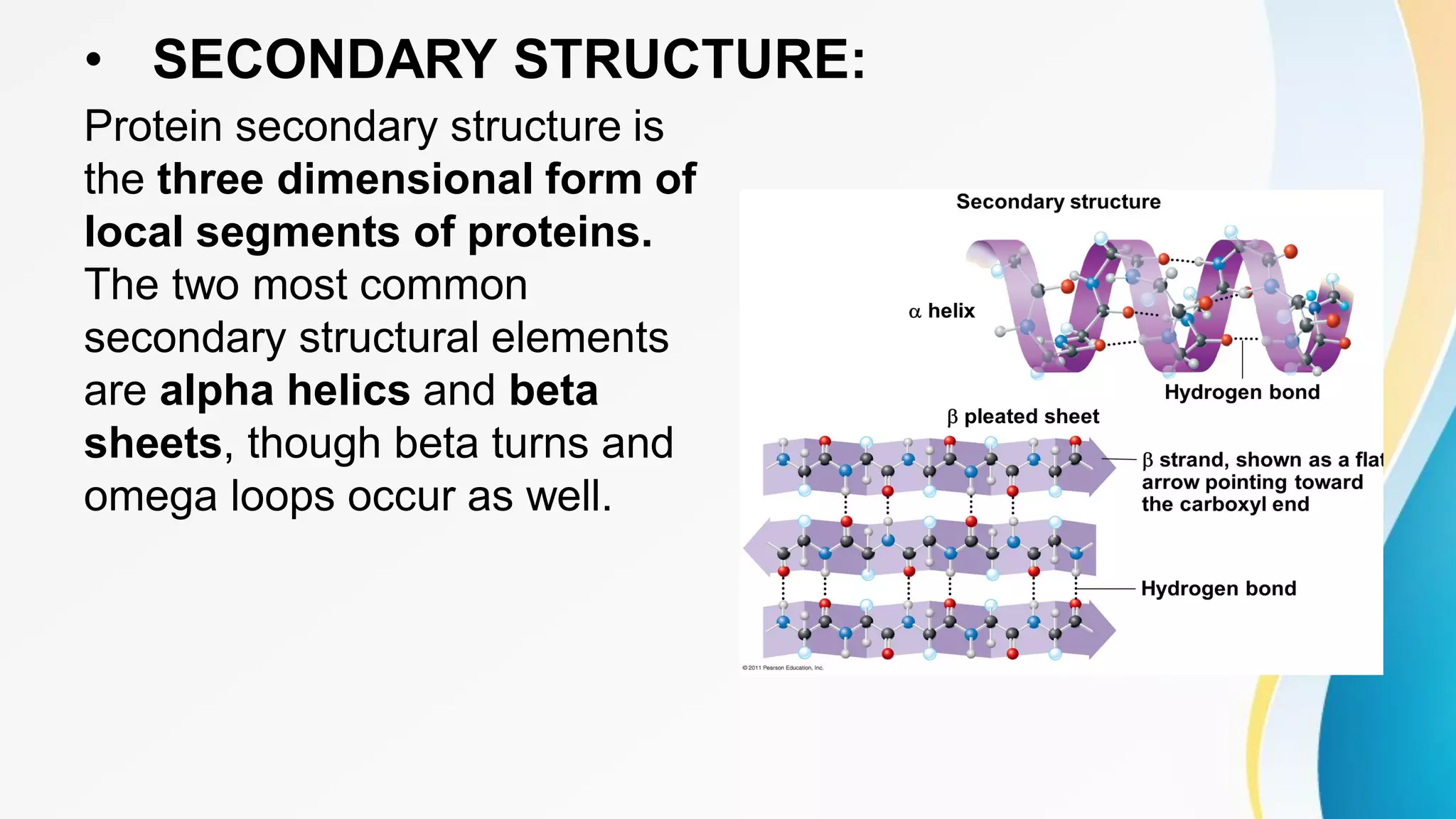
This document discusses protein and peptide drug delivery. It defines proteins and describes their primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. Proteins are classified based on structure and function. Common routes of administration for proteins and peptides include parenteral and non-parenteral routes. Parenteral routes include intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injections. Non-parenteral routes discussed are oral, nasal, buccal, ocular, rectal, and transdermal routes. Barriers to oral delivery of proteins include enzymatic degradation and lack of absorption. Strategies to overcome these barriers include chemical modification of proteins, use of absorption enhancers, and targeting specific transport mechanisms.