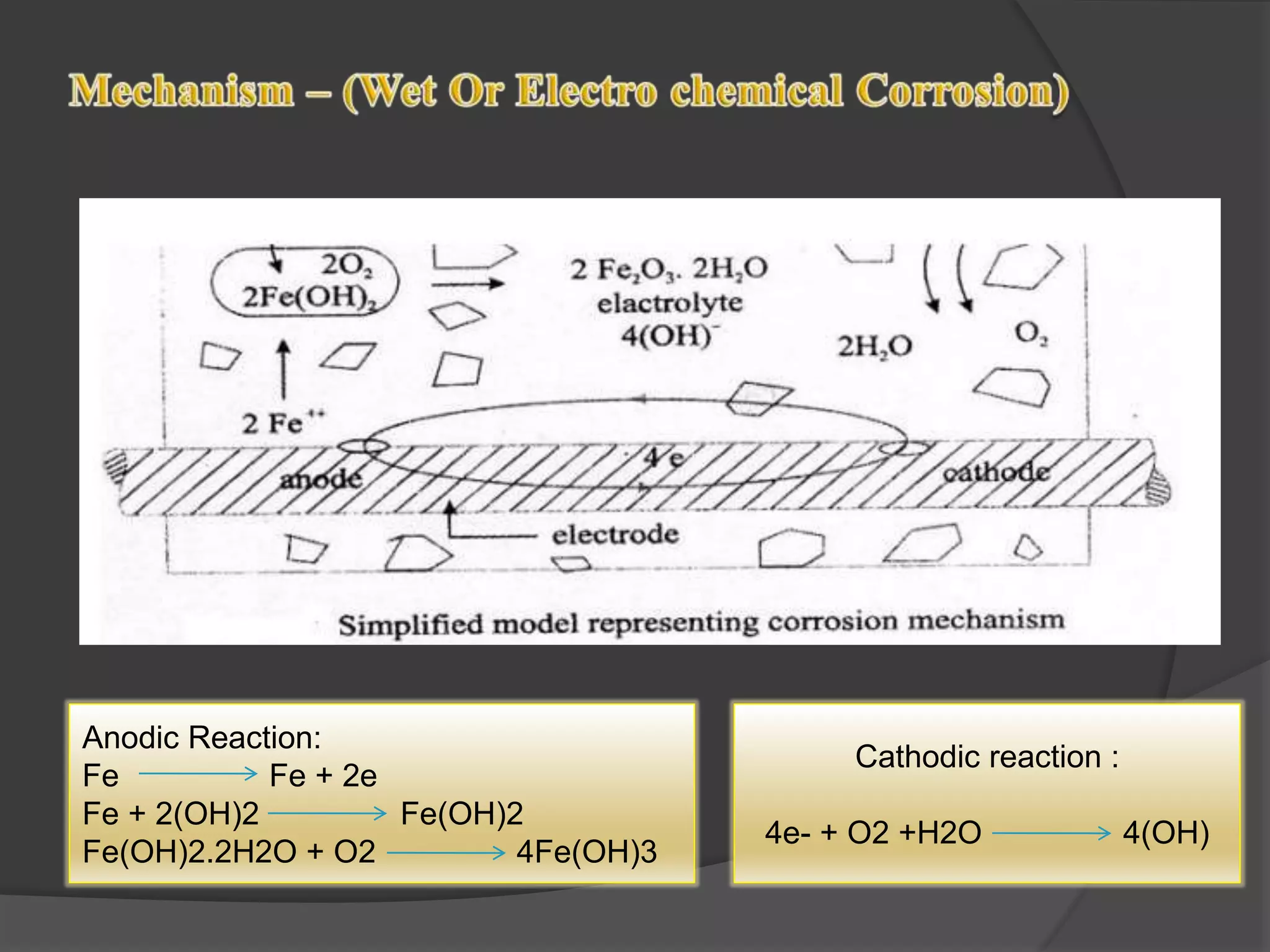
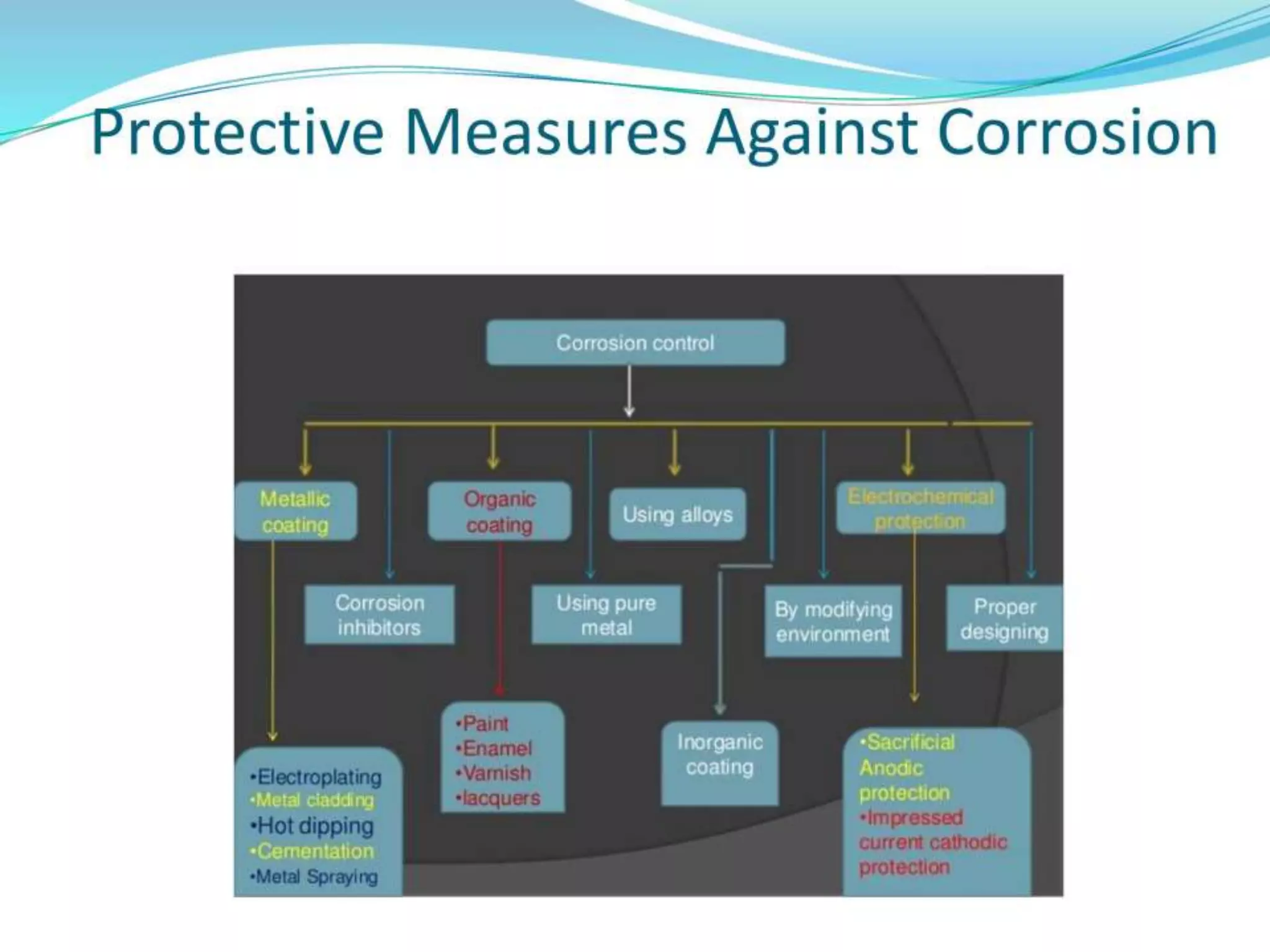
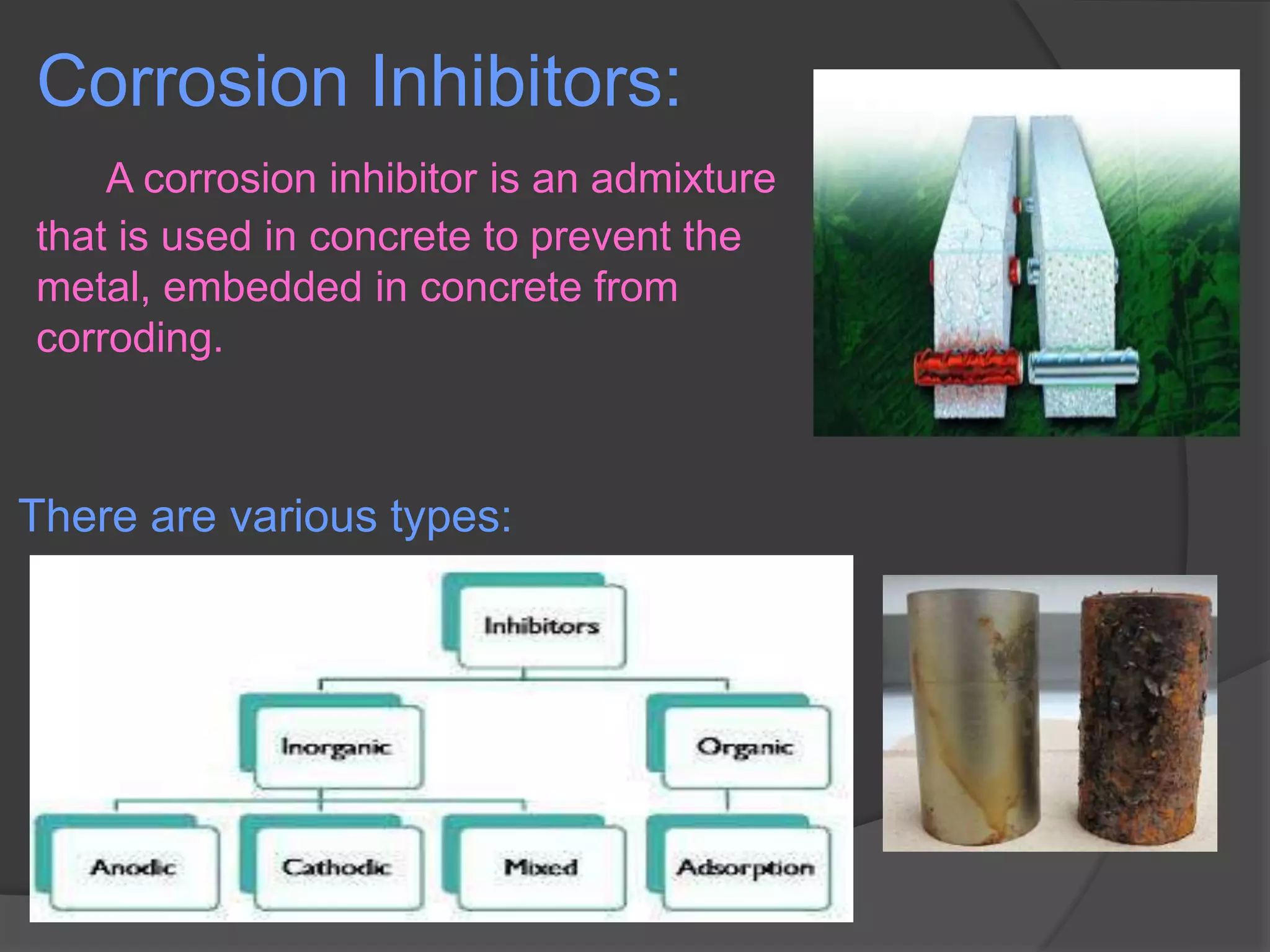
The document discusses corrosion protection techniques such as corrosion inhibitors and concrete coatings. It defines corrosion and corrosion inhibitors, describing the types of inhibitors and how they work to reduce corrosion. Organic inhibitors form protective films while inorganic inhibitors affect anodic or cathodic reactions. Concrete coatings are described as liquids applied to concrete to protect and beautify structures. Epoxy, polyurethane, polyaspartic and acrylic coatings are covered along with their advantages of being economical, durable and low maintenance and disadvantages like potential slipperiness.