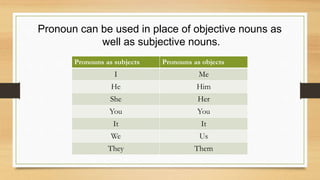
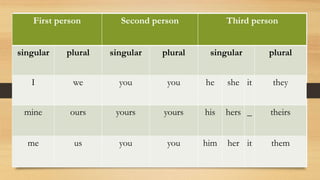
Pronouns are words used instead of nouns that have already been mentioned. Some common pronouns are he, she, it, I, we, they, you. Pronouns can be used as subjects or objects. There are different types of pronouns including personal pronouns that refer to the speaker, person spoken to, or person spoken about. Other pronoun types are possessive, reflexive, emphatic, interrogative, demonstrative, relative, distributive, reciprocal, and indefinite pronouns. An example is provided to illustrate the different pronoun types.