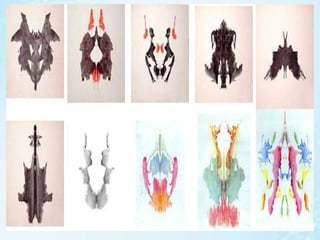
The document outlines various projective personality tests, detailing their history, methods of administration, interpretation, and issues related to reliability and validity. Key tests discussed include the Rorschach inkblot test, Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), House-Tree-Person test, and several others designed to elicit subconscious responses. While these tests can reveal hidden emotions and motivations, they require skilled administration and are subject to interpretation bias and other limitations.