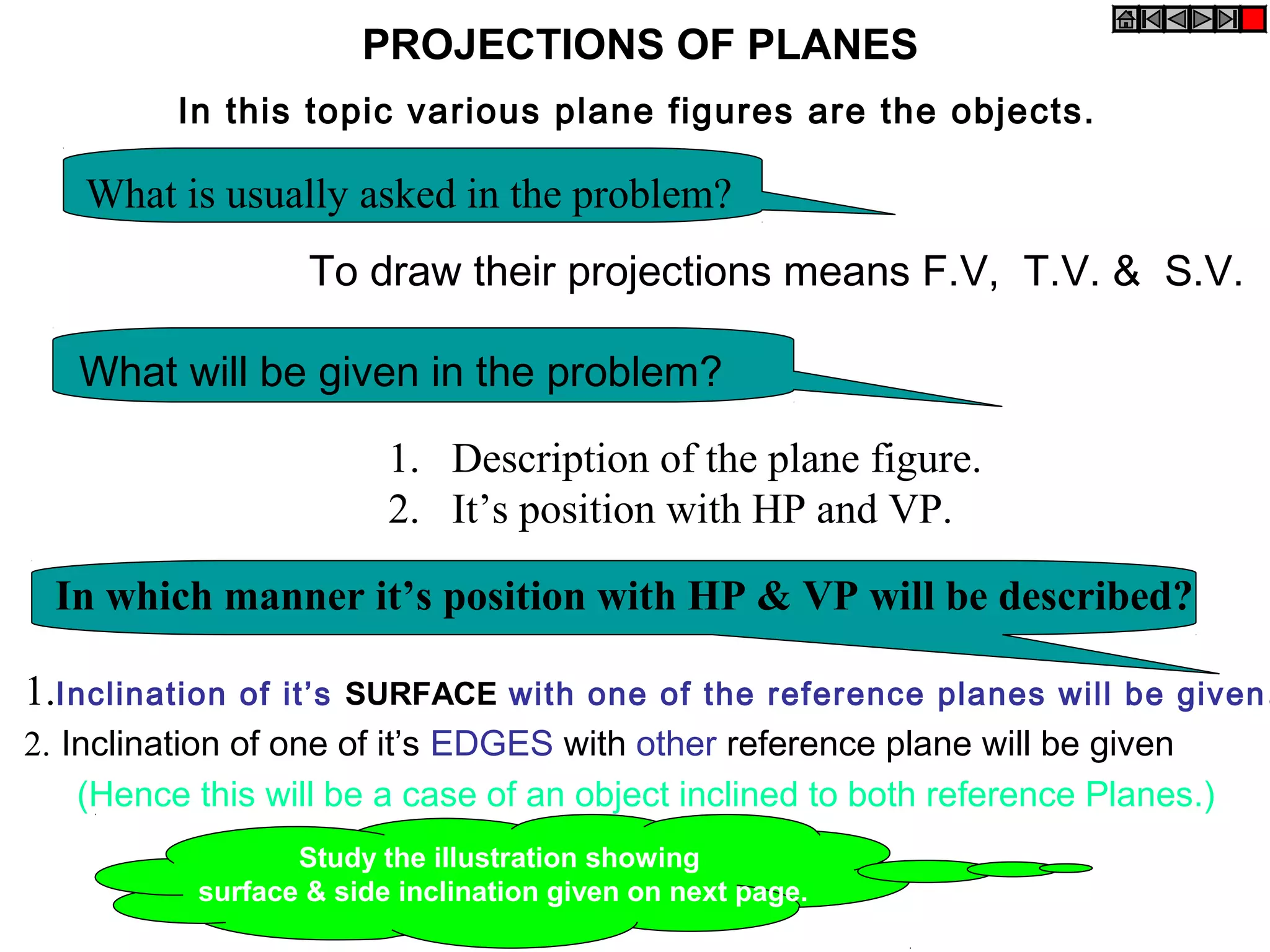
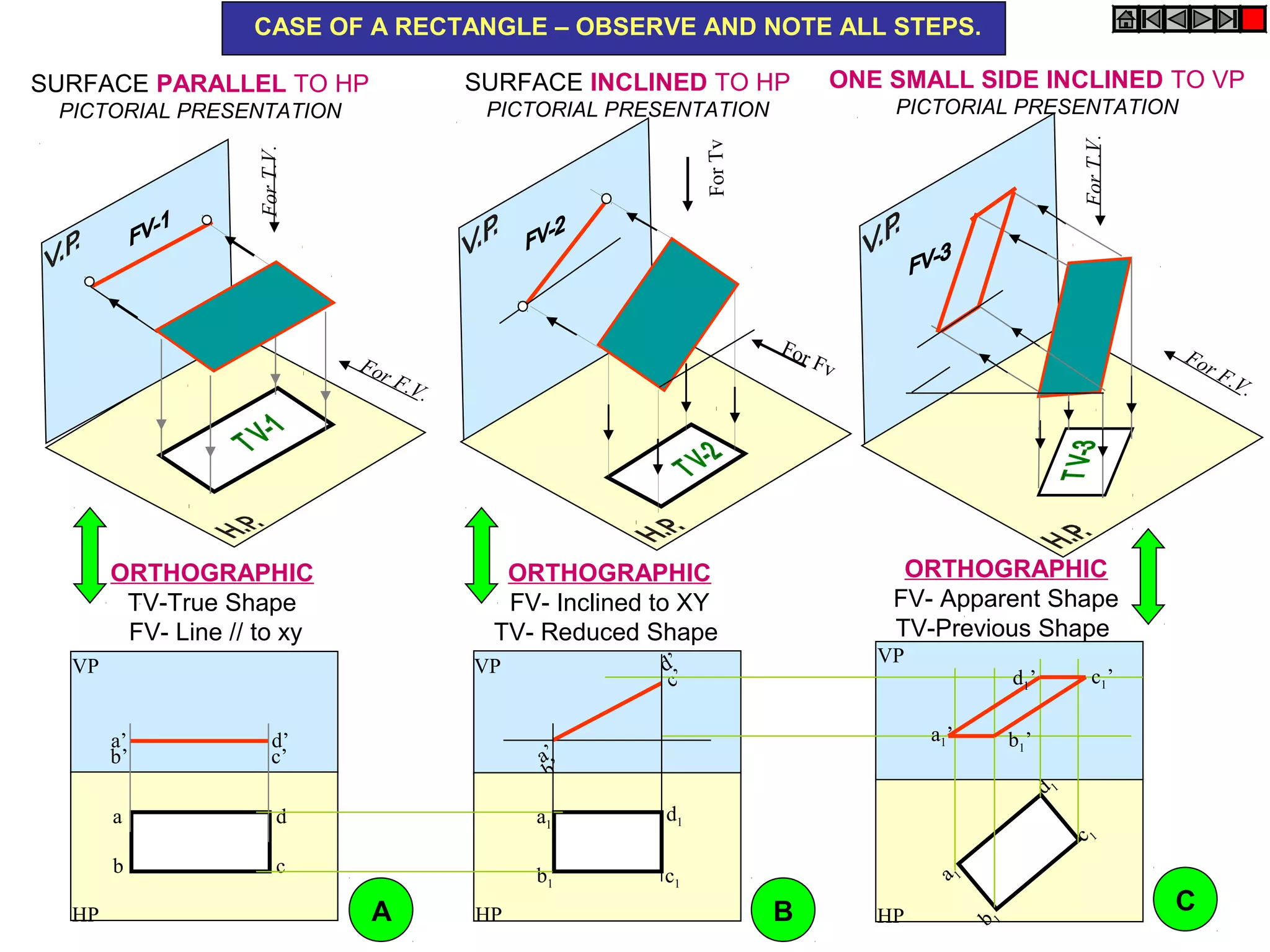
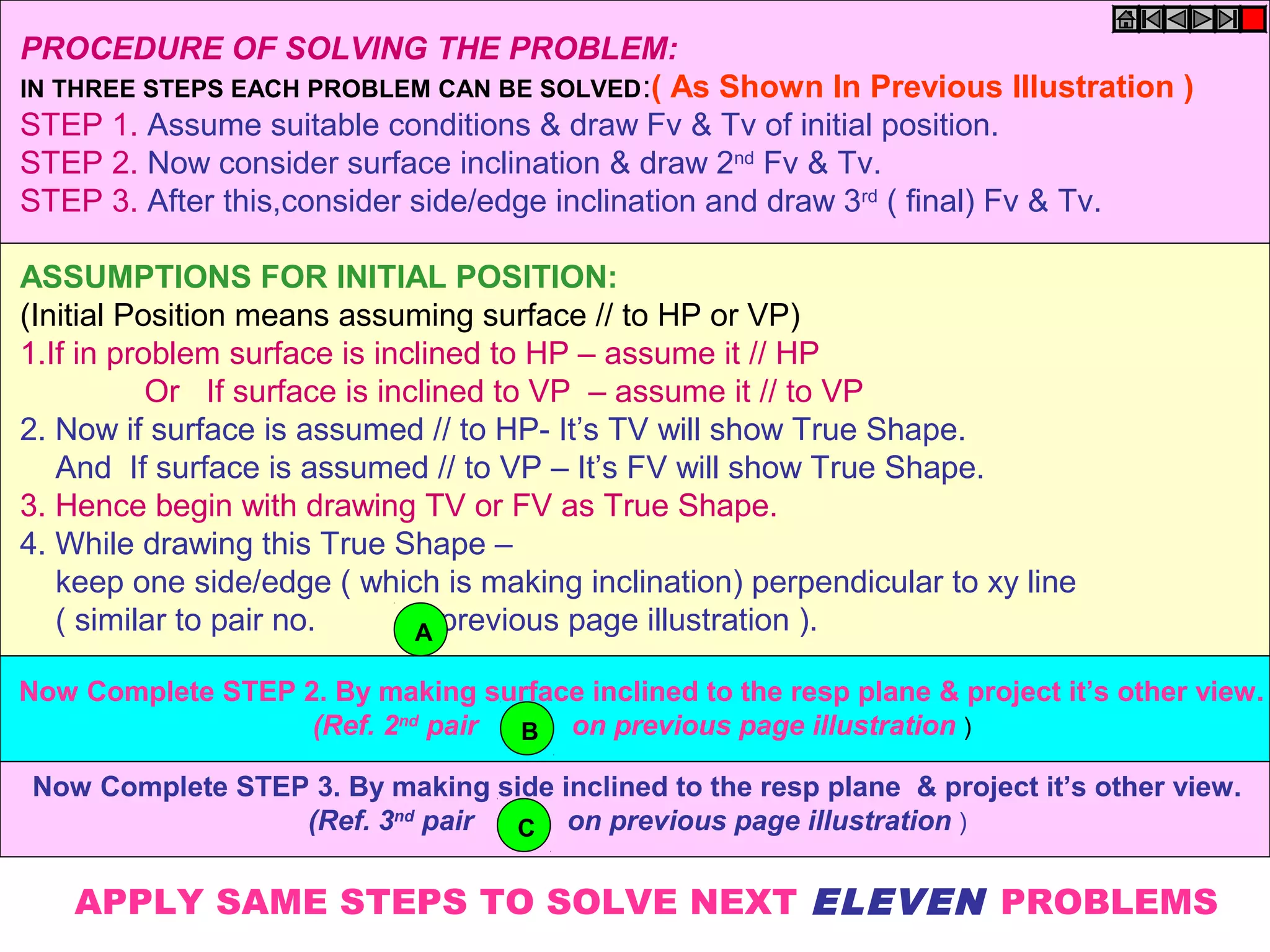
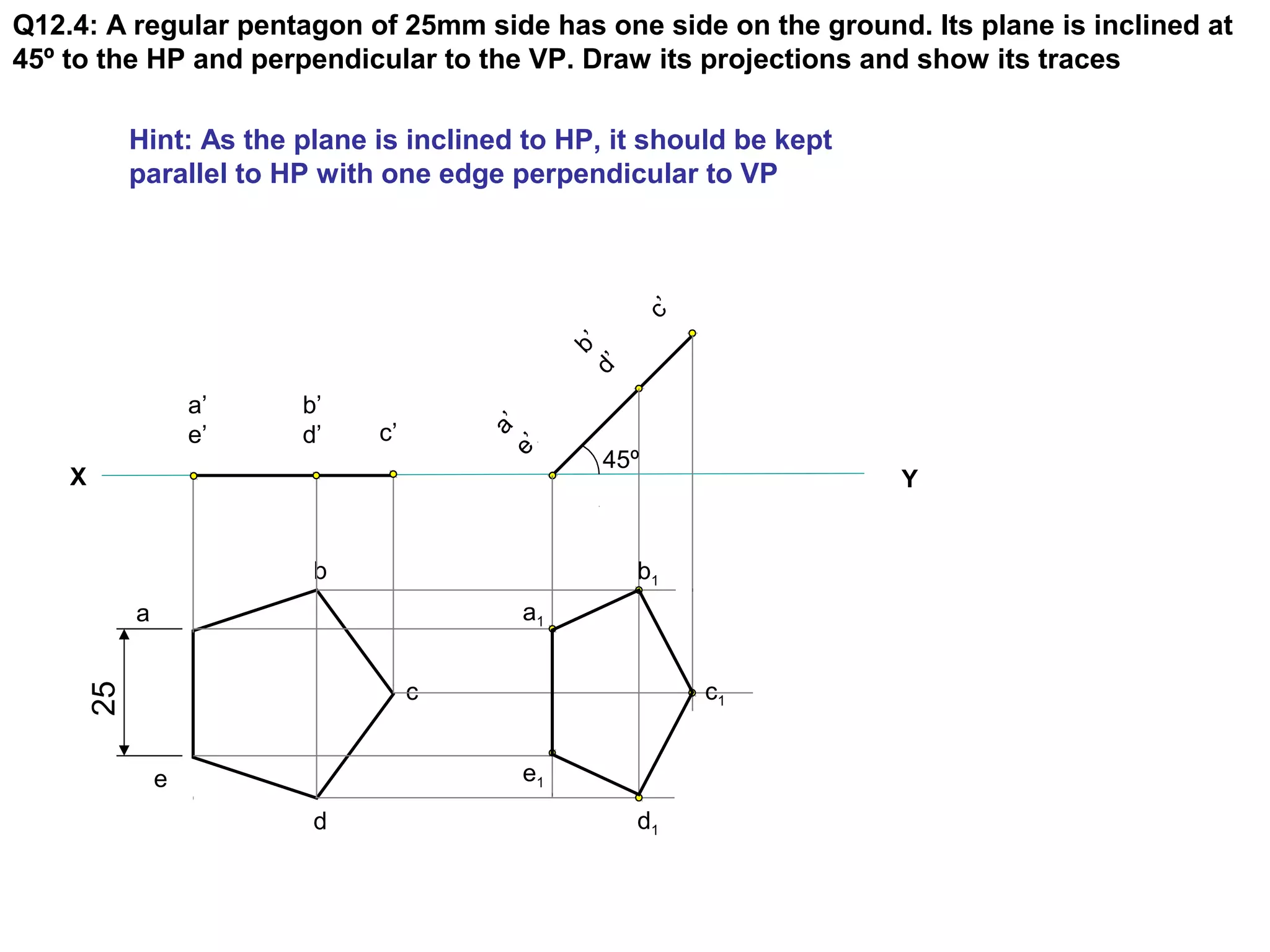
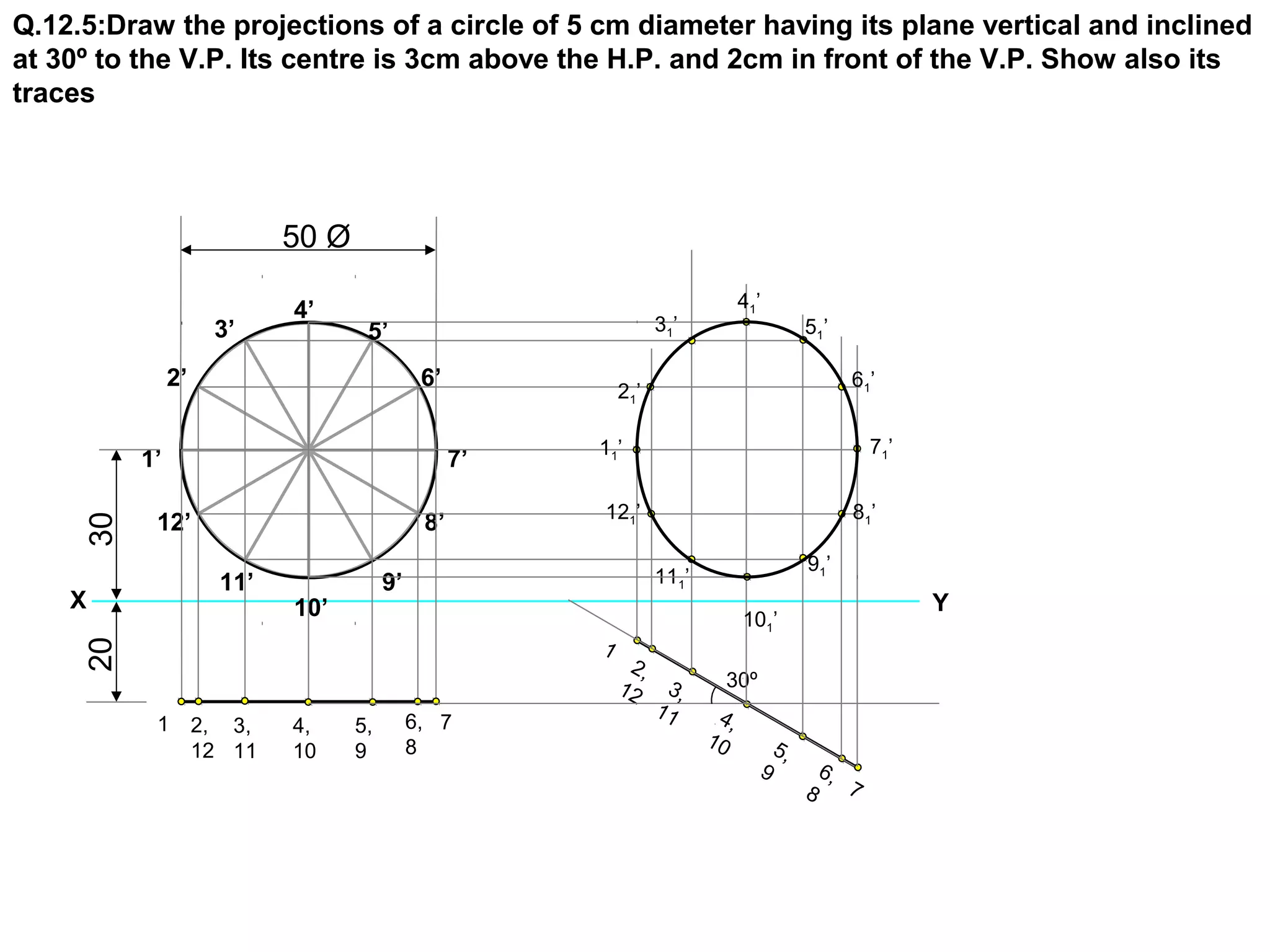
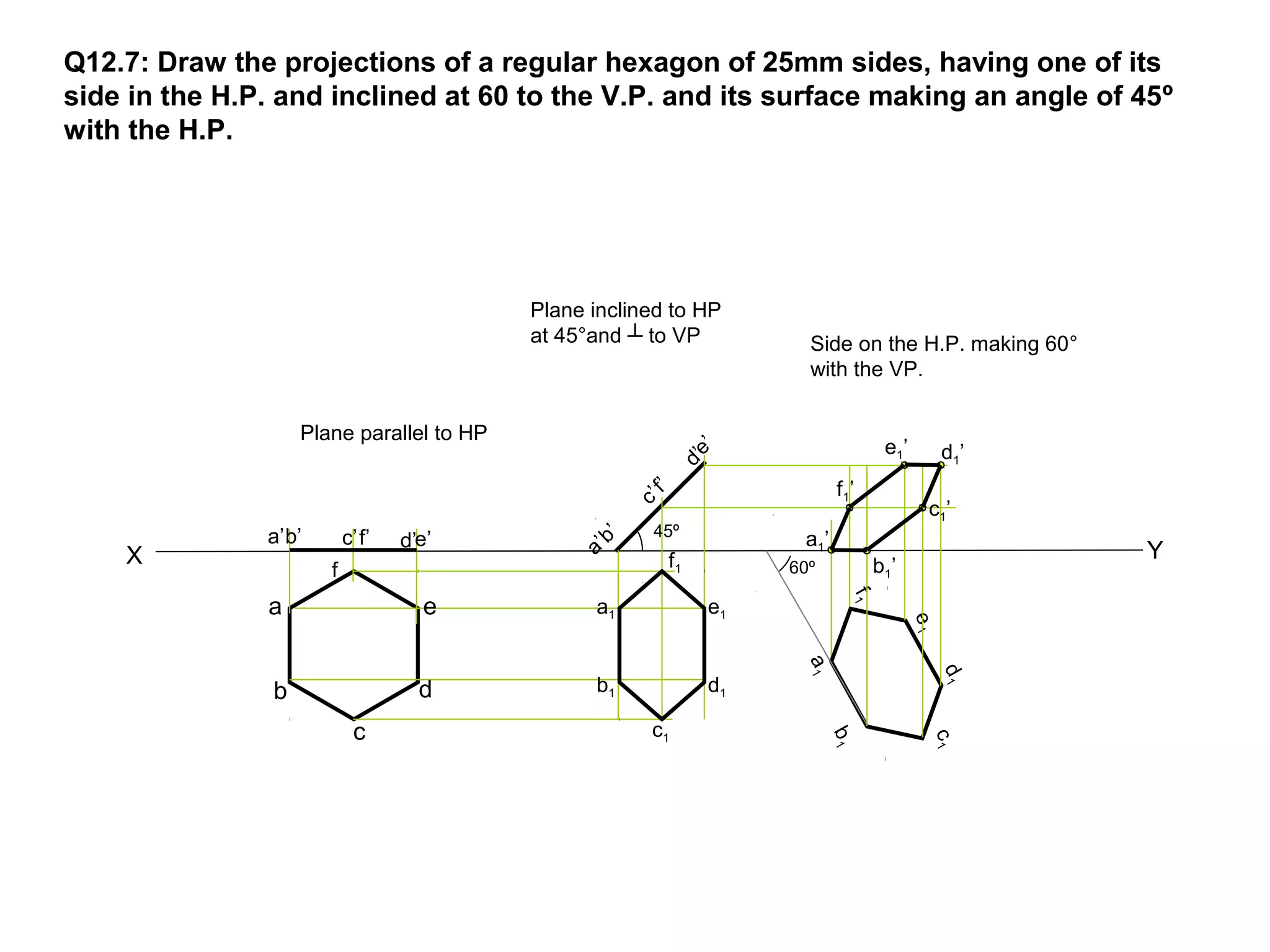
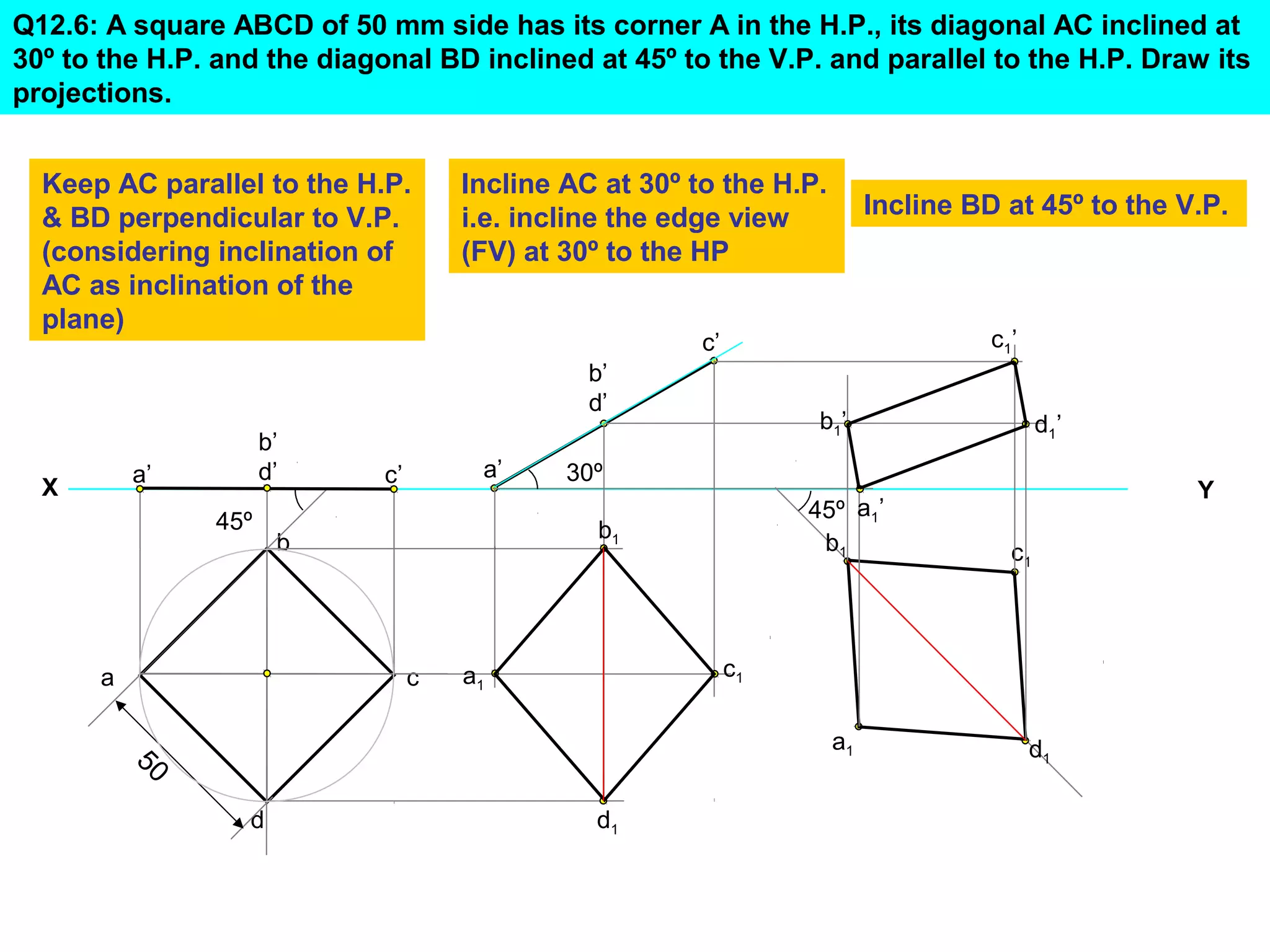
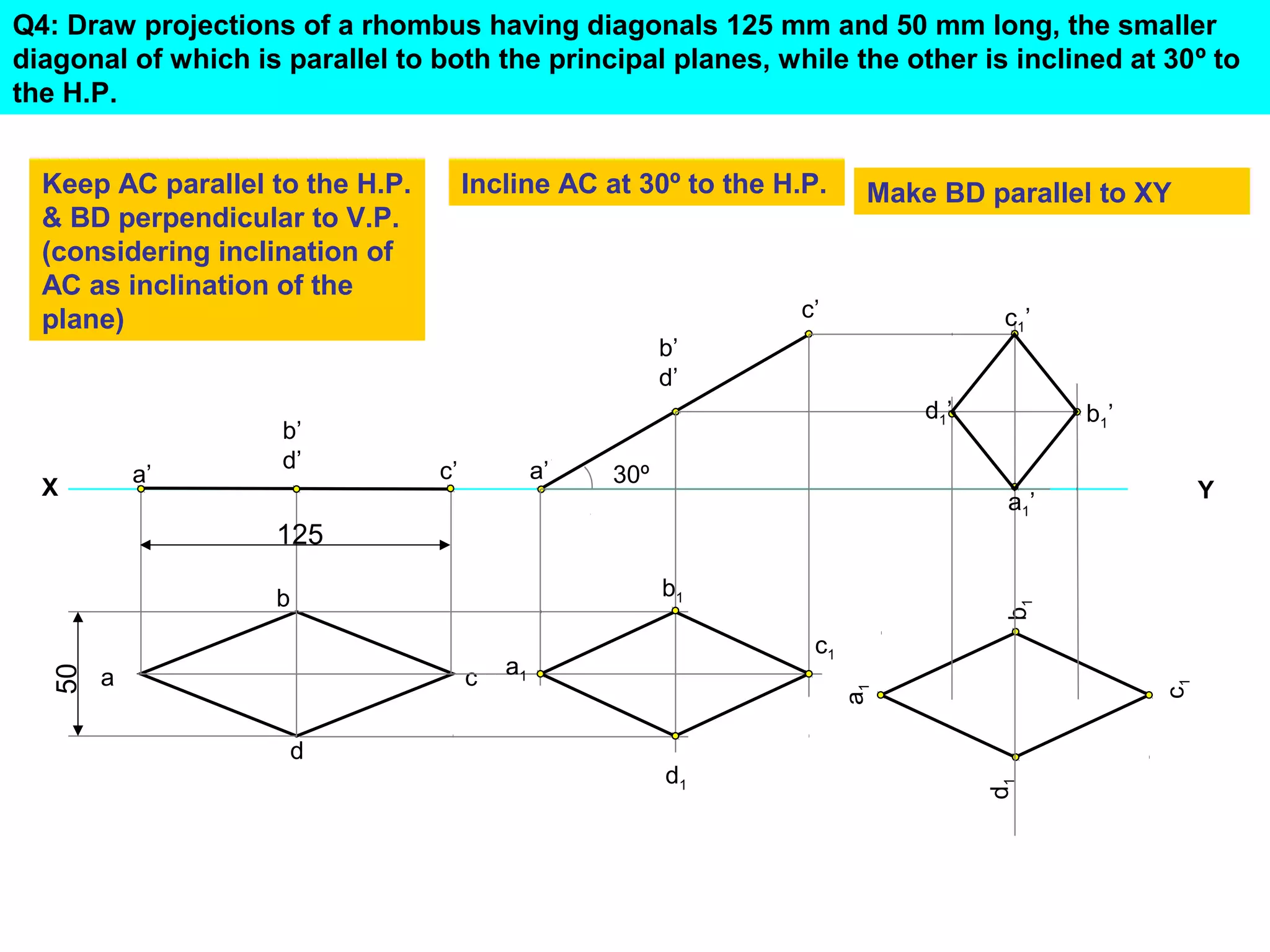
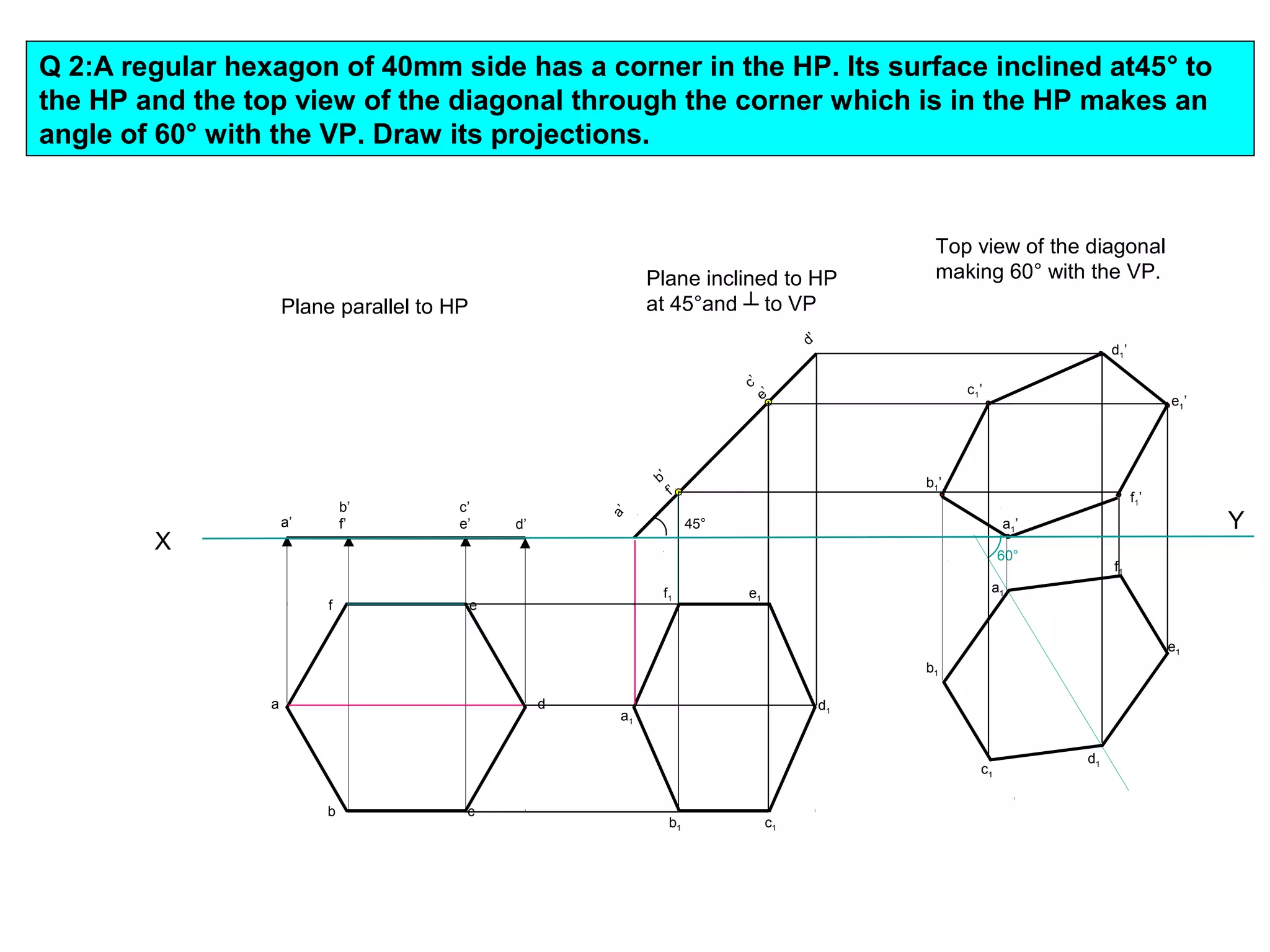
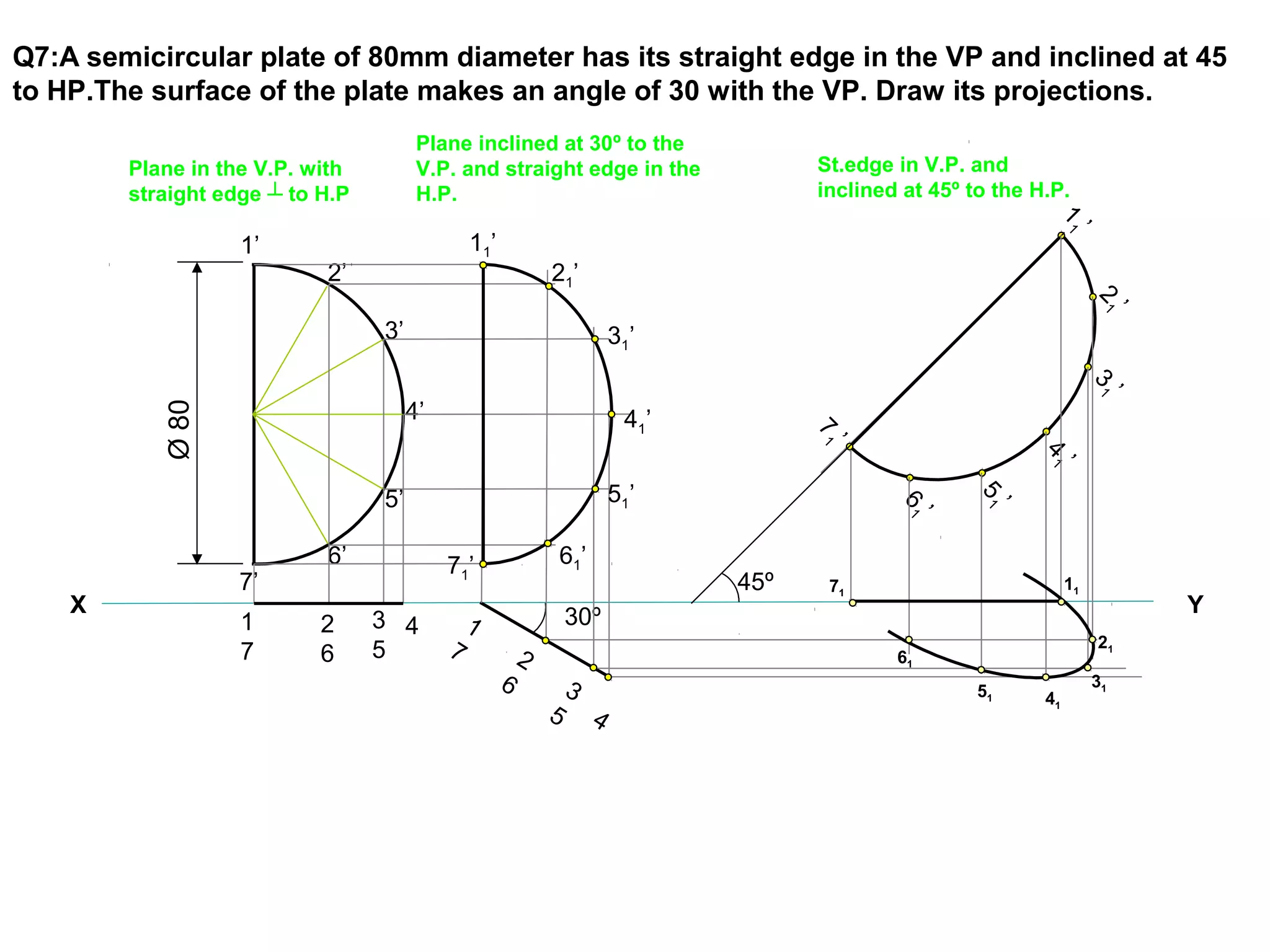
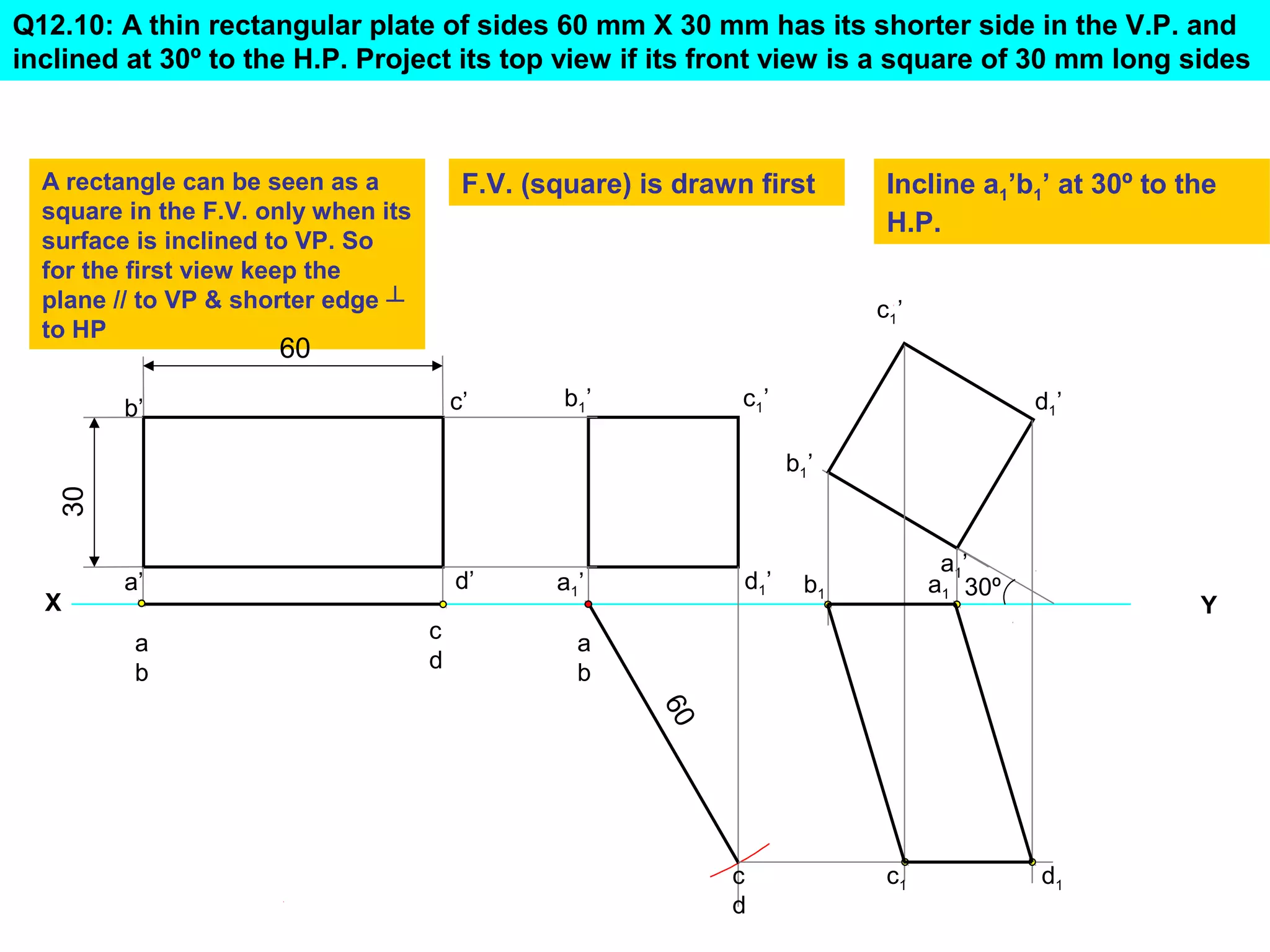
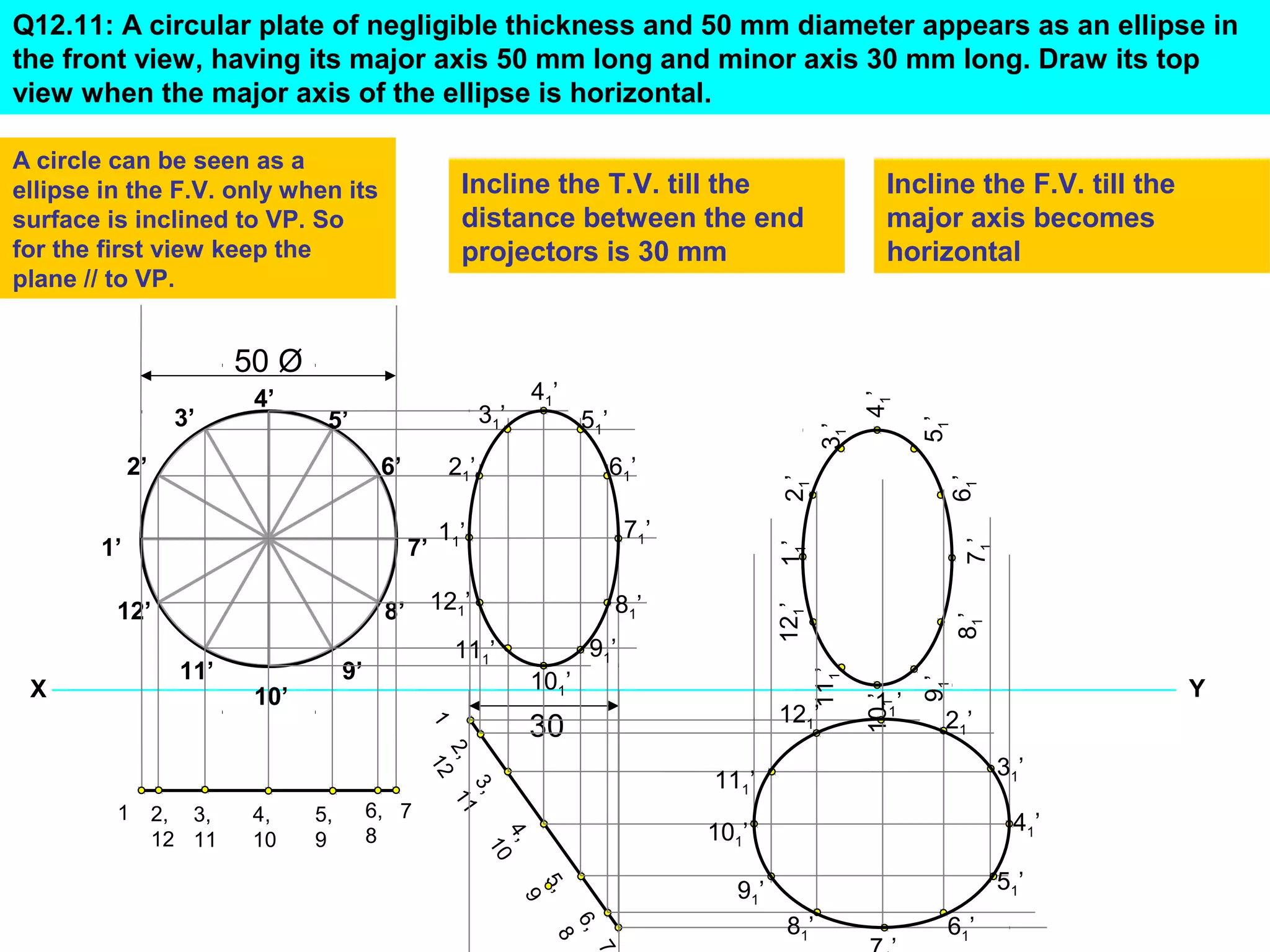
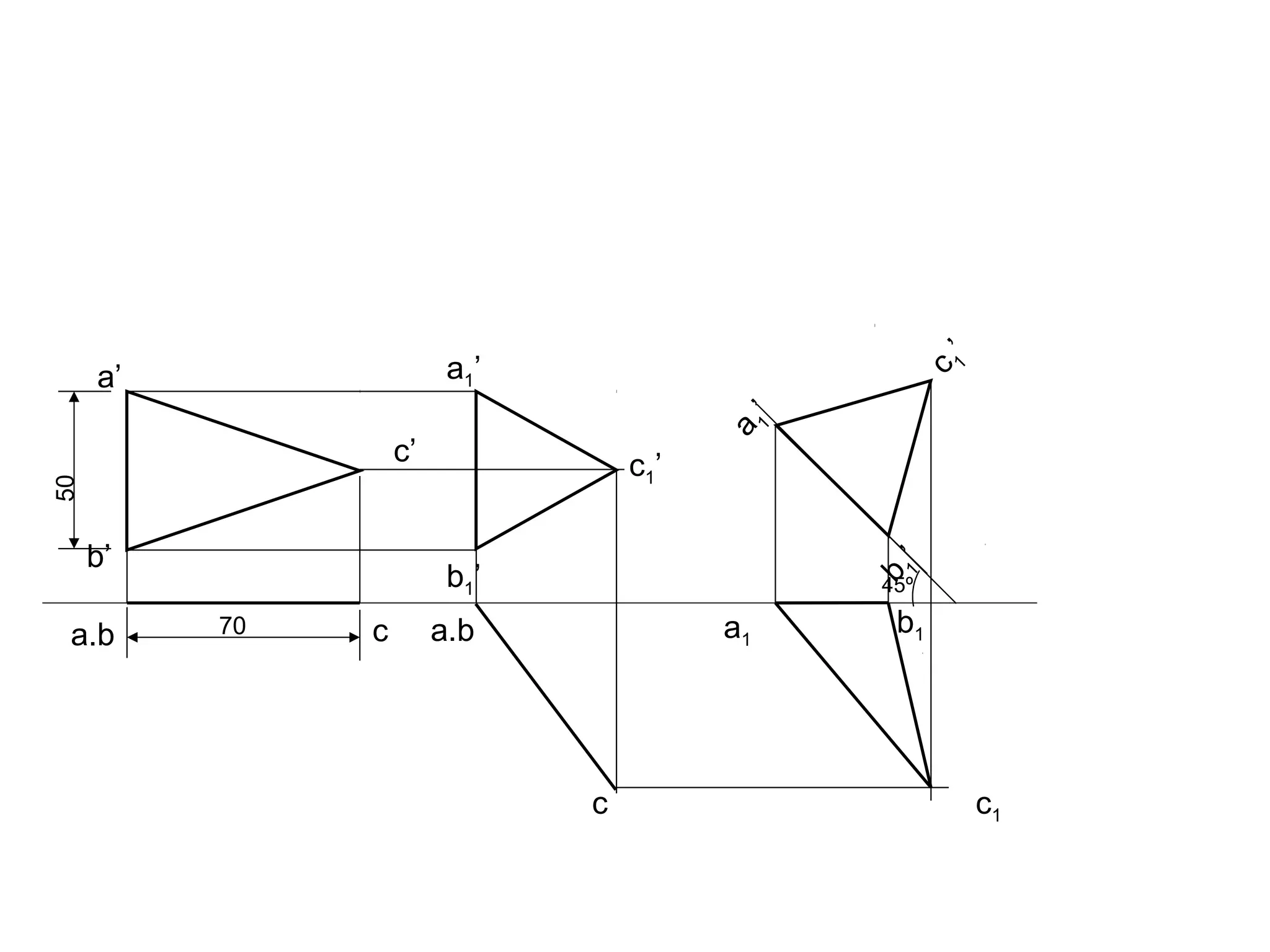
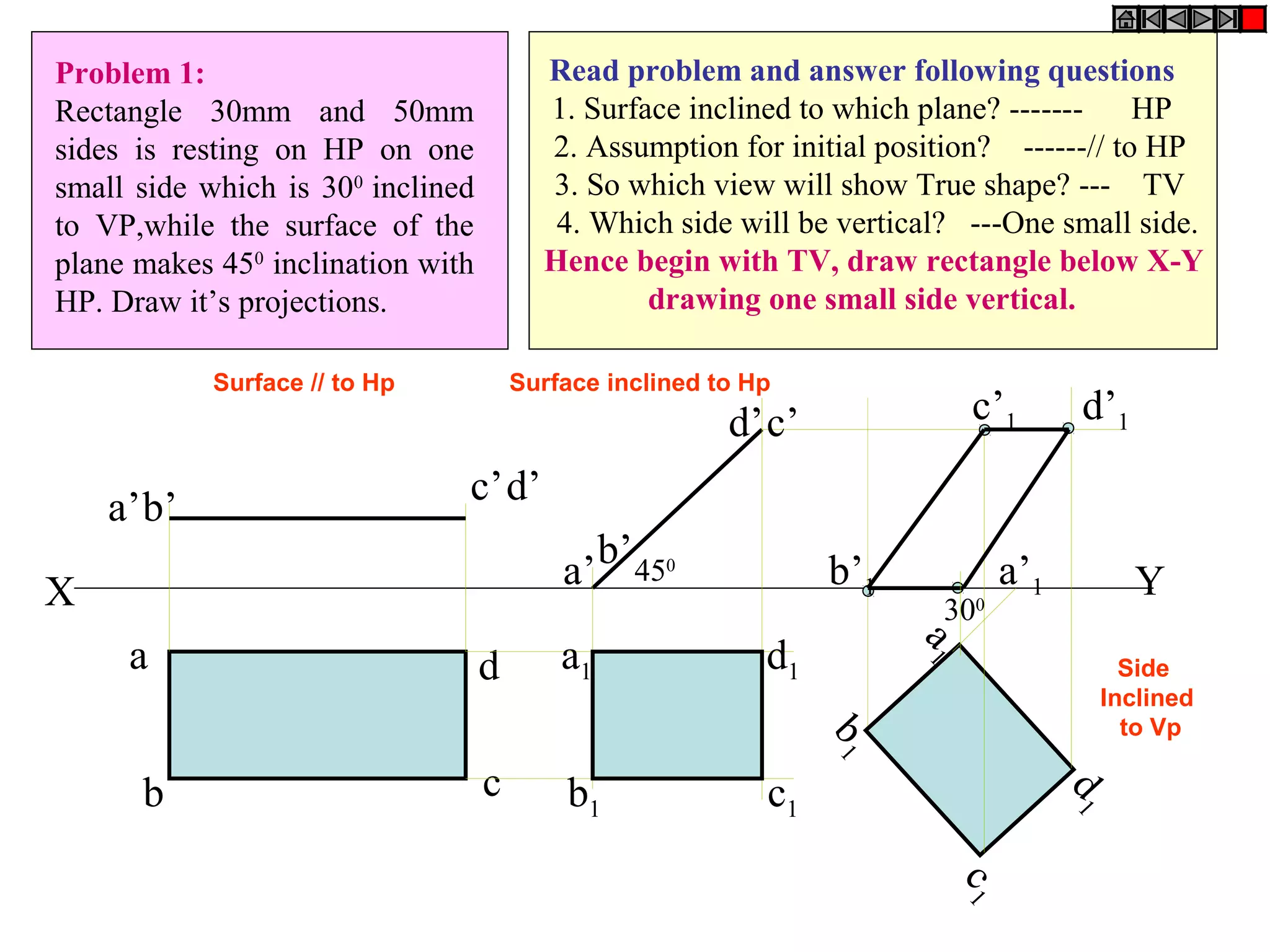
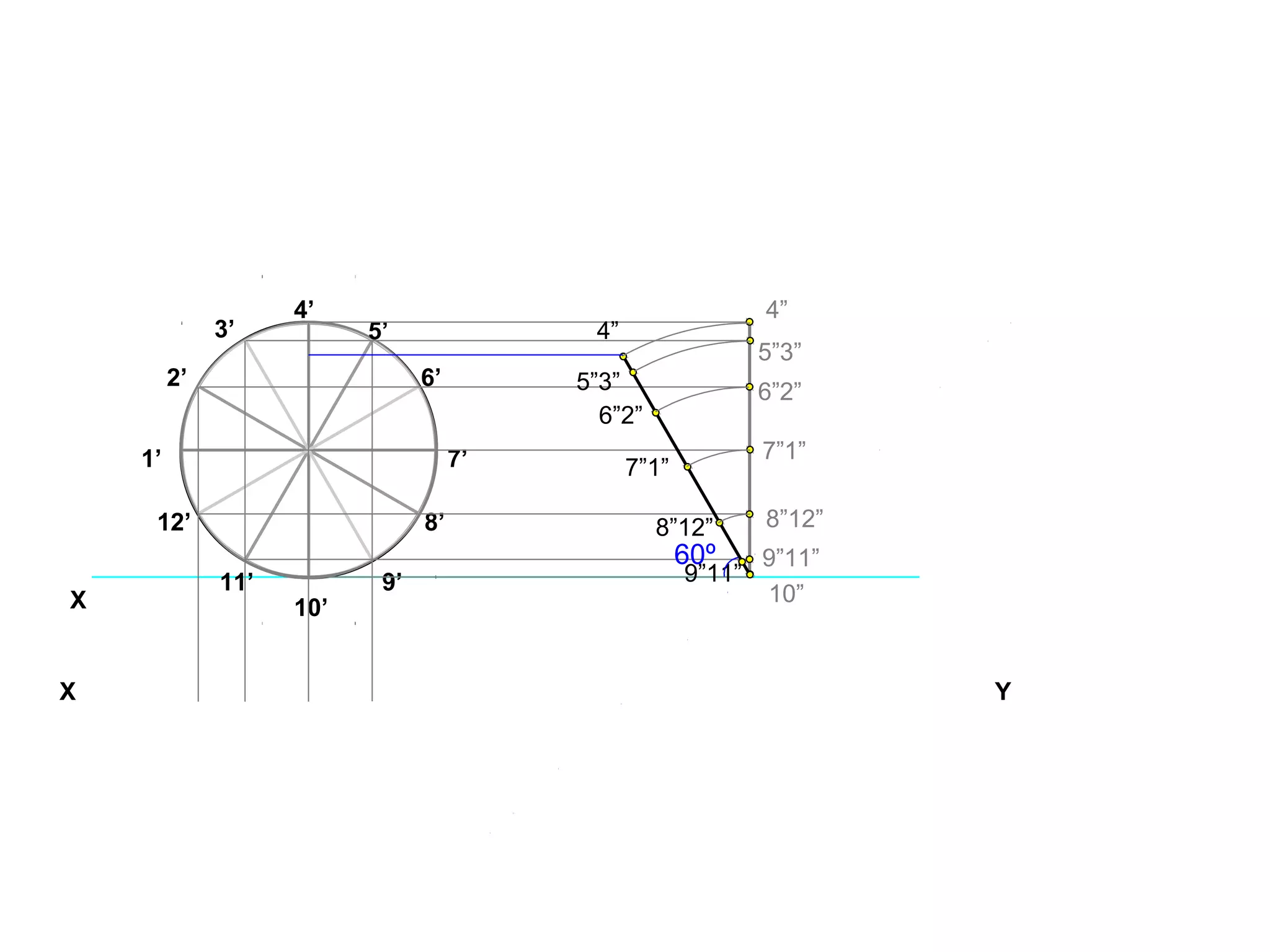
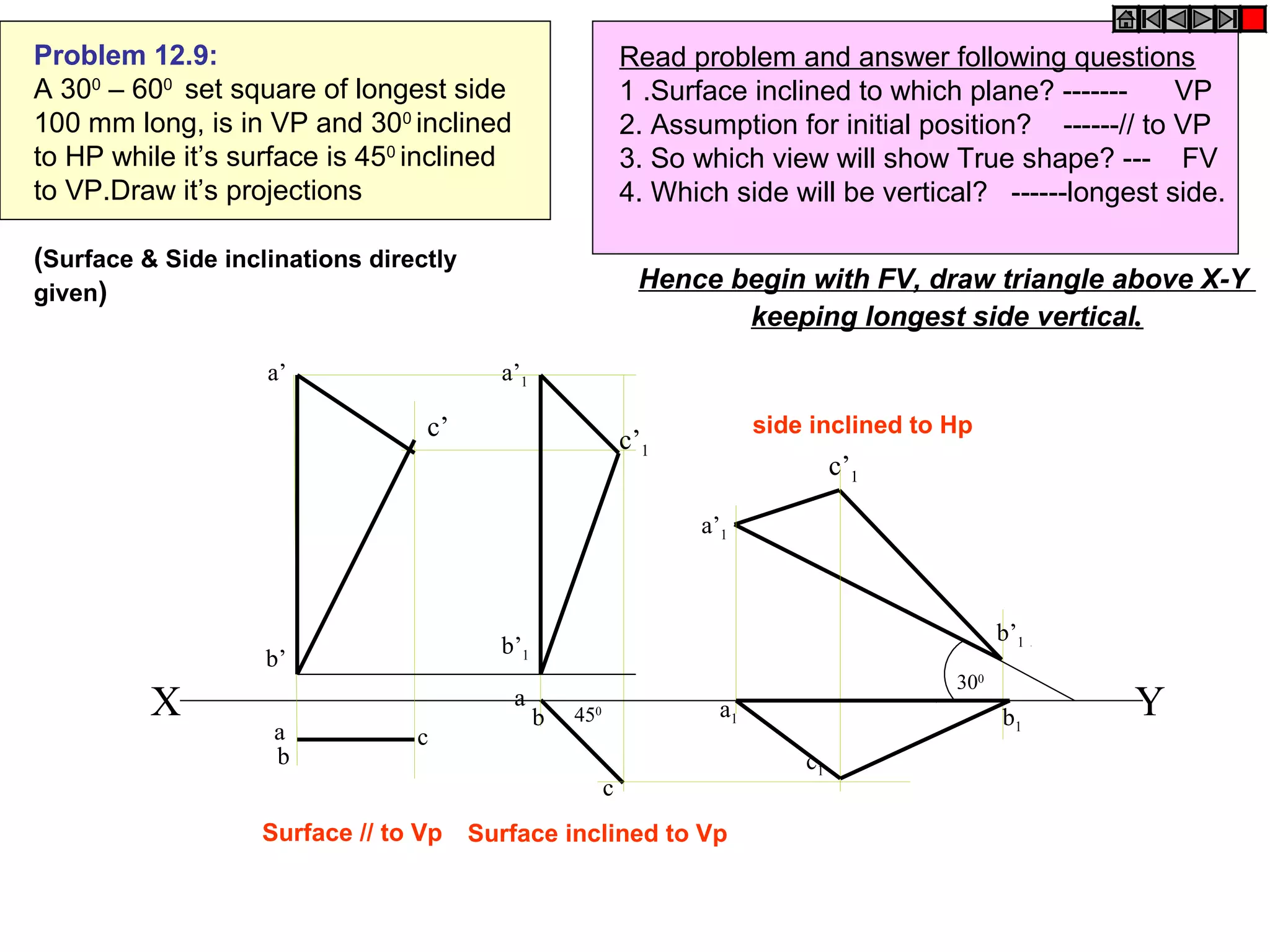
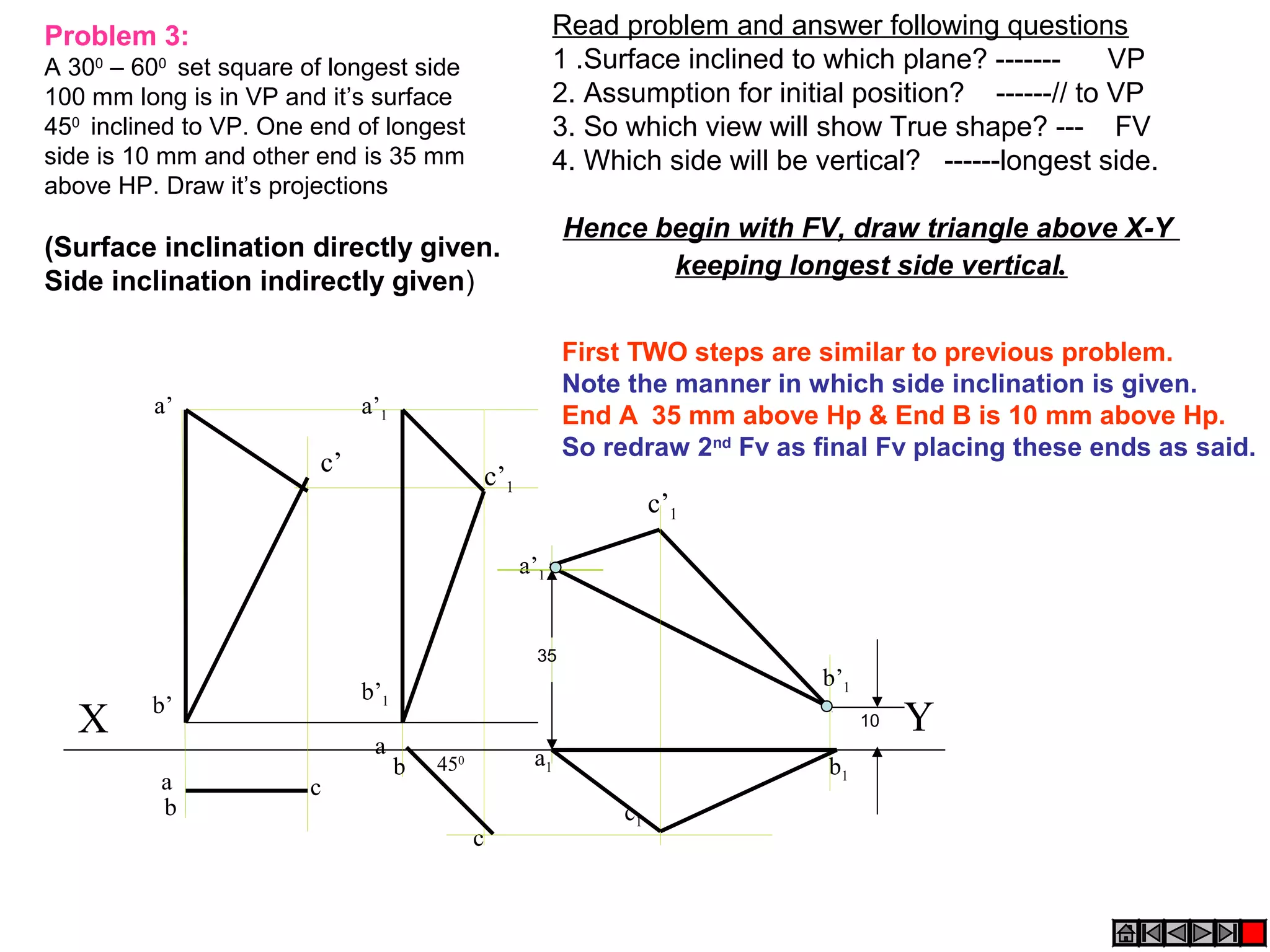
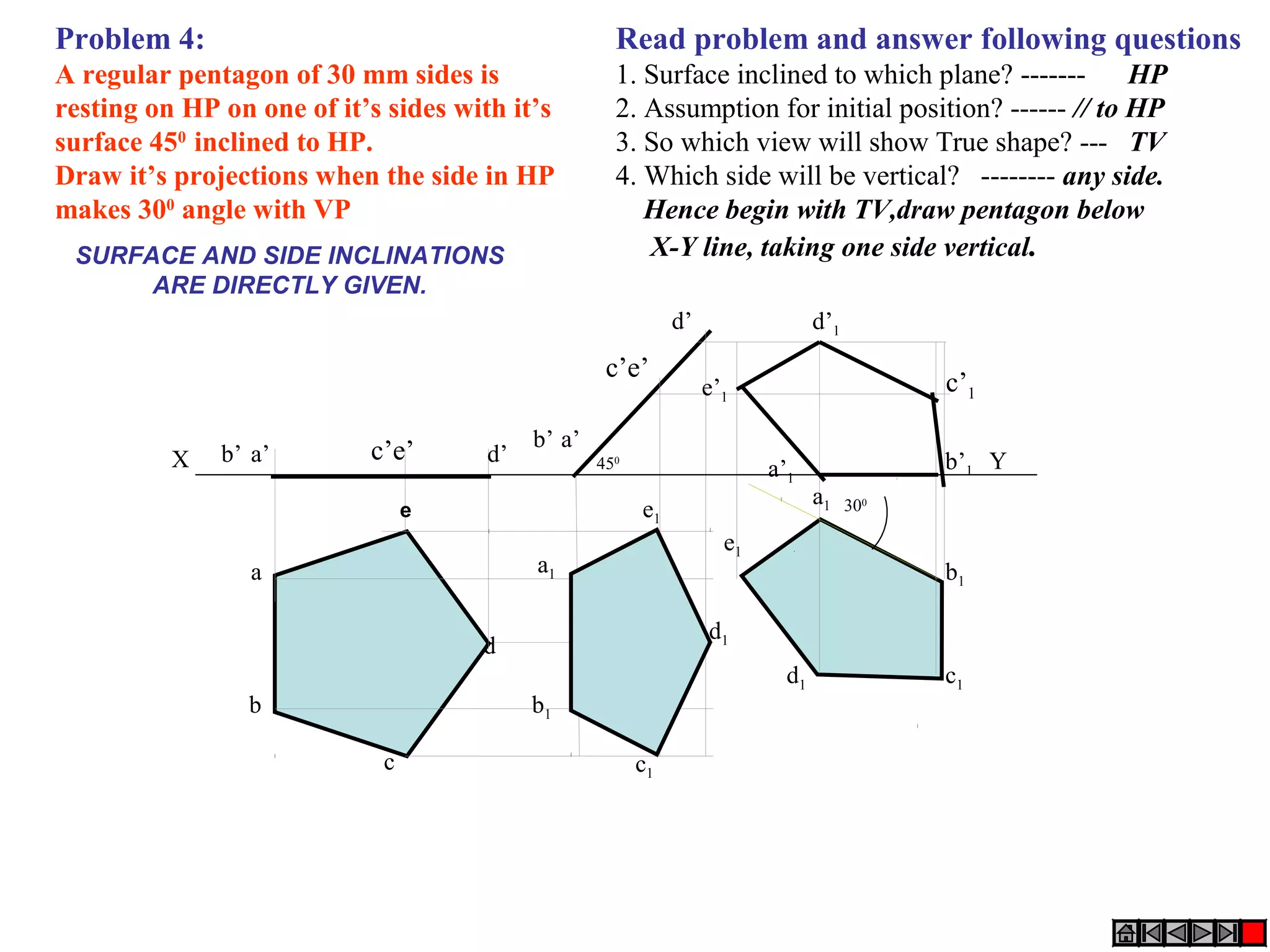
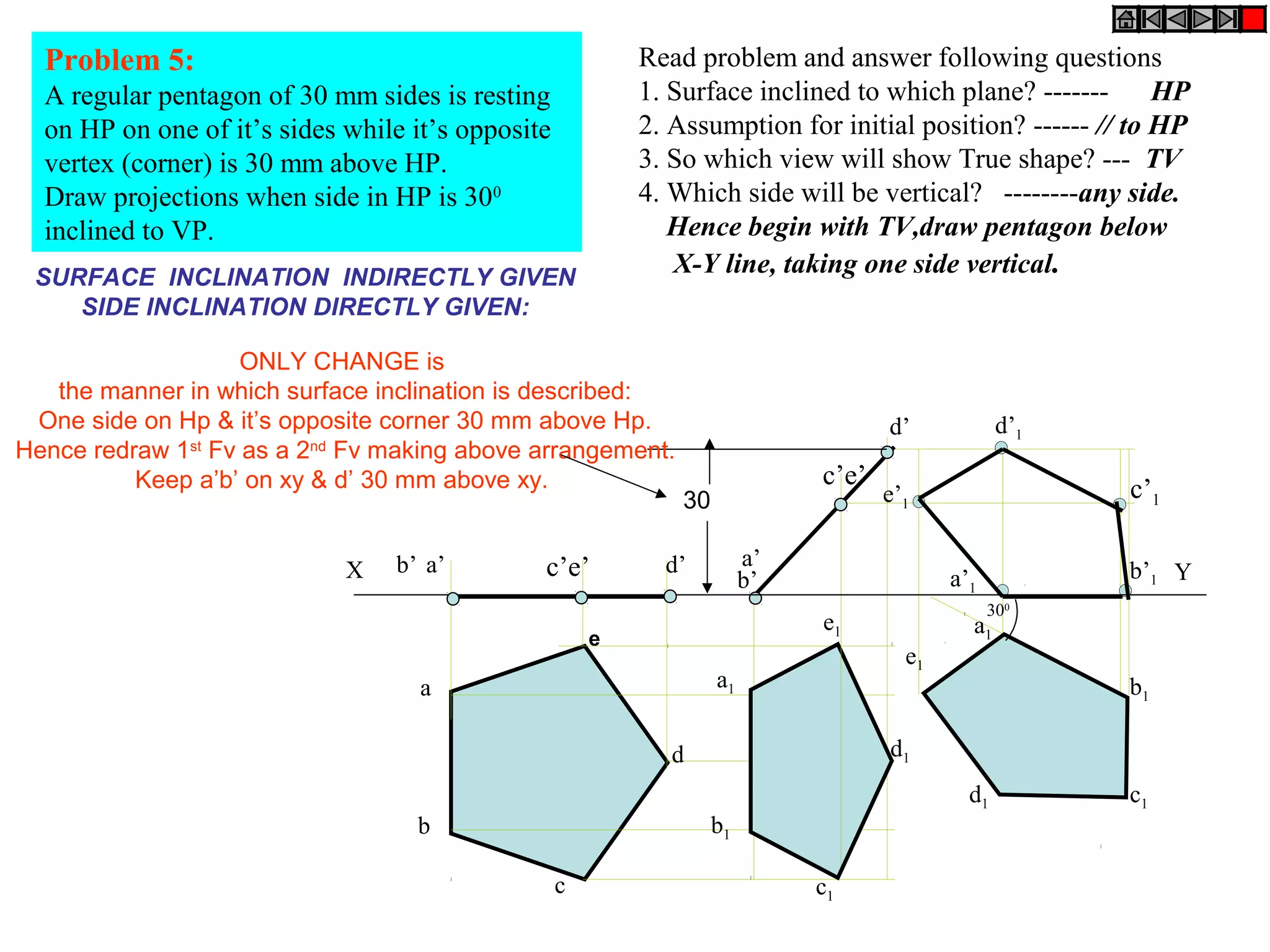
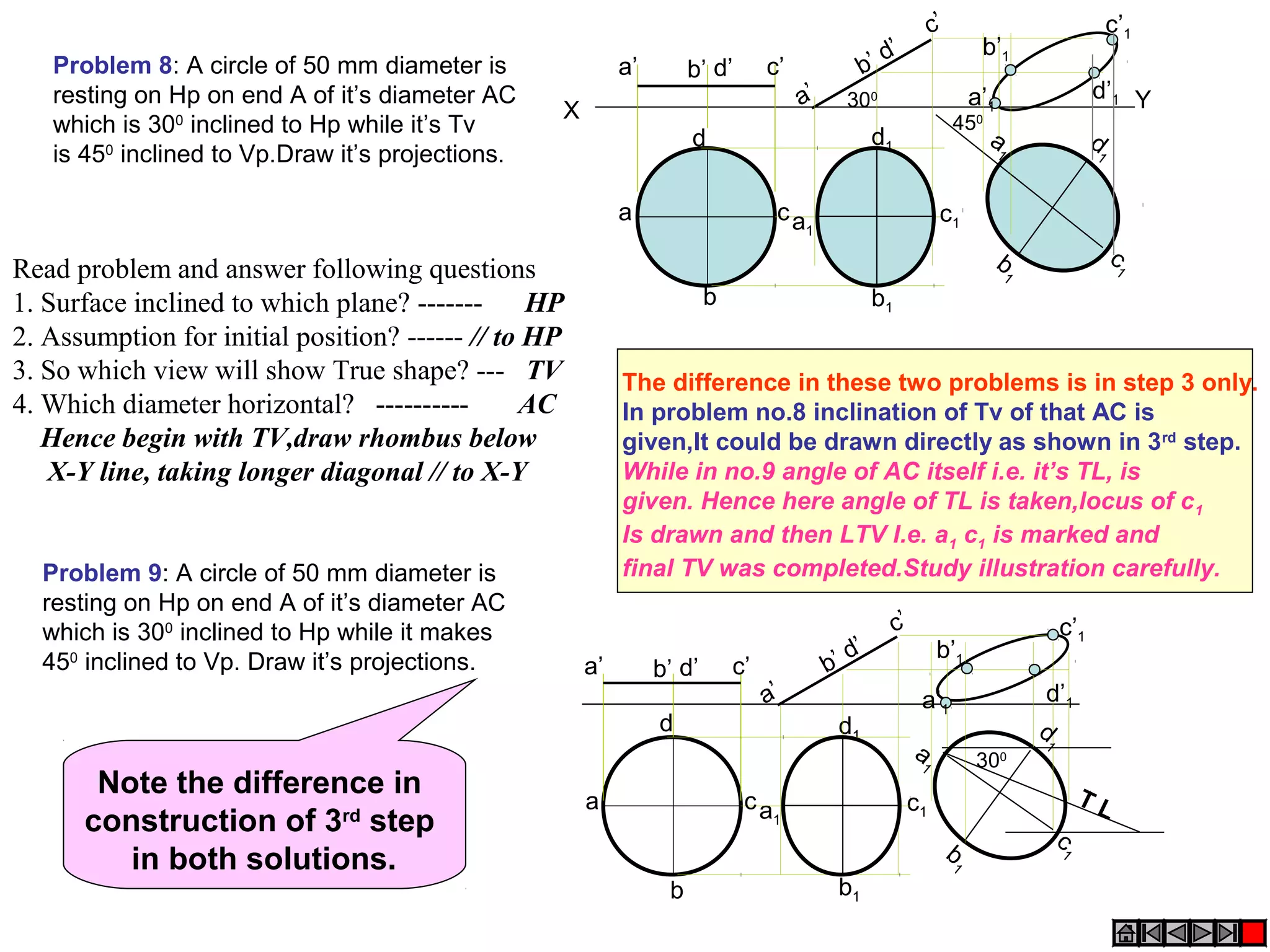
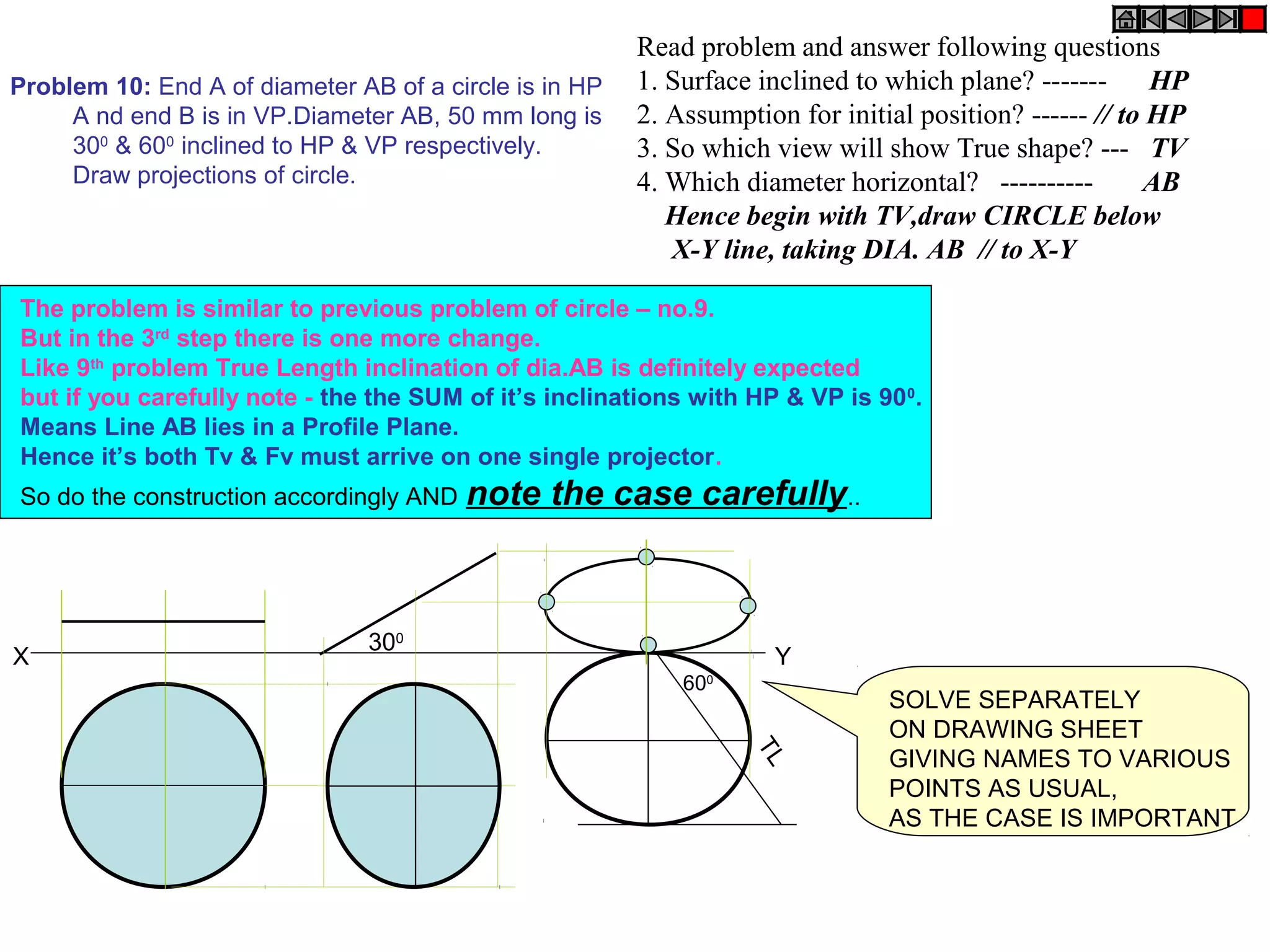
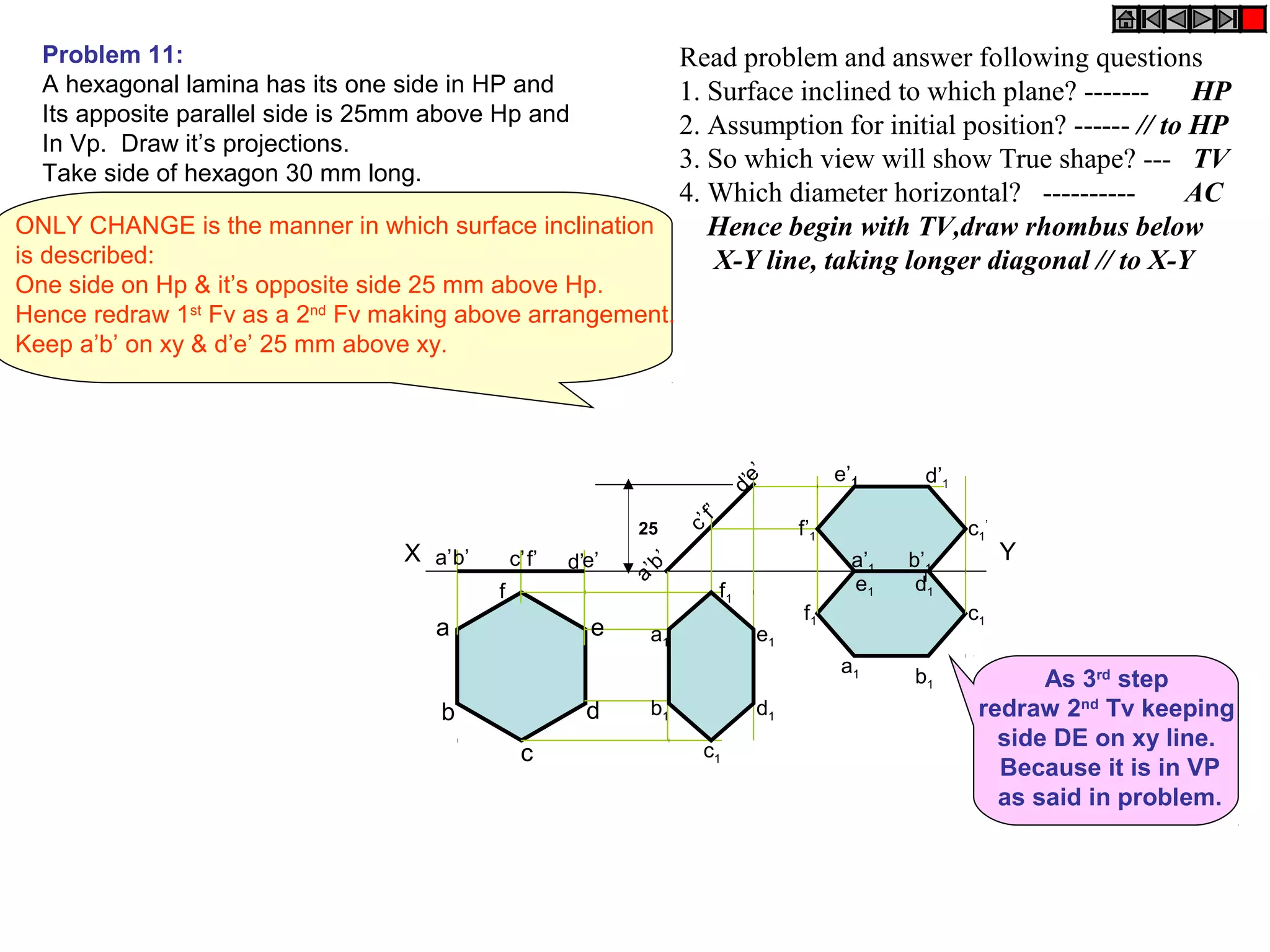
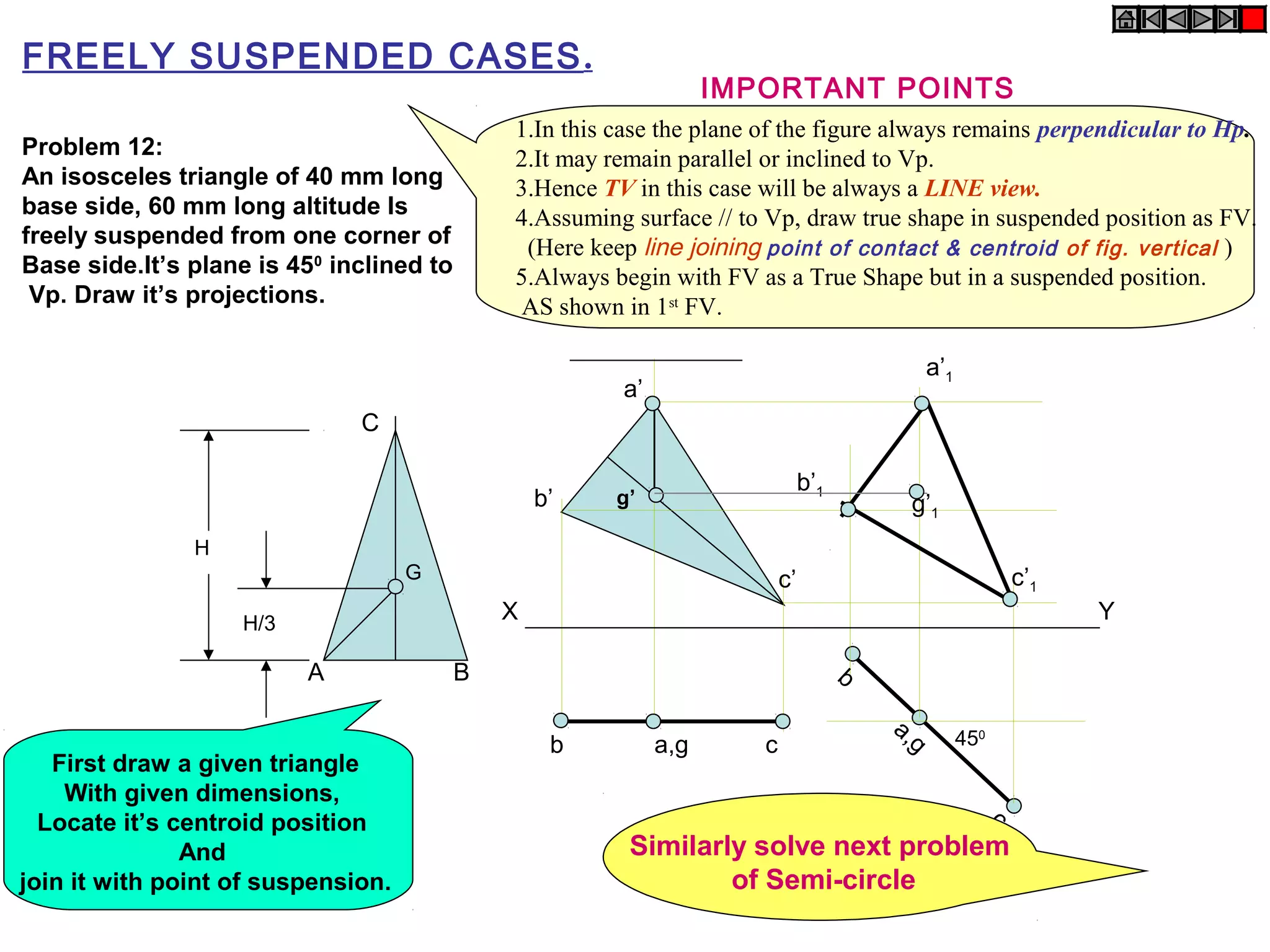
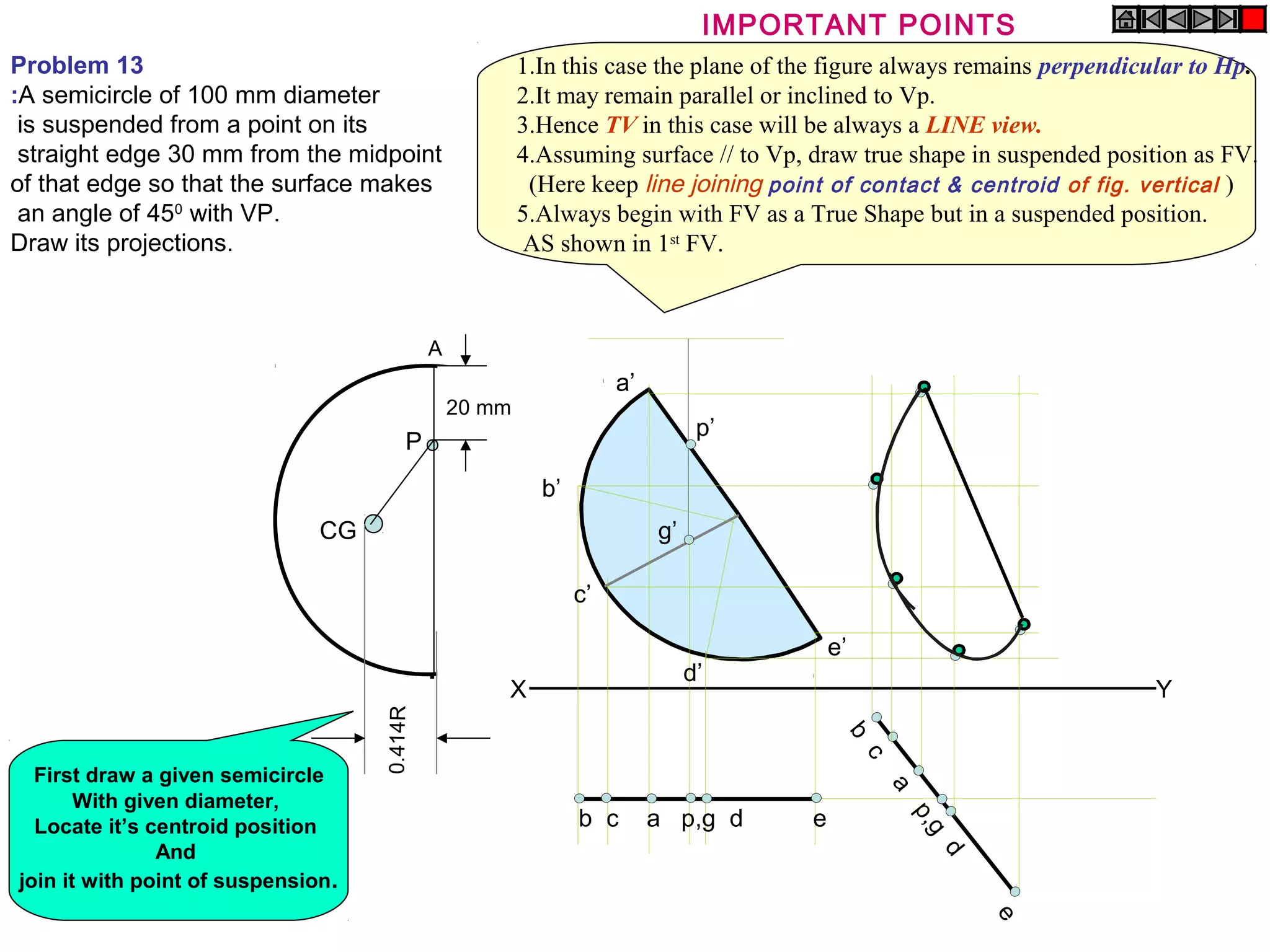
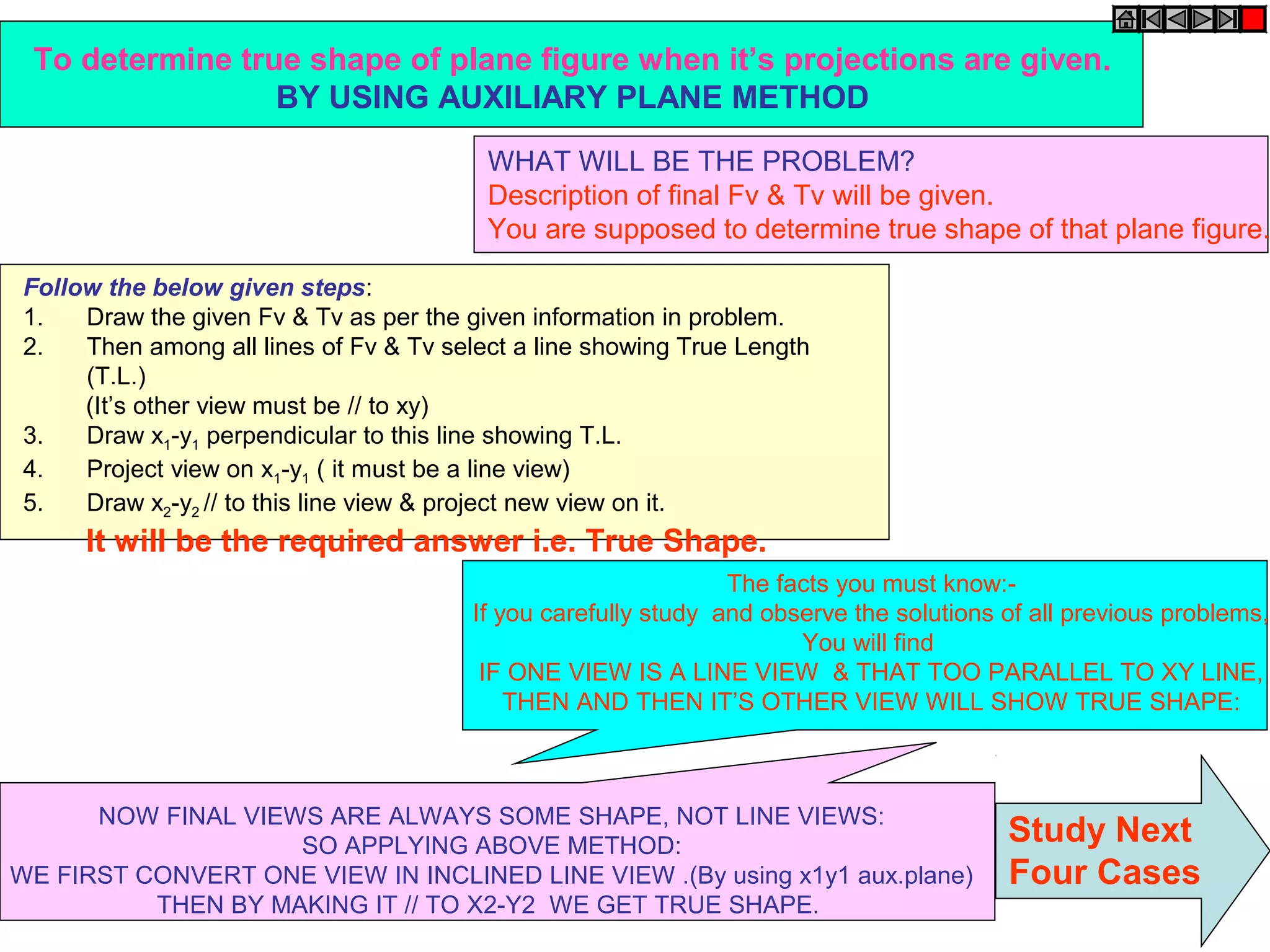
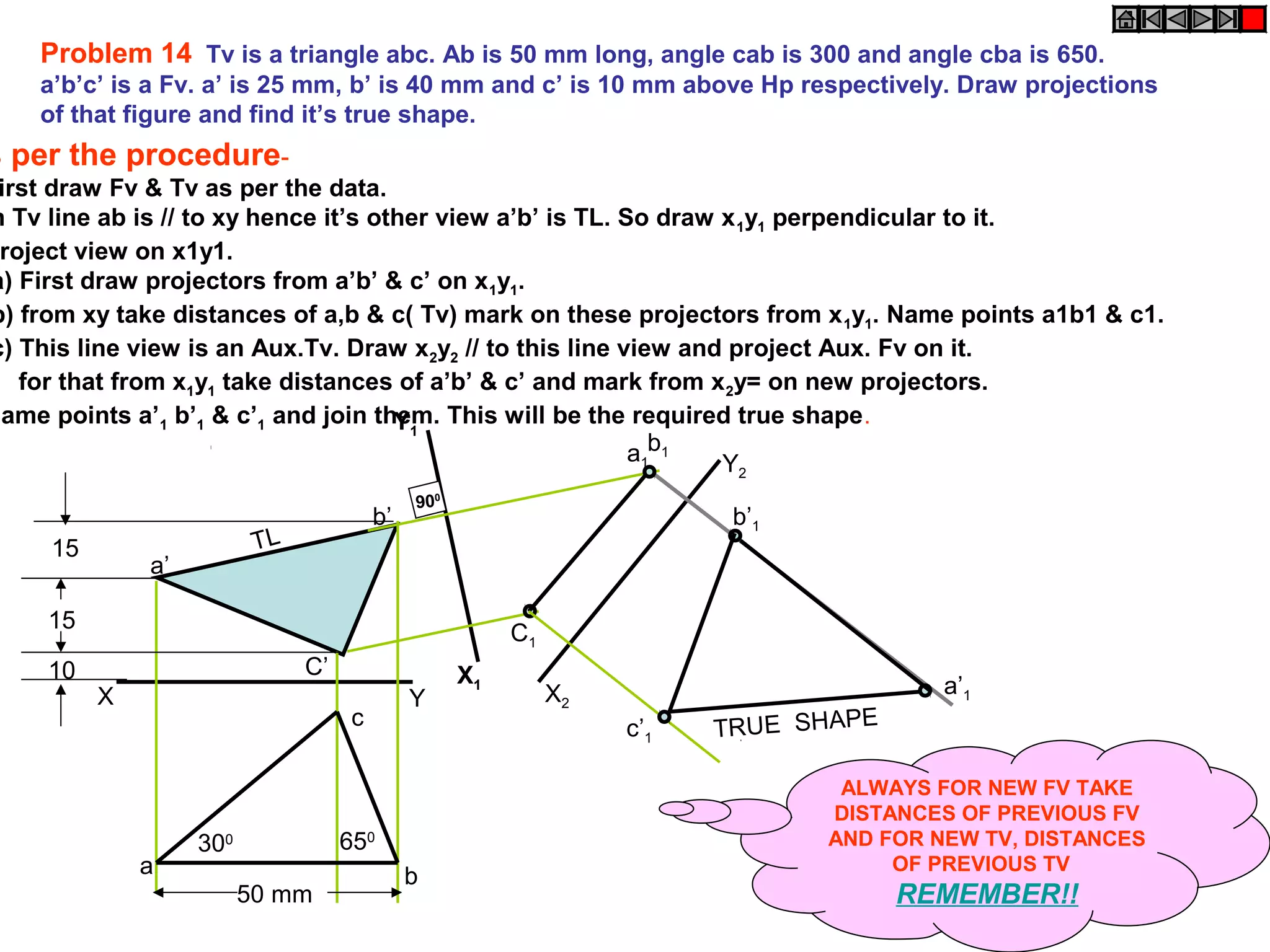
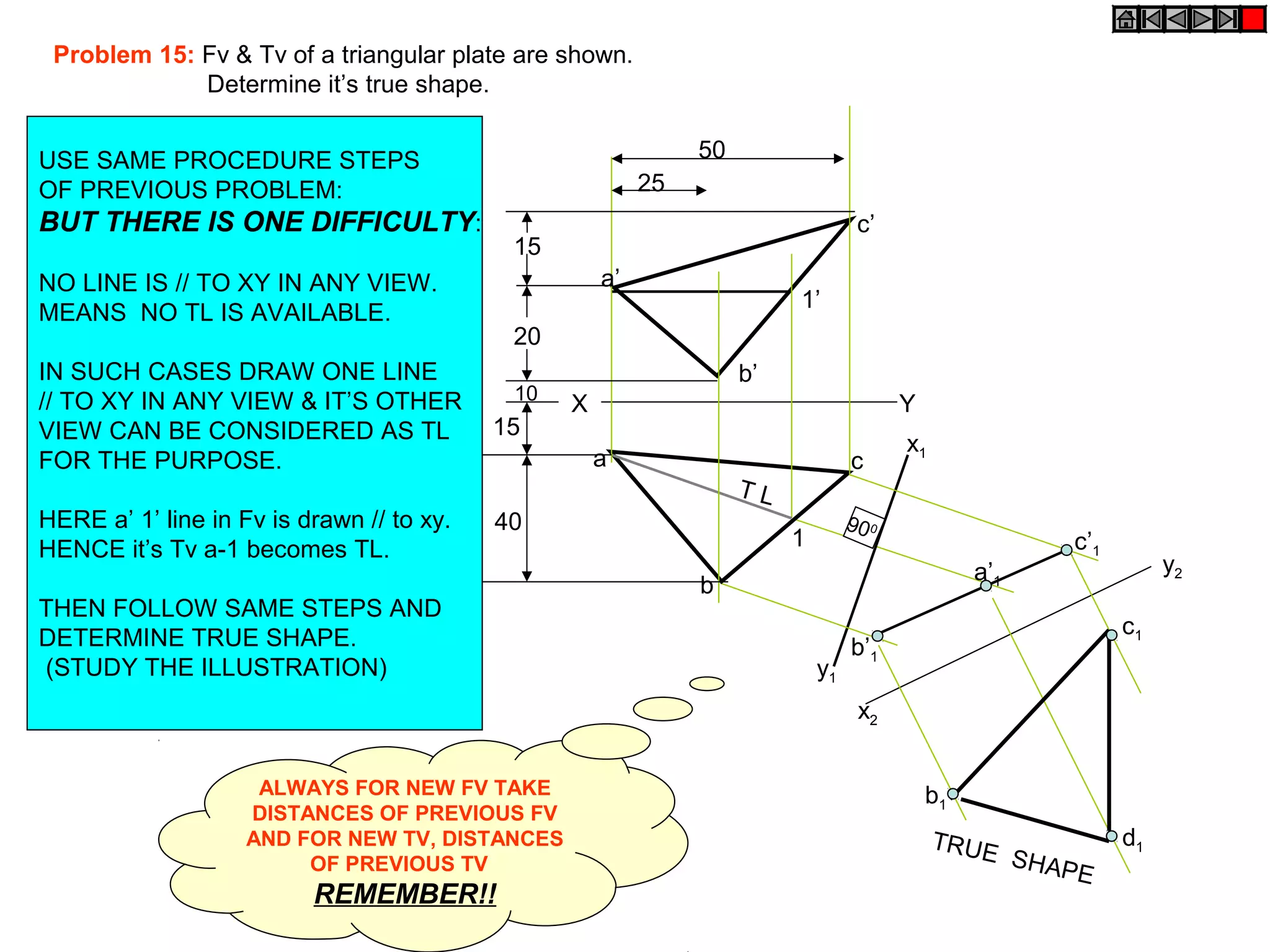
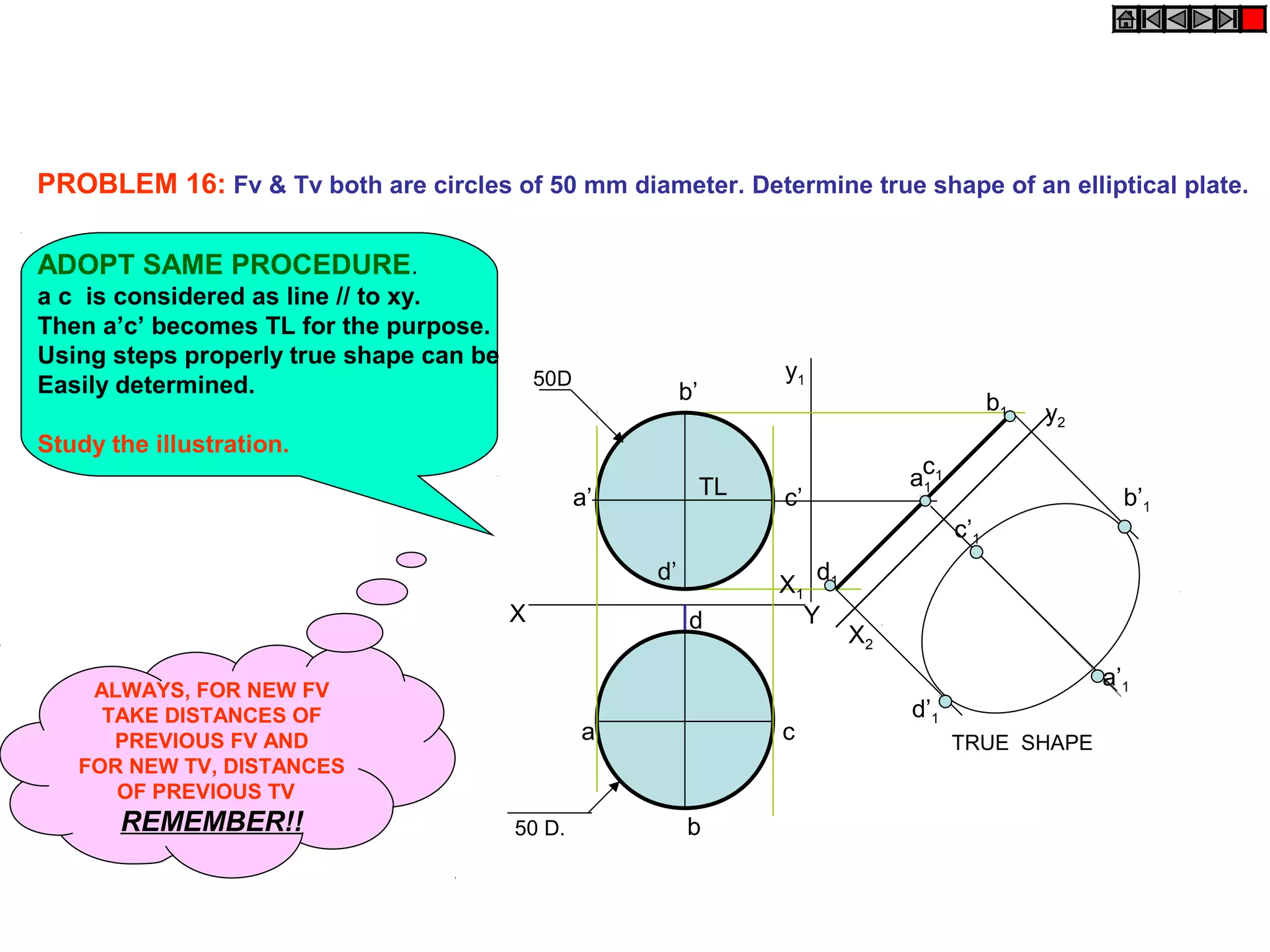
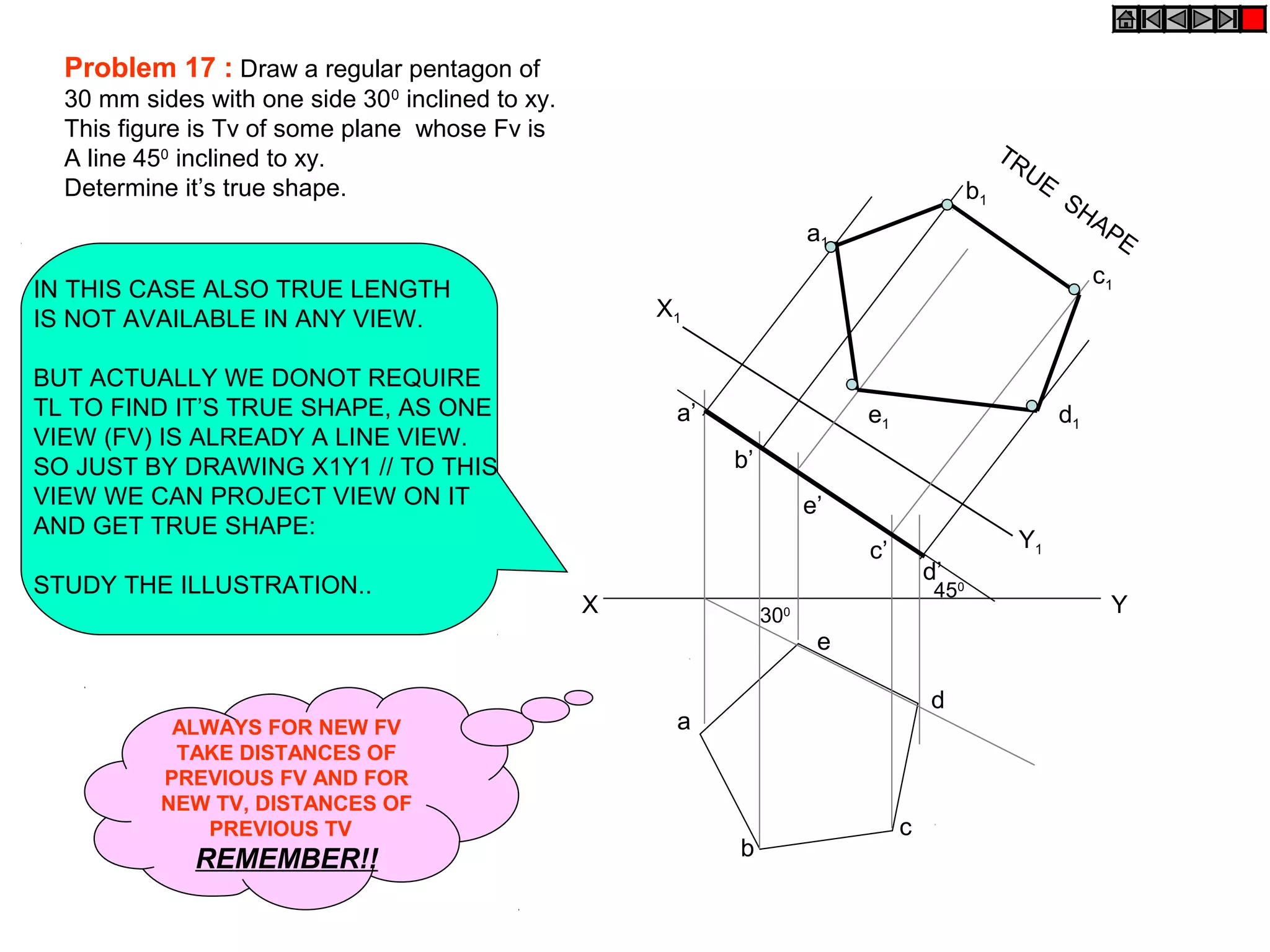
The document discusses the procedure for drawing projections of plane figures that are inclined to the horizontal and vertical planes. It provides examples of drawing projections for various objects including rectangles, triangles, circles, hexagons and pentagons in different orientations. The procedure involves three steps - drawing the initial projections assuming the plane is parallel to a reference plane, then drawing the second projections after inclining the surface, and finally the third projections after inclining an edge or side. Hints and solutions are provided for sample problems applying this three-step process.