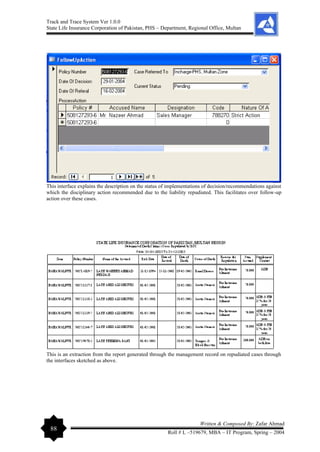
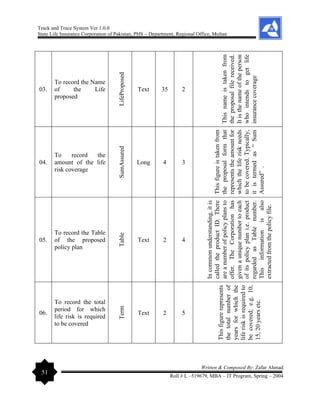
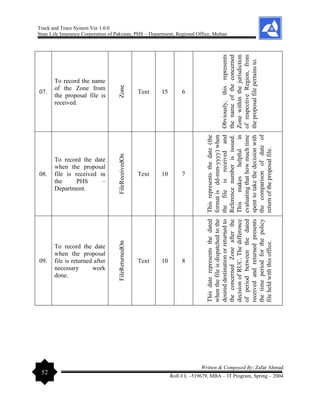
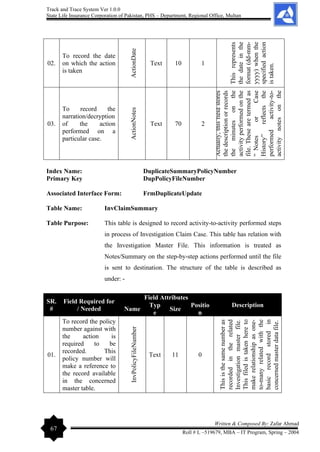
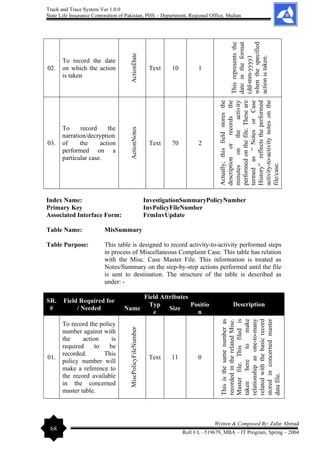
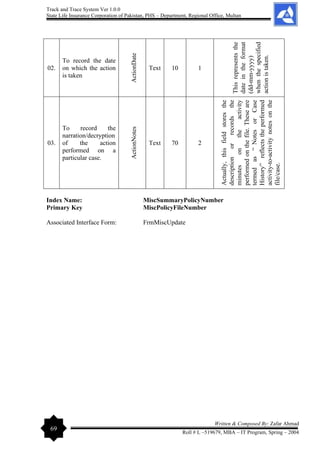
The document outlines the development of a 'Track and Trace System' software project by Zafar Ahmad for the State Life Insurance Corporation of Pakistan, aimed at improving the management of various filing and decision-making processes within the organization. It highlights the project's objectives, including enhancing efficiency in responding to queries and minimizing file loss, while also expressing gratitude to supervisors and contributors. The software is designed to streamline operations and facilitate better decision-making in the insurance claims process.
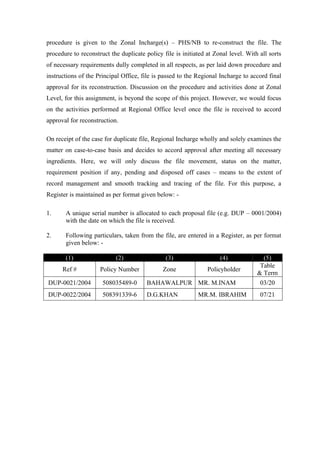
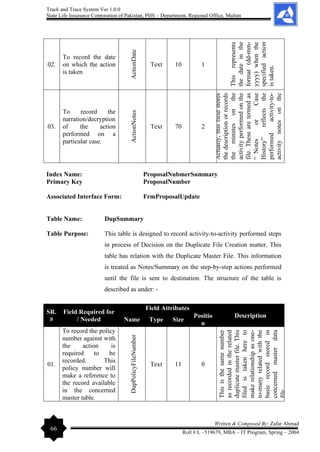
![Track and Trace System
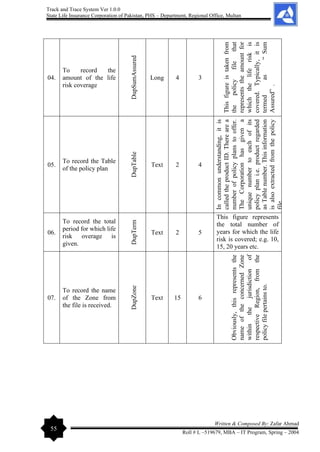
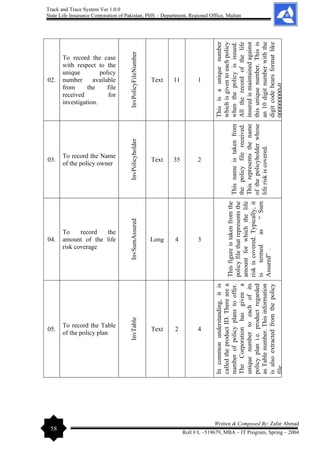
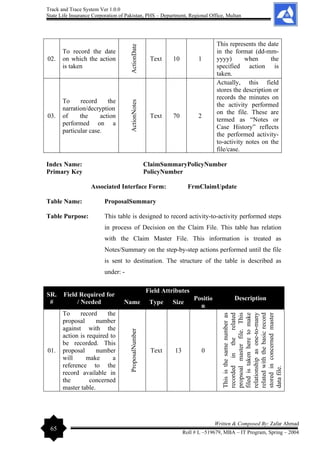
[T&TS]
Zafar Ahmad
Roll # L – 519679
MBA – IT Program
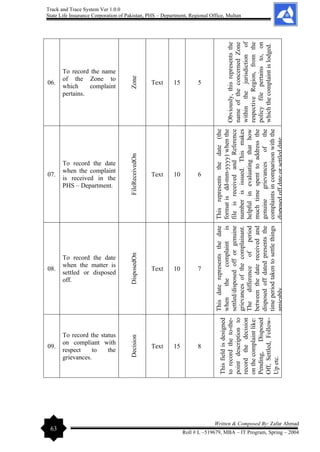
Ms. Shamoona Shahid
Course Leader
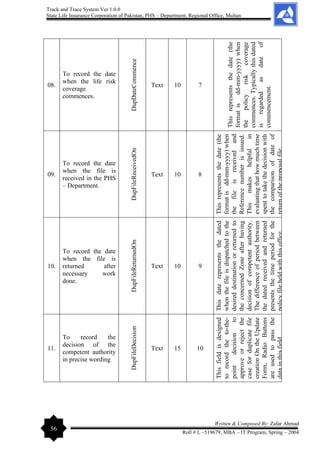
MIMS, Multan
Department of Computer Science
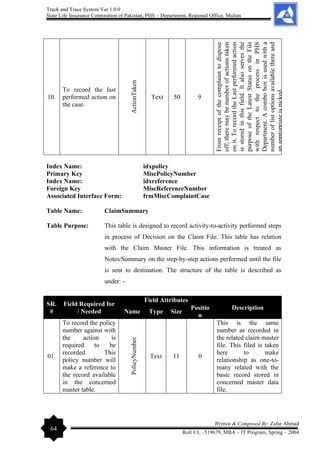
Allama Iqbal Open University
H – 8, Islamabad
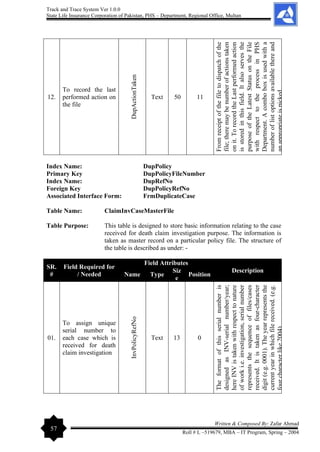
Year 2004
Developed By:
Supervised By:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectreportonpolicyfiletrackandtracesystem-240229065149-75e84078/75/Project-Report-on-Policy-File-Track-and-Trace-System-pdf-1-2048.jpg)





































![Track and Trace System Ver 1.0.0
State Life Insurance Corporation of Pakistan, PHS – Department, Regional Office, Multan
35
Written & Composed By: Zafar Ahmad
Roll # L –519679, MBA – IT Program, Spring – 2004
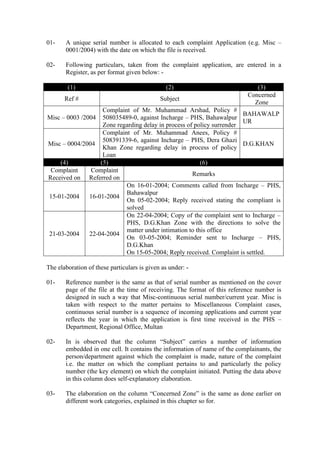
SR.
#
Item
Description
Cost
Associated
Required
For Project
Remarks
01. Hardware Rs. 50,000/= Nil
Supplied by the Department as
already there, provide by their
Principal Office
02. Software Rs.30,000/= Nil
Already Purchased by the
Corporation and provided to this
Office. This software is used to
develop this Project
03. Training - Nil
As already trained personnel is
working there; however,
orientation training on the
system may be provided by the
developer.
TOTAL COST Rs. 80,000/= Nil
As the system is being
developed to meet the
obligation for MBA – IT
degree. Hence Free of Cost.
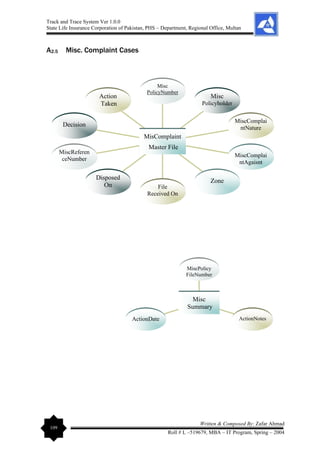
3.2.4 Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
To exhibit the requirements for the flow of data, we use data flow diagrams. Here again
hierarchy is expressed by layering, so that different levels of detail are shown in different
layers. We begin by considering the system as a transformer of data. We examine the data
that flows into the system, how it is transformed, and how it leaves the system. The
emphasis is on the flow of the data, not on the flow of control.
A DFD shows the flow of a data through a system. The system may be an organization, a
manual procedure, a software system, a mechanical system, a hardware system, or only
combination of these. A DFD shows the movement of data through the different
transformation or processes in the system. The processes are shown by named circles
(‘bubbles’) and named arrows entering or leaving the bubbles represent data flow. A
rectangle represents a source or sink, and is a net originator or consumer of data. A source
or a sink is typically outside the main system of study. [DFD can be shown in the
Appendices Section of this Report].
3.2.5 Prototyping Requirements
When a customer works with us to determine requirements, sometimes the customer is
uncertain of exactly what is required or needed. The requirement analysis may yield a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectreportonpolicyfiletrackandtracesystem-240229065149-75e84078/85/Project-Report-on-Policy-File-Track-and-Trace-System-pdf-47-320.jpg)






![Track and Trace System Ver 1.0.0
State Life Insurance Corporation of Pakistan, PHS – Department, Regional Office, Multan
41
Written & Composed By: Zafar Ahmad
Roll # L –519679, MBA – IT Program, Spring – 2004
4.2.1 Guidelines for Output Design
In order to make the output complete, concise, correct, there are certain guidelines to follow: -
• Make simple to read and interpret
• Title, date, time
• Section headings
• Column headings
• Expanded codes
• Legends
• Use consistent labels, spacing, etc.
• Right information, right place, right time
In the proposed system, printer generated reports are designed as output. [Glimpses on Reports
can be seen in the Appendices Section]
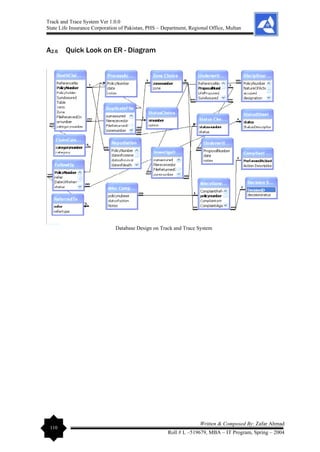
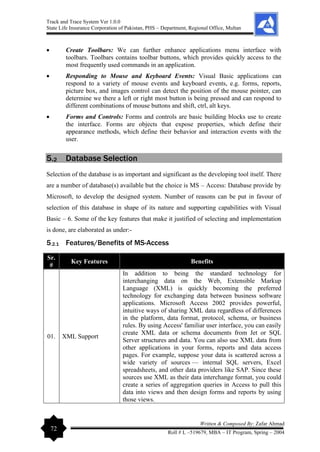
4.3 Database Design
The first sight that attracts the user is the interface. Attractive and convenient interface keep the
user in touch with the system. The user finds get job done in an easy and simple way. Graphic
User Interface (GUI) plays an important role in making things quiet easy for the user. The
following are the most common elements used to attract the user in this system
Windows: The most pervasive element used in GUIs is the window. It could be considered to be
a metaphor for a "window" into the computer, but it is dependent on idioms for its operation. The
GUI paradigm, however, allowed for the user to see into multiple areas within the computer, and
the window metaphor was born. Visual Basic does well in developing such interface as Multi
Document Interface (MDI).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectreportonpolicyfiletrackandtracesystem-240229065149-75e84078/85/Project-Report-on-Policy-File-Track-and-Trace-System-pdf-54-320.jpg)

![Track and Trace System Ver 1.0.0
State Life Insurance Corporation of Pakistan, PHS – Department, Regional Office, Multan
43
Written & Composed By: Zafar Ahmad
Roll # L –519679, MBA – IT Program, Spring – 2004
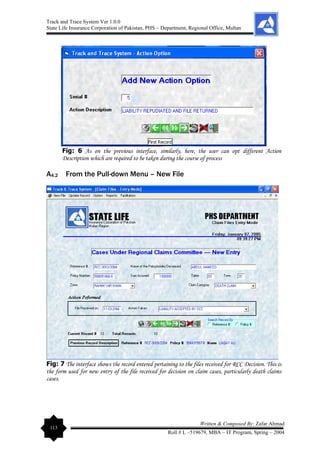
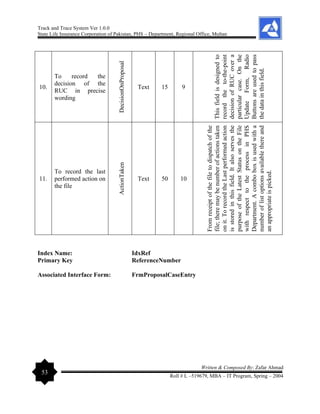
Radio Buttons: A radio button is small circle with some sort of label beside
it. A black dot inside the circle indicates that the button is selected. The
absence of a dot indicates that the button is unselected. When one button is
pushed in, whatever other button had been pushed in will pop out. In this way,
only one button can be pushed in at a time. Similarly, with the radio button form object, clicking
on one option will cause whatever other option that had been selected to become unselected. The
Radio button interface is designed to have a selection over Reference Number or Proposal/Policy
Number search in this Track and Trace System
Text Box: It is the most commonly used interface object. A text field is
simply a space in which the user can type text. Text fields are usually
contained within a rectangle, but it could just be space on a panel that can
accept text. Obviously, the Text Box(s) are used to contain data, show data and to pass on the
data to the database.
Labels: It is also most commonly used interface object. To mention caption of the Text Box and
to get the user recognized the purpose of the filed to which the label is associated, this object is
used so frequently.
Mask Box: In order to facilitate the user, Mask Edit Box is designed so that consistent data be
entered especially in Reference Number text box as RCC-____/____, Table/Term data entry,
Policy Number as _________-_ .
4.4 Database Design
With respect to the scope of the project database is designed keeping in view the normalization
of data, no redundancy, easy and fast access from the database and isolation of independent
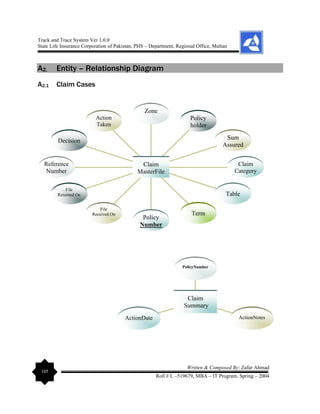
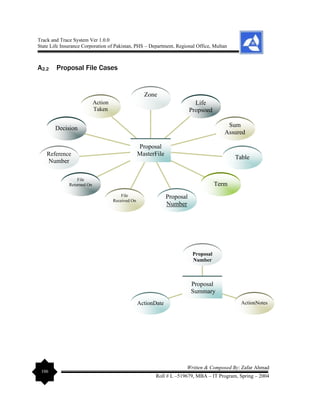
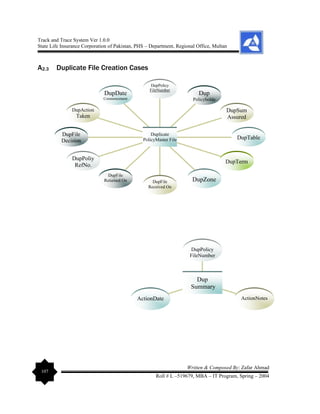
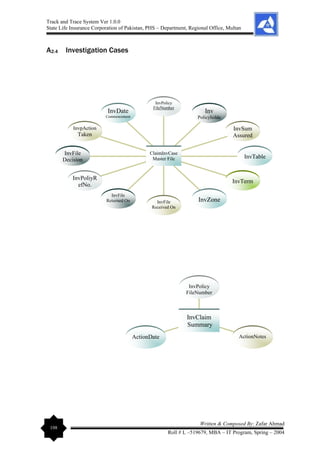
multiple relationships. The elaboration on Data Dictionary is given as under: - [Entity –
Relationship Diagram (ERD) can be viewed in the Appendices Section of this report].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectreportonpolicyfiletrackandtracesystem-240229065149-75e84078/85/Project-Report-on-Policy-File-Track-and-Trace-System-pdf-56-320.jpg)



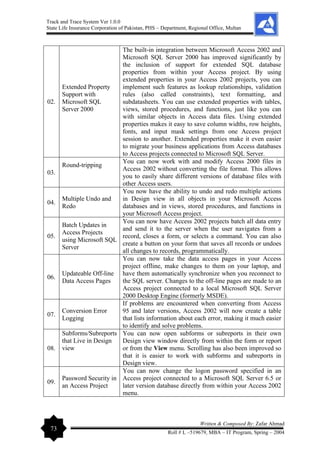
![Track and Trace System Ver 1.0.0
State Life Insurance Corporation of Pakistan, PHS – Department, Regional Office, Multan
74
Written & Composed By: Zafar Ahmad
Roll # L –519679, MBA – IT Program, Spring – 2004
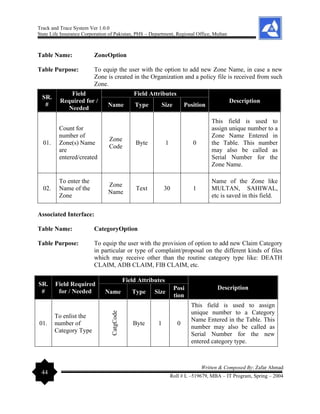
10.
The Linked Table
Wizard
The Linked Table Wizard guides you through the process of
linking your tables to a SQL Server database, and does this
all from within your Access project.
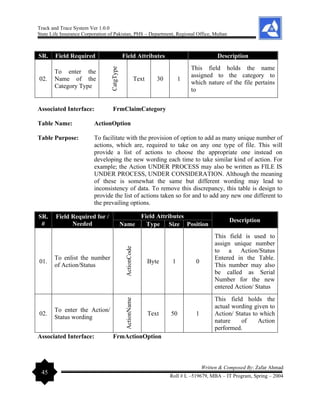
11.
Improved Support
for International
Complex-scripts
Access 2002 now exposes complex-script interface items
easily, which means that with a simple click, you can switch
the reading direction from left-to-right to right-to-left in
language-specific objects.
5.3 Hardware Used
With respect to the programming tool and database applied for the system development;
following hardware is put into operation to the get the work done. The Hardware profile
mentioned here as under is already available in the PHS – Department, Multan Region. So
there was no need of some thing extra to purchase for the proposed system as per design.
• PENTIUM – III 2.0 GHz
• WINDOWS XP [Licensed]
• Monitor IBM G74
• 128 MB RAM
• 40 GB HDD
• 1.44 FDD
• CD ROM Drive
• Key Board 104 Key
• Mouse A4 Tack
• Printer Cannon BJC – 4200
With help of all these ingredients, the proposed system is developed with out any
significant difficulty as the logistic support by the Department made it convenient to work
consistently with the added advantage of conducive environment in the office.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectreportonpolicyfiletrackandtracesystem-240229065149-75e84078/85/Project-Report-on-Policy-File-Track-and-Trace-System-pdf-88-320.jpg)