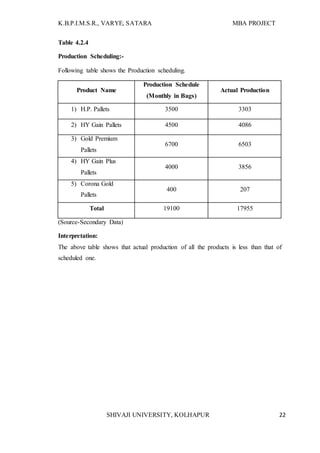
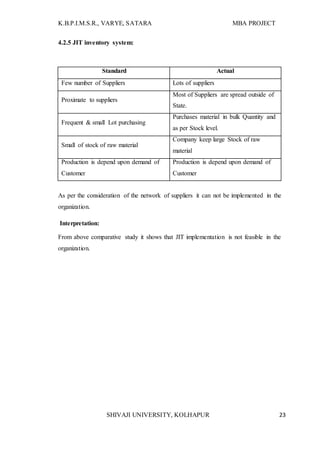
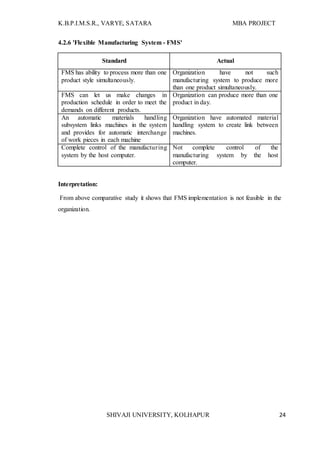
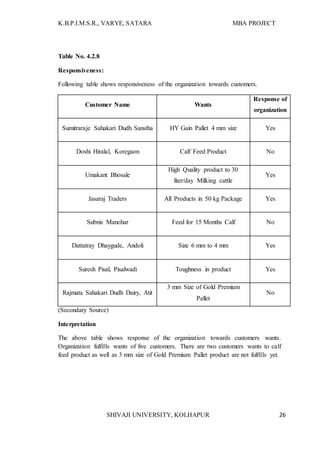
The document provides information about an MBA research project being conducted on supply chain management with respect to Shree Feed stuffs Industries Pvt. Ltd. It introduces the research topic, objectives, and methodology. The research aims to analyze the current supply chain management status of the company, identify problems, and provide suggestions for improvement. It will examine all aspects of the company's present supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution. The research is important as it can help the company better understand its supply chain and make improvements to integrate the partners more efficiently.